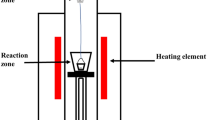
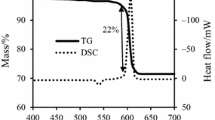
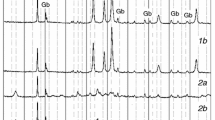
Abstract
The paper reports an investigation on the reduction of synthetic gypsum and a Tunisian phosphogypsum sample in pure nitrogen or loaded with H2O vapor, using graphite or natural coke. Thermogravimetry analysis in non-isothermal conditions showed that H2O gas has no effect on the onset temperature of reduction (T red), whereas the use of coke as a carbon source lowers the T red of about 50 °C but the reduction rate and the conversion degree into CaS are not significantly affected by the coke proportion. The activation energy and the reaction order were determined using the direct Arrhenius plot and the Coats–Redfern kinetic model. These models led to the same reaction order and to close values of activation energies. The FWO isoconversional method shows that the reduction is more complex than a one step process and leads to lower values of activation energy. Addition of 5% mass of various oxide lowered the activation energy; however, the use of the Co2O3/Co3O4 as additive seems to enhance more the reduction rate.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jansen M, Waller A, Verbiest J, Van Landschoot RC, Van Rosmalen GM. Incorporation of phosphoric acid in calcium sulphate hemihydrate from a phosphoric acid process. Ind Cryst. 1984;84:171–6.
Becker P. Phosphates and phosphoric acid. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1989.
Van der Sluis S, Meszaros Y, Gerda M, Marchee WGJ, Wesselimgh HA, Van Rosmalen GM. The digestion of phosphate ore in phosphoric acid. Ind Eng Chem Res. 1987;26:2501–5.
Huffmann EO, Cate WE, Deming ME, Elmore KL. Solubility of phosphates, rates of solution of calcium phosphates in phosphoric acid solutions. J Agric Food Chem. 1957;5(4):266–75.
Ben Brahim F, Mgaidi M, El Maaoui M. Kinetics of leaching of Tunisian phosphate ore particles in dilute phosphoric acid solutions. Can J Chem Eng. 1999;77:136–42.
Gioia F, Mura G, Viola A. Analysis, simulation and optimization of hemihydrate process for the production of phosphoric acid from calcareous phosphites. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev. 1977;16(3):390–9.
Shakourzadeh K, Bloise R, Baratin F. Crystallization of calcium sulphate hemihydrate in reagent-grade phosphoric acid. Ind Miner Tech. 1984;9:443–55.
Ardhaoui K, Ben Cherifa A, Jemal M. Calcium hydroxyapatite solubilisation in the hydrochloric and perchloric acids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;81:251–4.
Brahim K, Khattech I, Dubès JD, Jemal M. Etude cinétique et thermodynamique de la dissolution de la fluorapatite dans l’acide phosphorique. Thermochim Acta. 2005;436:43–50.
Brahim K, Antar K, Khattech I, Jemal M. Etude thermodynamique et cinétique de l’attaque de la fluorapatite par l’acide phosphorique. Ann Chim Sci Matér. 2006;31(5):611–20.
Dorozhkin SV. Dissolution kinetics of single fluoroapatite crystals in phosphoric acid solution under the conditions of the wet-process phosphoric acid production. J Prakt Chem. 1996;338:620–6.
Antar K, Jemal M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of the attack of a phosphate ore by acid solutions at different temperatures. Thermochim Acta. 2008;474:32–5.
Antar K, Jemal M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of the attack of fluorapatite by a mixture of sulfuric and phosphoric acids at 55 °C. Thermochim Acta. 2007;452:71–5.
Antar K, Brahim K, Jemal M. Etude cinétique et thermodynamique de l’attaque d’une fluorapatite par des melanges d’acides sulfurique et phosphorique à 25°C. Thermochim Acta. 2006;449:35–41.
Antar K. Thèse de Doctorat, University of Tunis El Manar, Faculty of Science of Tunis, Juin 2007.
Brahim K, Antar K, Khattech I, Jemal M. Effect of temperature on the attack of fluorapatite by aphosphoric acid solution. Sci Res Essays. 2008;3(1):35–9.
Abdel-Aal EA, Rashed MM, El-Shall H. Crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate at different supersaturation ratios and different free sulfate concentrations. Cryst Res Technol. 2004;39:313–21.
Rutherford PM, Dudas MI, Samek RA. Environmental impacts of phosphogypsum. Sci Total Environ. 1994;149:1–38.
Rouis MJ, Bensalah A. Phosphogypsum in Tunisia: environmental problems and required solutions. In: Proceedings of the third international symposium on phosphogypsum, Orlando, publication FIPR n° 01-060-083; 1990;1:87–105.
Ragin M, Brooks R, Donalds B. Recovery of sulfur from phosphogypsum: Conversion of calcium sulfate to calcium sulfide. Mines Rep. Invest. 1990;R1:9323.
Trikk EIA, Turn L, Kysik R. Estin svtead akademie. Toim, Keem. 1989;38(3):150–8.
Rice DA, May A, Carter OC, Swanton RG. Recovery of sulfur from phosphogypsum: Conversion of calcium sulfide to sulfur. Trans. Soc. Min. Eng. 1988;284:1848–53.
Sebbahi S, Chameikh MLO, Sahban F, Aride J, Benarafa L, Belkbir L. Thermal behaviour of Moroccan phosphogypsum. Thermochim Acta. 2007;302:69–75.
Kuusik R, Saikkonen P, Niinisto L. Thermal decomposition of calcium sulfate in carbon monoxide. J Therm Anal. 1985;30:187–93.
Gruncharov I, Kirilov PL, Pelovski Y, Dombalov I. Isothermal gravimetrical kinetic study of the decomposition of phosphogypsum under CO–CO2–Ar atmosphere. Thermochim Acta. 1985;92:173–6.
Gruncharov I, Pelovski Y, Dombalov I, Kirilov PL. Thermochemical decomposition of phosphogypsum under H2–CO2–Ar atmosphere. Thermochim Acta. 1985;93:617–20.
Yang X, Zhang Z, Wang X, Yang L, Zhong B, Liu J. Thermodynamic study of phosphogypsum decomposition by sulfur. J Chem Thermodyn. 2013;57:39–45.
Reddy PP, Ratinam M, Sundaram N, Satyanarayananan AK. Studies on the reduction of gypsum to calcium sulphide. Chem Age India. 1967;18(4):282–8.
Strydom CA, Groenewald EM, Potgieter JH. Thermogravimetric studies of the synthesis of CaS from gypsum, CaSO4·2H2O and phosphogypsum. J Therm Anal. 1997;49:1501–7.
Van der Merwe EM, Strydom CA, Potgieter JH. Thermogravimetric analysis of the reaction between carbon and CaSO4·2H2O, gypsum and phosphogypsum in an inert atmosphere. Thermochim Acta. 1999;340–341:431–7.
Sebbahi S, Sahban F, Chameikh MLO, Taibi M, Boukhari A, Aride J. Thermogravimetric and kinetic study of maroccan phosphogypsum in presence of coal. Phys Chem News. 2007;33:126–33.
Alimi F, Elfil H, Gadri A. Kinetics of the precipitation of calcium sulfate dihydrate in a desalination unit. Desalination. 2003;157:9–16.
ICDD File Number 33-311.
Lide DR. CRC Hand book of chemistry and physics, 79th ed. 1998–1999.
Guilhot B. Etude des formes hydrates du sulfate de calcium (gypse-plâtres). Thèse de Doctorat, Faculté des Sciences de l’université de Grenoble, 1970.
Hudson-Lamb FL, Strydom CA, Potgieter JH. The thermal dehydration of natural gypsum and pure calcium sulphate dihydrate (gypsum). Thermochim Acta. 1996;282–283:483–93.
Strydom CA, Potgieter JH. Dehydration behaviour of a natural gypsum and a phosphogypsum during milling. Thermochim Acta. 1999;332:89–96.
Saeed M, Khalique A, Mansoor S, Bhatty MK. Studies on the reduction of gypsum to calcium sulphite with mineral coal as the reactant. Pak J Sci Ind Res. 1983;26(4):272–4.
Kale BB, Pande AR, Gokarn AN. Studies in the carbothermic reduction of phosphogypsum. Metall Trans B. 1992;23B:567–72.
Turkdogan ET, Vinters JV. Reduction of calcium sulphate by carbon. Trans Inst Min Metall Sect. 1976;C85:117–27.
Mu J, Raremba G. Effect of carbon and silica on the reduction of calcium sulfate. Thermochim Acta. 1987;114:389–92.
Wieczorek-Cuirowa K. The thermal behaviour of compounds in the Ca–S–O system. J Therm Anal. 1992;38:523–30.
Database of the AMCSD n°0013978.
Brown ME, Dollimore D, Galwey AK. Reactions in the solid state. Comprehensive chemical kinetics. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1980. p. 22.
Vyazovkin S, Chrissafis K, Di Lorenzo ML, Koga N, Pijolat M, Roduit B, Sbirrazzuoli N, Sunol JJ. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for collecting experimental thermal analysis data for kinetic computations. Thermochim Acta. 2014;590:1–23.
Vyazovkin S, Wight CA. Model-free and model-fitting approaches to kinetic analysis of isothermal and nonisothermal data. Thermochim Acta. 1999;340–341:53–68.
Sbirrazzuoli N, Vincent L, Vyazovkin S. Comparison of several computational procedures for evaluating the kinetics of thermally simulated condensed phase reactions. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 2000;54:53–60.
Coats AW, Redfern JP. Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetry data. Nature. 1964;201:68–9.
Pilawka R, Maka H. Kinetics of thermal decomposition of isocyanate-epoxy materials crosslinked in the presence of 1-ethylimidazole accelerator. Polimery. 2014;59(3):409–19.
Apaydin-Varol E, Polat S, Putun AE. Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal decomposition behaviour of polycarbonate—a TGA–FTIR study. Therm Sci. 2014;18(3):833–42.
Khaghanikavkani E, Farid MM. Thermal pyrolysis of polyethylene: kinetic study. Energy Sci Technol. 2011;2(1):1–10.
Yan Y, Xu J, Pang H, Zhang R, Liao B. Thermal decomposition and kinetics of rigid polyurethane foams derived from sugarcane bagasse. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater. 2009;24(5):776–80.
Jelić D, Mentus S, Penavin-Škundrić J, Bodroža D, Antunović B. A thermogravimetric study of reduction of silver oxide under non-isothermal conditions. Contemp Mater. 2010;I-2:144–50.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38:1881–6.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. A quick direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. Polymer Lett. 1966;4:322–8.
Doyle CD. Estimating isothermal life from thermogravimetric data. J Appl Polym Sci. 1962;6:639–42.
Akahira T, Sunose T. Method of determinating activation deterioration constant of electrical insulating materials. Res Rep Chiba Inst Technol Sci Technol. 1971;16:22–31.
El-Sayed Saad A, Mostafa ME. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetic parameters determination of biomass fuel powders by differential thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA/DTG). Energy Convers Manag. 2014;85:165–72.
Alaba PA, Sani YM, Wan Daud WMA. A comparative study on thermal decomposition behavior of biodiesel samples produced from shea butter over microand mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolites using different kinetic models. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:943–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antar, K., Jemal, M. A thermogravimetric study into the effects of additives and water vapor on the reduction of gypsum and Tunisian phosphogypsum with graphite or coke in a nitrogen atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim 132, 113–125 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6871-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6871-6