Abstract
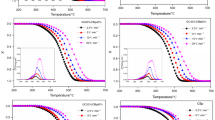
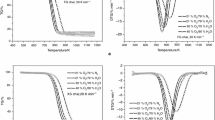
The combustion behaviors and kinetic parameters of three parent coals (A1, A2, and A3) and their blends (A1/A2 and A2/A3) have been evaluated under oxidizing atmosphere (O2 and N2 mixtures), using a non-isothermal thermo-gravimetric analyzer. The aim of this study is to investigate the interaction between the blended components during the process of co-combustion, and the effects of blending ratio and oxygen concentration (10, 15, and 21%) on combustion performance of blended coals. When high reactivity and low reactivity coals are co-combusted, double peaks are observed in the DTG curves, and significant interaction occurs in the temperature range between the two peaks (T p1 and T p2). The activation energies obtained by Coats–Redfern method indicate that the activation energies of blended coals are lower than that of parent coals. The combustibility index S is used to evaluate the combustion performance of blended coals, and the results show the non-additive effects of the combustion characteristics of blended coals. The increased oxygen concentration results in a significant improvement of combustion performance of blended coals. In addition, as the blending ratio of high reactivity coal is increased, the oxygen can greatly enhance the combustion stability of blended coals.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheng C, Moghtaderi B, Gupta R, Wall TF. A computational fluid dynamics based study of the combustion characteristics of coal blends in pulverised coal-fired furnace. Fuel. 2004;83(11–12):1543–52.
Shen YS, Guo BY, Yu AB, Zulli P. A three-dimensional numerical study of the combustion of coal blends in blast furnace. Fuel. 2009;88(2):255–63.
Peralta D, Paterson NP, Dugwell DR, Kandiyoti R. Coal blend performance during pulverised-fuel combustion: estimation of relative reactivities by a bomb-calorimeter test. Fuel. 2001;80(11):1623–34.
Qiu J, Li F, Zeng H, Yao B, Ma Y. Determination of optimum blending ratio during coal blends combustion. Combust Sci Technol. 2000;157(1):167–84.
Peralta D, Paterson NP, Dugwell DR, Kandiyoti R. Development of a reactivity test for coal-blend combustion: the laboratory-scale suspension-firing reactor. Energy Fuel. 2002;16(2):404–11.
Majid AA, Paterson N, Reed GP, Dugwell DR, Kandiyoti R. Further development of a suspension fired reactor to assess the relative performance and synergistic effects during the combustion of coal blends. Energy Fuel. 2005;19(3):968–76.
Xu Y, Lin S, Yuan H, Zhu K, He X, Chen G. Thermogravimetric analysis on the combustion characteristics for blended coals. Challenges of power engineering and environment. Proceedings of the International Conference on Power Engineering. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin; 2007. 3, pp.153–156.
Li Y, Wang C, Chen H. Study on combustion characteristics of blended coals. Front Energy Power Eng China. 2007;1(1):96–100.
Biswas S, Choudhury N, Sarkar P, Mukherjee A, Sahu SG, Boral P, et al. Studies on the combustion behaviour of blends of Indian coals by TGA and drop tube furnace. Fuel Process Technol. 2006;87(3):191–9.
Ulloa C, Borrego AG, Helle S, Gordon AL. Char characterization and DTF assays as tools to predict burnout of coal blends in power plants. Fuel. 2005;84(2–3):247–57.
Du S, Chen W, Lucas JA. Pulverized coal burnout in blast furnace simulated by a drop tube furnace. Energy. 2010;35(2):576–81.
Artos V, Scaroni AW. T.g.a. and drop-tube reactor studies of the combustion of coal blends. Fuel. 1993;72(7):927–33.
Kurose R, Ikeda M, Makino H, Kimoto M, Miyazaki T. Pulverized coal combustion characteristics of high-fuel-ratio coals. Fuel. 2004;83(13):1777–85.
Gil MV, Casal D, Pevida C, Pis JJ, Rubiera F. Thermal behaviour and kinetics of coal/biomass blends during co-combustion. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101(14):5601–8.
Xu Y, Zhang C, Xia J, Duan Y, Yin J, Chen G. Experimental study on the comprehensive behavior of combustion for blended coals. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng. 2010;5(3):435–40.
Liu GH, Ma XQ, Yu Z. Experimental and kinetic modeling of oxygen-enriched air combustion of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2009;29(2):792–6.
Bilbao R, Mastral JF, Aldea ME, Ceamanos J. Kinetic study for the thermal decomposition of cellulose and pine sawdust in an air atmosphere. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 1997;39(1):53–64.
Liu NA, Fan W, Dobashi R, Huang L. Kinetic modeling of thermal decomposition of natural cellulosic materials in air atmosphere. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2002;63(2):303–25.
Shen DK, Gu S, Luo KH, Bridgwater AV, Fang MX. Kinetic study on thermal decomposition of woods in oxidative environment. Fuel. 2009;88(6):1024–30.
Li C, Yamamoto Y, Suzuki M, Hirabayashi D, Suzuki K. Study on the combustion kinetic characteristics of biomass tar under catalysts. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95(3):991–7.
Yağmur S, Durusoy T. Kinetics of combustion of oil shale with polystyrene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;96(1):189–94.
Niu S, Lu C, Han K, Zhao J. Thermogravimetric analysis of combustion characteristics and kinetic parameters of pulverized coals in oxy-fuel atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98(1):267–74.
Fang MX, Shen DK, Li YX, Yu CJ, Luo ZY, Cen KF. Kinetic study on pyrolysis and combustion of wood under different oxygen concentrations by using TG-FTIR analysis. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2006;77(1):22–7.
Coats AW, Redfern JP. Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature. 1964;201(4914):68–9.
Zhou L, Wang Y, Huang Q, Cai J. Thermogravimetric characteristics and kinetic of plastic and biomass blends co-pyrolysis. Fuel Process Technol. 2006;87(11):963–9.
Fangxian L, Shizong L, Youzhi C. Thermal analysis study of the effect of coal-burning additives on the combustion of coals. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95(2):633–8.
Dumanli A, Taş S, Yürüm Y. Co-firing of biomass with coals. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;103(3):925–33.
Rao TR, Sharma A. Pyrolysis rates of biomass materials. Energy. 1998;23(11):973–8.
Varhegyi G, Antal MJ, Szekely T, Szabo P. Kinetics of the thermal decomposition of cellulose, hemicellulose, and sugarcane bagasse. Energy Fuel. 1989;3(3):329–35.
Cumming JW. Reactivity assessment of coals via a weighted mean activation energy. Fuel. 1984;63(10):1436–40.
Junhu Z, Chuanjuan P, Weijuan Y, Jianzhong L, Jun C, Kefa C. Thermo-gravimetric research on dynamic combustion reaction parameters of blended coals. Power Eng J. 2005;25(2):207–11.
Chuanjuan P, Junhu Z, Jun C, Weijuan Y, Kefa C. Research on the pyrolysis kinetics of blended coals. Proc CSEE. 2007;27(17):6–10.
Luo SY, Xiao B, Hu ZQ, Liu SM, Guan YW. Experimental study on oxygen-enriched combustion of biomass micro fuel. Energy. 2009;34(11):1880–4.
Acknowledgements
The financial supports from National Natural Science Foundation of China (50676076) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Wang, C. et al. Experimental study on interaction and kinetic characteristics during combustion of blended coals. J Therm Anal Calorim 107, 935–942 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1657-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1657-8