Abstract
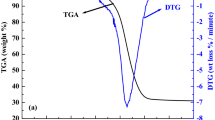
The reuse of coal gangue for energy recovery is developing rapidly in China, due to its advantage in achieving both economic and environmental benefits. Low-quality coal is often added to elevate the calorific value of the fuel. In this paper, the combustion characteristics as well as pollutant emissions (SO2 and NO) of coal gangue, low-quality coal and their blends at different proportions were investigated by using both thermal analysis and fixed-bed reactor. Results showed that compared with pure coal gangue, co-combustion with low-quality coal lowered ignition and burnout temperature, but only slightly decreased the activation energy. In regard to pollution emissions, the coal addition contributed to the tailing peak of SO2 emission during co-combustion, which may influence the desulfurization process. The co-combustion elevated the NO yield due to high nitrogen content in the coal used. An increase in char content with increasing coal ratio in turn promoted a reduction in NO.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu HB, Liu ZL. Recycling utilization patterns of coal mining waste in China. Resour Conserv Recycl. 2010;54(12):1331–40.
Zhao YC, Zhang JY, Chou CL, Li Y, Wang ZH, Ge YT, Zheng CG. Trace element emissions from spontaneous combustion of gob piles in coal mines, Shanxi, China. Int J Coal Geol. 2008;73(1):52–62.
Nichol D, Tovey NP. Remediation and monitoring of a burning coal refuse bank affecting the Southsea Looproad at Brymbo, North Wales. Eng Geol. 1998;50(3–4):309–18. doi:10.1016/s0013-7952(98)00030-1.
Ardejani FD, Shokri BJ, Bagheri M, Soleimani E. Investigation of pyrite oxidation and acid mine drainage characterization associated with Razi active coal mine and coal washing waste dumps in the Azad shahr-Ramian region, northeast Iran. Environ Earth Sci. 2010;61(8):1547–60.
Meng FR, Yu JL, Tahmasebi A, Han YN. Pyrolysis and combustion behavior of coal gangue in O-2/CO2 and O-2/N-2 mixtures using thermogravimetric analysis and a drop tube furnace. Energy Fuel. 2013;27(6):2923–32.
The China Resources Utilization Annual Report (2012). http://hzs.ndrc.gov.cn/newgzdt/201304/t20130412_536759.html.
Xiao HM, Ma XQ, Liu K. Co-combustion kinetics of sewage sludge with coal and coal gangue under different atmospheres. Energy Convers Manag. 2010;51(10):1976–80.
Zhou CC, Liu GJ, Cheng SW, Fang T, Lam PKS. Thermochemical and trace element behavior of coal gangue, agricultural biomass and their blends during co-combustion. Bioresour Technol. 2014;166:243–51.
Xiao HM, Ma XQ, Lai ZY. Isoconversional kinetic analysis of co-combustion of sewage sludge with straw and coal. Appl Energy. 2009;86(9):1741–5.
Liu Z, Zhang YS, Zhong LC, Orndroff W, Zhao HY, Cao Y, Zhang K, Pan WP. Synergistic effects of mineral matter on the combustion of coal blended with biomass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113(2):489–96.
Yi QG, Qi FJ, Cheng G, Zhang YG, Xiao B, Hu ZQ, Liu SM, Cai HY, Xu S. Thermogravimetric analysis of co-combustion of biomass and biochar. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;112(3):1475–9.
Backreedy RI, Jones JM, Ma L, Pourkashanian M, Williams A, Arenillas A, Arias B, Pis JJ, Rubiera F. Prediction of unburned carbon and NOx in a tangentially fired power station using single coals and blends. Fuel. 2005;84(17):2196–203.
Haykiri-Acma H, Yaman S, Kucukbayrak S. Co-combustion of low rank coal/waste biomass blends using dry air or oxygen. Appl Therm Eng. 2013;50(1):251–9.
Faundez J, Arias B, Rubiera F, Arenillas A, Garcia X, Gordon AL, Pis JJ. Ignition characteristics of coal blends in an entrained flow furnace. Fuel. 2007;86(14):2076–80.
Jia CX, Wang Q, Ge JX, Xu XF. Pyrolysis and combustion model of oil sands from non-isothermal thermogravimetric analysis data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116(2):1073–81.
Lei M, Wang CB, Wang SL. Effect of pyrolysis characteristics on ignition mechanism and NO emission of pulverized coal during oxy-fuel combustion. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117(2):665–73.
Cheng HF, Liu QF, Zhang S, Wang SQ, Frost RL. Evolved gas analysis of coal-derived pyrite/marcasite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116(2):887–94.
Querol X, Izquierdo M, Monfort E, Alvarez E, Font O, Moreno T, Alastuey A, Zhuang X, Lu W, Wang Y. Environmental characterization of burnt coal gangue banks at Yangquan, Shanxi Province, China. Int J Coal Geol. 2008;75(2):93–104.
Sun YZ, Fan JS, Qin P, Niu HY. Pollution extents of organic substances from a coal gangue dump of Jiulong coal mine, China. Environ Geochem Health. 2009;31(1):81–9.
Zhou CC, Liu GJ, Yan ZC, Fang T, Wang RW. Transformation behavior of mineral composition and trace elements during coal gangue combustion. Fuel. 2012;97:644–50. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2012.02.027.
Chen Y, Mori S, Pan WP. Studying the mechanisms of ignition of coal particles by TG-DTA. Thermochim Acta. 1996;275(1):149–58.
Tahmasebi A, Kassim MA, Yu JL, Bhattacharya S. Thermogravimetric study of the combustion of Tetraselmis suecica microalgae and its blend with a Victorian brown coal in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 atmospheres. Bioresour Technol. 2013;150:15–27.
Otero M, Calvo LF, Gil MV, Garcia AI, Moran A. Co-combustion of different sewage sludge and coal: a non-isothermal thermogravimetric kinetic analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(14):6311–9.
Doyle C. Estimating isothermal life from thermogravimetric data. J Appl Polym Sci. 1962;6(24):639–42.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. General treatment of the thermogravimetry of polymers. J Res Nat Bur Stand. 1966;70(6):487–523.
Ozawa T. Estimation of activation energy by isoconversion methods. Thermochim Acta. 1992;203:159–65.
Idris SS, Rahman NA, Ismail K. Combustion characteristics of Malaysian oil palm biomass, sub-bituminous coal and their respective blends via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Bioresour Technol. 2012;123:581–91.
Chen LG, Bhattacharya S. Sulfur emission from victorian brown coal under pyrolysis, oxy-fuel combustion and gasification conditions. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47(3):1729–34.
Paulik F, Paulik J, Arnold M. Kinetics and mechanism of the decomposition of pyrite under conventional and quasi-isothermal quasi-isobaric thermoanalytical conditions. J Therm Anal. 1982;25(2):313–25.
Hu GL, Dam-Johansen K, Stig W, Hansen JP. Decomposition and oxidation of pyrite. Prog Energ Combust. 2006;32(3):295–314.
Glarborg P, Jensen AD, Johnsson JE. Fuel nitrogen conversion in solid fuel fired systems. Prog Energy Combust. 2003;29(2):89–113.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support by the Common Development Fund of Beijing and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51172001, 51172003 and 51272005). Supports by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2012 AA06A114) and Key Projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program (2013 BAC14B07 and 2011 BAB03B02) are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Nakano, J., Liu, L. et al. Co-combustion and emission characteristics of coal gangue and low-quality coal. J Therm Anal Calorim 120, 1883–1892 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4477-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4477-4