Abstract
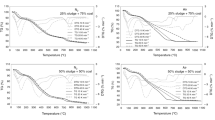
The combustion characteristics of coal sludge were investigated with thermogravimetric analysis at different heating rates (10, 20, 30, 40 °C min−1). The influences of heating rates on the combustion behavior of coal sludge were studied. The research found that the value of general combustion parameters for Taiyuan coal sludge (TY) is the lowest, for Shuozhou coal sludge (SZ) is the highest, and for Jincheng coal sludge (JC) is in middle at any heating rate. The experimental results indicated that a higher heating rate is useful for the combustion performance of coal sludge in this study. Kinetic parameters of the coal sludge samples were evaluated with the Ozawa–Flynn–Wall (OFW) and distributed activation energy model (DAEM) method. The activation energy values obtained from the DAEM method are a little lower than the ones obtained from the OFW method for every kind of coal sludge. The activation energy values of JC were 119.62 and 113.63 kJ mol−1 obtained by OFW and DAEM methods, respectively, and were lower than corresponding values of TY and SZ. Higher amounts of alkaline metal (Na and K), alkaline earth metals (Ca and Mg), Fe and Ti in JC may play a major role in lowering the activation energy values. The present results have important significance for understanding the characteristics of combustion of coal sludge.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duan LB, Liu DY, Chen XP, Zhao CS. Fly ash recirculation by bottom feeding on a circulating fluidized bed boiler co-burning coal sludge and coal. Appl Energy. 2012;95:295–9.
Kök MV. Temperature-controlled combustion and kinetics of different rank coal samples. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;79(1):175–80.
Elbeyli İY, Pişkin S. Combustion and pyrolysis characteristics of tunçblek lignite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;83(3):721–6.
Özbas KE, Kök MV. Effect of heating rate on thermal properties and kinetics of raw and cleaned coal samples. Energy Sour. 2003;25(1):33–42.
Altun NE, Hicyilmaz C, Kök MV. Effect of Different binders on the combustion properties of lignite part I. Effect on thermal properties. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;65(3):787–95.
Ren J, Xie CJ, Guo X, Qin ZF, Lin JY, Li Z. Combustion characteristics of coal gangue under an atmosphere of coal mine methane. Energy Fuels. 2014;28(6):3688–95.
Wang HY, Zhang JL, Wang GW, Xu RS, Zhang PC, Liu SY, et al. Characteristics and kinetic analysis of co-combustion of brown coal and anthracite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126(2):447–54.
Zou C, Zhang L, Cao SY, Zheng CG. A study of combustion characteristics of pulverized coal in O2/H2O atmosphere. Fuel. 2014;115:312–20.
Xu Y, Zhang YF, Zhang GJ, Guo YF, Zhang J, Li GQ. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of two Chinese low-rank coals. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;122(2):975–84.
Zhang YY, Nakano J, Liu LL, Wang XD, Zhang ZT. Co-combustion and emission characteristics of coal gangue and low-quality coal. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120(3):1883–92.
Wang CA, Liu YH, Zhang XM, Che DF. A study on coal properties and combustion characteristics of blended coals in Northwestern China. Energy Fuels. 2011;25(8):3634–45.
Niu SL, Lu CM, Han KH, Zhao JL. Thermogravimetric analysis of combustion characteristics and kinetic parameters of pulverized coals in oxy-fuel atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98(1):267–74.
Zhang KH, Zhang K, Cao Y, Pan WP. Co-combustion characteristics and blending optimization of tobacco stem and high-sulfur bituminous coal based on thermogravimetric and mass spectrometry analyses. Bioresour Technol. 2013;131:325–32.
Nie QH, Sun SZ, Li ZQ, Zhang XJ, Wu SH, Qin YK. Thermogravimetric analysis on the combustion characteristics of brown coal blends. J Combust Sci Technol. 2001;7(1):72–6.
Li XG, Ma BG, Xu L, Hu ZW, Wang XG. Thermogravimetric analysis of the co-combustion of the blends with high ash coal and waste tyres. Thermochim Acta. 2006;441(1):79–83.
Li QZ, Zhao CS, Chen XP, Wu WF, Li YJ. Comparison of pulverized coal combustion in air and in O2/CO2 mixtures by thermo-gravimetric analysis. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2009;85(1–2):521–8.
Cheng JY, Sun XX. Determination of the devolatilization index and combustion characteristic index of pulverized coals. Power Eng. 1987;7(5):33–6.
Sima-Ella E, Mays TJ. Analysis of the oxidation reactivity of carbonaceous materials using thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;80(1):109–13.
Sanchez ME, Otero M, Gómez X, Morán A. Thermogravimetric kinetic analysis of the combustion of biowastes. Renew Energy. 2009;34(6):1622–7.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermodynamic data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38:1881–6.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. Polym Lett. 1966;4:323–8.
Cd D. Kinetic analysis of thermogravimetric data. J Appl Polym Sci. 1961;5(15):285–92.
Miura K, Maki T. A simple method for estimating f(E) and ko(E) in the distributed activation energy model. Energy Fuels. 1998;12(5):864–9.
Avrami MJ. Kinetics of phase change. I General theory. Chem Phys. 1939;7:1103–12.
Mj A. Kinetics of phase change II. Transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei. Chem Phys. 1940;8:212–24.
Mj A. Kinetics of phase change III. Granulation, phase change, and microstructure. Chem Phys. 1941;9:177–84.
Idris SS, Rahman NA, Ismail K. Combustion characteristics of Malaysian oil palm biomass, sub-bituminous coal and their respective blends via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Bioresour Technol. 2012;123:581–91.
Zhou ZJ, Hu X, You Z, Wang ZH, Zhou JH, Cen KF. Oxy-fuel combustion characteristics and kinetic parameters of lignite coal from thermo-gravimetric data. Thermochim Acta. 2013;553:54–9.
Buratti C, Barbanera M, Bartocci P, Fantozzi F. Thermogravimetric analysis of the behavior of sub-bituminous coal and cellulosic ethanol residue during co-combustion. Bioresour Technol. 2015;186:154–62.
Kok MV. Simultaneous thermogravimetry–calorimetry study on the combustion of coal samples: effect of heating rate. Energy Convers Manag. 2012;53(1):40–4.
Koga N, Šesták J. Kinetic compensation effect as a mathematical consequence of the exponential rate-constant. Thermochim Acta. 1991;182(2):201–8.
Wang CA, Zhang XM, Liu YH, Che DF. Pyrolysis and combustion characteristics of coals in oxyfuel combustion. Appl Energy. 2012;97:264–73.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Shanxi coal-based low carbon joint fund (U1610254), Shanxi Provincial Science and Technology Major Programs (MD2015-01), Shanxi Provincial Programs for Coal-based key Science and Technology Development (MD2014-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Wang, B. & Cheng, F. Thermal and kinetic characteristics of combustion of coal sludge. J Therm Anal Calorim 129, 1899–1909 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6341-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6341-1