Abstract
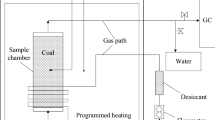
Oxyfuel combustion represents one way for cleaner energy production using coal as combustible. The comparison between the oxycombustion and the conventional air combustion process starts with the investigation of the pyrolysis step. The aim of this contribution is to evaluate the impact of N2 (for conventional air combustion) and CO2 (for oxy-fuel combustion) atmospheres during pyrolysis of three different coals. The experiments are conducted in a drop tube furnace over a wide temperature range 800–1400 °C and for residence time ranging between 0.2 and 1.2 s. Coal devolatilized in N2 and CO2 atmospheres at low temperatures (< 1200 °C) provides similar results regarding mass loss, char combustion in thermogravimetric analysis and CO concentration. At higher temperatures (> 1200 °C) and longer residence times (> 0.5 s), the char-CO2 reaction is clearly observed, whose intensity depends on the nature of the coal. Furthermore, the volatile yields are simulated using Kobayashi’s scheme and kinetic parameters are predicted for each coal. The char gasification under CO2 is also accounted for by the model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du R, Wu K, Zhang L, Xu D, Chao C, Zhang B. A sectioning method for the kinetics study on anthracite pulverized coal combustion. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130(3):2293–9.
CO2 Emissions From Fuel Combustion Highlights. CO2 emissions from fuel combustion highlights. 2015. [cited 2016 Mar 21]. Available from: http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/CO2EmissionsFromFuelCombustionHighlights2015.pdf.
Fujimori T, Yamada T. Realization of oxyfuel combustion for near zero emission power generation. Proc Combust Inst. 2013;34(2):2111–30.
Singh D, Croiset E, Douglas PL, Douglas MA. Techno-economic study of CO2 capture from an existing coal-fired power plant: MEA scrubbing vs. O2/CO2 recycle combustion. Energy Convers Manag. 2003;44(19):3073–91.
Cormos C-C. Oxy-combustion of coal, lignite and biomass: a techno-economic analysis for a large scale Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) project in Romania. Fuel. 2016;169:50–7.
Buhre BJP, Elliott LK, Sheng CD, Gupta RP, Wall TF. Oxy-fuel combustion technology for coal-fired power generation. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2005;31(4):283–307.
Bejarano PA, Levendis YA. Single-coal-particle combustion in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 environments. Combust Flame. 2008;153(1–2):270–87.
Li Q, Zhao C, Chen X, Wu W, Lin B. Properties of char particles obtained under O2/N2 and O2/CO2 combustion environments. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif. 2010;49(5):449–59.
Qiao Y, Zhang L, Binner E, Xu M, Li C-Z. An investigation of the causes of the difference in coal particle ignition temperature between combustion in air and in O2/CO2. Fuel. 2010;89(11):3381–7.
Rathnam RK, Elliott LK, Wall TF, Liu Y, Moghtaderi B. Differences in reactivity of pulverised coal in air (O2/N2) and oxy-fuel (O2/CO2) conditions. Fuel Process Technol. 2009;90(6):797–802.
Heuer S, Senneca O, Wütscher A, Düdder H, Schiemann M, Muhler M, et al. Effects of oxy-fuel conditions on the products of pyrolysis in a drop tube reactor. Fuel Process Technol. 2016;150:41–9.
Tomaszewicz M, Tomaszewicz G, Sciazko M. Experimental study on kinetics of coal char-CO2 reaction by means of pressurized thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130(3):2315–30.
Solomon PR, Fletcher TH, Pugmire RJ. Progress in coal pyrolysis. Fuel. 1993;72(5):587–97.
Solomon PR, Fletcher TH. Impact of coal pyrolysis on combustion. Symp Int Combust. 1994;25(1):463–74.
Steer JM, Marsh R, Greenslade M, Robinson A. Opportunities to improve the utilisation of granulated coals for blast furnace injection. Fuel. 2015;151:40–9.
Li X, Rathnam RK, Yu J, Wang Q, Wall T, Meesri C. Pyrolysis and combustion characteristics of an Indonesian low-rank coal under O2/N2 and O2/CO2 conditions†. Energy Fuels. 2010;24(1):160–4.
Gil MV, Riaza J, Álvarez L, Pevida C, Pis JJ, Rubiera F. Oxy-fuel combustion kinetics and morphology of coal chars obtained in N2 and CO2 atmospheres in an entrained flow reactor. Appl Energy. 2012;91(1):67–74.
Molina A, Shaddix CR. Ignition and devolatilization of pulverized bituminous coal particles during oxygen/carbon dioxide coal combustion. Proc Combust Inst. 2007;31(2):1905–12.
Shaddix CR, Molina A. Particle imaging of ignition and devolatilization of pulverized coal during oxy-fuel combustion. Proc Combust Inst. 2009;32(2):2091–8.
Chang Q, Gao R, Li H, Dai Z, Yu G, Liu X, et al. Effects of CO2 on coal rapid pyrolysis behavior and chemical structure evolution. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2017;128:370–8.
Brix J, Jensen PA, Jensen AD. Coal devolatilization and char conversion under suspension fired conditions in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 atmospheres. Fuel. 2010;89(11):3373–80.
Borrego AG, Alvarez D. Comparison of chars obtained under oxy-fuel and conventional pulverized coal combustion atmospheres. Energy Fuels. 2007;21(6):3171–9.
Zhao H, Cao Y, Orndorff W. Gasification characteristics of coal char under CO2 atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116:1267–72.
Zhang X, Liu Y, Wang C, Che D. Experimental study on interaction and kinetic characteristics during combustion of blended coal. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:935–42.
Relcom—Reliable Combustion. [cited 2016 Jun 30]. Available from: http://www.relcomeu.com/.
Kobayashi H. Devolatilization of pulverized coal at high temperatures. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology; 1976 [cited 2016 Jun 13]. Available from: http://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/26754.
Relcom—Reliable Combustion—Fuels. [cited 2016 Jun 30]. Available from: http://www.relcomeu.com/projects_fuels.php.
Zellagui S, Schönnenbeck C, Zouaoui-Mahzoul N, Leyssens G, Authier O, Thunin E, et al. Pyrolysis of coal and woody biomass under N2 and CO2 atmospheres using a drop tube furnace—experimental study and kinetic modeling. Fuel Process Technol. 2016;148:99–109.
Zellagui S, Trouvé G, Schönnenbeck C, Zouaoui-Mahzoul N, Brilhac J-F. Parametric study on the particulate matter emissions during solid fuel combustion in a drop tube furnace. Fuel. 2017;189:358–68.
Naredi P, Pisupati S. Effect of CO2 during coal pyrolysis and char burnout in oxy-coal combustion. Energy Fuels. 2011;25(6):2452–9.
Zanzi R, Sjöström K, Björnbom E. Rapid high-temperature pyrolysis of biomass in a free-fall reactor. Fuel. 1996;75(5):545–50.
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, et al. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem. 2015;87(9–10):1051–69.
Du S-W, Chen W-H, Lucas JA. Pulverized coal burnout in blast furnace simulated by a drop tube furnace. Energy. 2010;35(2):576–81.
Smoot LD, Smith PJ. Coal combustion and gasification. New York: Plenum Press; 1985.
Idris SS, Rahman NA, Ismail K, Alias AB, Rashid ZA, Aris MJ. Investigation on thermochemical behaviour of low rank Malaysian coal, oil palm biomass and their blends during pyrolysis via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Bioresour Technol. 2010;101(12):4584–92.
Morgan ME, Dekker JSA. Characterisation of the combustion performance of a suite of pulverised coals: report on the CC 1 trials. IJmuiden: International Energy Agency, International Flame Research Foundation; 1988.
Authier O, Thunin E, Plion P, Schönnenbeck C, Leyssens G, Brilhac J-F, et al. Kinetic study of pulverized coal devolatilization for boiler CFD modeling. Fuel. 2014;122:254–60.
Everson RC, Neomagus HWJP, Kaitano R, Falcon R, du Cann VM. Properties of high ash coal-char particles derived from inertinite-rich coal: II. Gasification kinetics with carbon dioxide. Fuel. 2008;87(15–16):3403–8.
Wang G, Zhang J, Hou X, Shao J, Geng W. Study on CO2 gasification properties and kinetics of biomass chars and anthracite char. Bioresour Technol. 2015;177:66–73.
Tomaszewicz M, Labojko G, Tomaszewicz G, Kotyczka-Moranska M. The kinetics of CO2 gasification of coal char. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:1327–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zellagui, S., Schönnenbeck, C., Zouaoui, N. et al. Fast pyrolysis of coals under N2 and CO2 atmospheres. J Therm Anal Calorim 133, 1535–1547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7218-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7218-7