Abstract
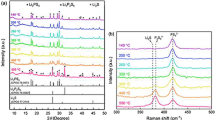
Li3PS4 is the most typical solid electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium batteries. However, to date, there are few reports on Li3PS4 solid electrolyte synthesized using the solution process. Here, β-Li3PS4 solid electrolytes were prepared via liquid-phase synthesis by dissolving Li2S and P2S5 in ethylenediamine (EDA) to form a homogeneous solution of Li3PS4. Since EDA is a basic protonic solvent, it effectively suppressed the decomposition of Li3PS4. An intermediate phase consisting of Li3PS4 and EDA was formed as a precursor after drying the EDA solution at 200 °C under vacuum. After heat treatment at temperatures above 260 °C, β-Li3PS4 was crystallized from the precursor. The ionic conductivity of the prepared β-Li3PS4 was 5.0 × 10−5 S cm−1 at 25 °C and the activation energy for conduction was 35 kJ mol−1. The obtained EDA solution of Li3PS4 will be effective in forming electrolyte-electrode interfaces with the large contact areas in all-solid-state batteries.

Highlights
-
β-Li3PS4 is prepared via liquid-phase synthesis using a ethylenediamine solution.
-
Ethylenediamine effectively suppresses the decomposition of PS43−.
-
The ionic conductivity of the prepared β-Li3PS4 is 5.0 × 10−5 S cm−1 at 25 °C.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/35104644
Kamaya N, Homma K, Yamakawa Y, Hirayama M, Kanno R, Yonemura M, Kamiyama T, Kato Y, Hama S, Kawamoto K, Mitsui A (2011) A lithium superionic conductor. Nat Mater 10:682–686. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3066
Kato Y, Hori S, Saito T, Suzuki K, Hirayama M, Mitsui A, Yonemura M, Iba H, Kanno R (2016) High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat Energy 1:16030. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2016.30
Mizuno F, Hayashi A, Tadanaga K, Tatsumisago M (2005) New, highly ion‐conductive crystals precipitated from Li2S–P2S5 glasses. Adv Mater 17:918–921. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200401286
Miura A, Rosero-Navarro NC, Sakuda A, Tadanaga K, Phuc NHH, Matsuda A, Machida N, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2021) Synthesis of sulfide solid electrolytes from Li2S and P2S5 in anisole. J Mater Chem A 9:400–405. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA08658D
Liu Z, Fu W, Payzant EA, Yu X, Wu Z, Dudney NJ, Kiggans J, Hong K, Rondinone AJ, Liang C (2013) Anomalous high ionic conductivity of nanoporous β-Li3PS4. J Am Chem Soc 135:975–978. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3110895
Wang H, Hood ZD, Xia Y, Liang C (2016) Fabrication of ultrathin solid electrolyte membranes of β-Li3PS4 nanoflakes by evaporation-induced self-assembly for all-solid-state batteries. J Mater Chem A 4:8091–8096. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA02294D
Phuc NHH, Totani M, Morikawa K, Muto H, Matsuda A (2016) Preparation of Li3PS4 solid electrolyte using ethyl acetate as synthetic medium. Solid State Ion 288:240–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2015.11.032
Phuc NHH, Morikawa K, Mitsuhiro T, Muto H, Matsuda A (2017) Synthesis of plate-like Li3PS4 solid electrolyte via liquid-phase shaking for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Ionics 23:2061–2067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2035-8
Choi S, Lee S, Park J, Nichols WT, Shin D (2018) Tailored Li2S–P2S5 glass-ceramic electrolyte by MoS2 doping, possessing high ionic conductivity for all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries. Appl Surf Sci 444:10–14. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA10142A
Xu RC, Wang XL, Zhang SZ, Xia Y, Xia XH, Wu JB, Tu JP (2018) Rational coating of Li7P3S11 solid electrolyte on MoS2 electrode for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 374:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.10.093
Rangasamy E, Liu Z, Gobet M, Pilar K, Sahu G, Zhou W, Wu H, Greenbaum S, Liang C (2015) An iodide-based Li7P2S8I superionic conductor. J Am Chem Soc 137:1384–1387. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja508723m
Wang Y, Liu Z, Zhu X, Tang Y, Huang F (2013) Highly lithium-ion conductive thio-LISICON thin film processed by low-temperature solution method. J Power Sources 224:225–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.09.097
Choi YE, Park KH, Kim DH, Oh DY, Kwak HR, Lee Y-G, Jung YS (2017) Coatable Li4SnS4 solid electrolytes prepared from aqueous solutions for all‐solid‐state lithium‐ion batteries. ChemSusChem 10:2605–2611. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201700409
Yubuchi S, Uematsu M, Hotehama C, Sakuda A, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2019) An argyrodite sulfide-based superionic conductor synthesized by a liquid-phase technique with tetrahydrofuran and ethanol. J Mater Chem A 7:558–566. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA09477B
Teragawa S, Aso K, Tadanaga K, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2014) Preparation of Li2S–P2S5 solid electrolyte from N-methylformamide solution and application for all-solid-state lithium battery. J Power Sources 248:939–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.09.117
Hayashi A, Hama S, Morimoto H, Tatsumisago M, Minami T (2001) Preparation of Li2S–P2S5 amorphous solid electrolytes by mechanical milling. J Am Ceram Soc 84:477–479. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2001.tb00685.x
Ozturk T, Ertas E, Mert O (2010) A berzelius reagent, phosphorus decasulfide (P4S10), in organic syntheses. Chem Rev 110:3419–3478. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900243d
Mizuno F, Hayashi A, Tadanaga K, Tatsumisago M (2005) Mechanochemical synthesis of lithium ion conducting glasses and glass–ceramics in the system Li2S–P–S. Solid State Ion 176:2349–2353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2005.03.025
Funding
This work was partially supported by JST ALCA-SPRING (Grant JPMJAL1301), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, A., Kimura, T., Sakuda, A. et al. Liquid-phase synthesis of Li3PS4 solid electrolyte using ethylenediamine. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 101, 2–7 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05524-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05524-y