Abstract
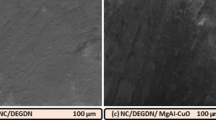
The effect of MnC2O4 nanoparticles on the thermal decomposition of double-base propellant composed of nitrocellulose (NC) and triethylene glycol dinitrate (TEGDN) has been investigated by TG/DSC–MS–FTIR coupling technique. The results show that the decomposition of TEGDN/NC propellant has two stages, the first stage is the volatility and decomposition of TEGDN, the second is the decomposition of NC. The addition of MnC2O4 nanoparticles gets the onset temperature of first stage higher, and makes the activation energy of decomposition of TEGDN grow by about 20–30 kJ/mol. The catalytic also accelerates the total weight loss, and makes the peak temperatures of DSC curves higher. The activation energy of the second stage has a decrease of 20–40 kJ/mol. MS and FTIR analysis show that the catalyst gets the gas products of macromolecular significantly reduce, while small molecules increase significantly. It also results in the decrease of H2O, N2O, and NO2, and the increase of NO and HCN. Above all, the catalytic improves the thermal stability of TEGDN/NC propellant, make it more safety in storage, and make the decomposition easier and more thorough in main reaction zone.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen P, Zhao FQ, Li SW, Yin CM. Thermal decomposition characteristics of triethylene glycol dinitrate. Initiators Pyrotech. 1999;3:5–10.
Brown LD, Korte DW Jr. Primary dermal irritation potential of triethyleneglycol dinitrate (TEGDN) in rabbits. Pentagon reports A443602; 1989.
Huang K. Catalytic effects on the combustion performance of the TEGND/NC propellant [D]. Nanjjing: Nanjing university of Science and Technology; 2008.
Wei W, Jiang X, Lu L, Yang X, Wang X. Study on the catalytic effect of NiO nanoparticles on the thermal decomposition of TEGDN/NC propellant. J Hazard Mater. 2009;168:838–42.
Wenxian W, Bingbing C, Xiaohong J, Ludu L. The catalytic effect of NiO on thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102(3):863–6.
Yi J, Zhao F, Xu S, Zhang L, Gao H, Hu R. Effects of pressure and TEGDN content on decomposition reaction mechanism, and kinetics of DB gun propellant containing the mixed ester of TEGDN and NG. J Hazard Mater. 2009;165:853–9.
Yi J, Xu S, Ma X. Non-isothermal thermal decomposition reaction kinetics of TEGDN gun propellant. Chinese J Exp Propellants. 2007;30(4):67–71.
Alcolea A, Ibarra I, Caparrós A, Rodríguez R. Study of the MS response by TG–MS in an acid mine drainage efflorescence. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;101(3):1161–5.
Rejitha KS, Ichikawa T, Mathew S. Decomposition studies of [Ni(NH3)6]X2 (X = Cl, Br) in the solid state using TG-MS and TR-XRD. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;103(2):515–23.
Xie W, Pan W-P. Thermal characterization of materials using evolved gas analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;65:669–85.
NIST Chemistry Webbook Standard Reference Database, No. 69, Sep 2008 Release (http://www.webbook.nist.gov/chemistry).
Liu Q, Lv C, Yang Y, He F, Ling L. Investigation on the effects of fire retardants on the thermal decomposition of wood-derived rayon fiber in an inert atmosphere by thermogravimetry–mass spectrometer. Thermochim Acta. 2004;419:205–9.
Chen P, Zhao FQ, Li SW, Yin CM. Thermal decomposition characteristics of triethyleneglycol dinitrate. Initiators Pyrot. 1999;80(3):5–10 (in Chinese).
Dong Q. Infrared spectrometry. Beijing: Petroleum Chemical Industry Press; 1977. p. 165–70.
Friedman HL. Kinetics and gaseous products of thermal decomposition of polymers. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem. 1976;1(1):57–79.
Wang YP, Zhu JW, Yang XJ, Lu LD, Wang X. Preparation of NiO nanoparticles and their catalytic activity in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Thermochim Acta. 2005;437:106–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chenxia, K., Huang, C. et al. Effect of MnC2O4 nanoparticles on the thermal decomposition of TEGDN/NC propellant. J Therm Anal Calorim 109, 171–176 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1694-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1694-3