Abstract
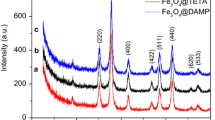
An amino-functionalized poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) were obtained over magnetite particles. The materials obtained were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). ATR-FTIR spectra showed adsorption bands attributed to the amino-functionalized polymeric network and the Fe–O bonds of magnetite, while XRD patterns indicated that magnetite was covered with an amorphous material, the PDMS polymeric network. Thermal analysis showed that the obtained materials were thermally stable up to 300 °C. SEM micrographs revealed that the polymer network coated the magnetite particles, since the surface roughness decrease. Adsorption of Cu(II) was conducted in aqueous medium at different pH values, contact times, and metal ion concentrations. The adsorption capacities obtained were of 0.56, 0.44, and 0.41 mmol L−1 for the materials with a decreasing content of amino group, respectively. Nonlinear kinetic model equations were applied, showing that the materials with lower and higher content of APTMS was described by chemisorption model, while that the intermediary content by a pseudo-second-order fit. The experimental data of adsorption isotherm were studied by various models and Sips model exhibited the best fit for all materials.

Highlights
-
Magnetite grains were covered by an elastomeric network functionalized with amino groups.
-
Simple preparation of the adsorbent.
-
Adsorption equilibrium are reached after 36 h immersion in aqueous solution.
-
Magnetic separation of the solution after adsorption.
-
Promising adsorption capacities for copper ions in aqueous media.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishra SP (2014) Adsorption-desorption of heavy metal ions. Curr Sci 107:601–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2011.01.010
Al-Homaidan AA, Al-Houri HJ, Al-Hazzani AA et al. (2014) Biosorption of copper ions from aqueous solutions by Spirulina platensis biomass. Arab J Chem 7:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.05.022
de Luna MDG, Flores ED, Cenia MCB, Lu M-C (2015) Removal of copper ions from aqueous solution by adlai shell (Coix lacryma-jobi L.) adsorbents. Bioresour Technol 192:841–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.018
Hernández-Morales V, Nava R, Acosta-Silva YJ et al. (2012) Adsorption of lead (II) on SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieve functionalized with –NH2 groups. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 160:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2012.05.004
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
Pan B, Pan B, Zhang W et al. (2009) Development of polymeric and polymer-based hybrid adsorbents for pollutants removal from waters. Chem Eng J 151:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.02.036
Giraldo L, Moreno-Piraján JC (2013) Study on the adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution on modified SBA-15. Mater Res 16:745–754. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392013005000051
Bhattacharyya KG, Gupta SS (2008) Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: a review Adv Colloid Interface Sci 140:114–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2007.12.008
Zhang L, Zeng Y, Cheng Z (2016) Removal of heavy metal ions using chitosan and modified chitosan: a review. J Mol Liq 214:175–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.12.013
Sadeek SA, Negm NA, Hefni HHH, Abdel Wahab MM (2015) Metal adsorption by agricultural biosorbents: adsorption isotherm, kinetic and biosorbents chemical structures. Int J Biol Macromol 81:400–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.031
Ihsanullah AbbasA, Al-Amer AM et al. (2016) Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by advanced carbon nanotubes: critical review of adsorption applications. Sep Purif Technol 157:141–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.11.039
Kumar R, Jain SK, Verma S, Malodia P (2015) Mercapto functionalized silica entrapped polyacrylamide hydrogel: arsenic adsorption behaviour from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 456:241–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.06.026
Hokkanen S, Repo E, Suopajarvi T et al. (2014) Adsorption of Ni(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by amino modified nanostructured microfibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 21:1471–1487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0240-4
Han Y, Fang K, Gu X et al. (2012) Amino-functionalized mesoporous silicas MCM-48 as Zn(II) sorbents in water samples. J Chem Eng Data 57:2059–2066. https://doi.org/10.1021/je3003496
Hakami O, Zhang Y, Banks CJ (2012) Thiol-functionalised mesoporous silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles for high efficiency removal and recovery of Hg from water. Water Res 46:3913–3922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.04.032
dos Santos MP, Magosso HA, Yoshida IVP, Gushikem Y (2012) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS)-Schiff base, a new polymeric network and its adsorbent capability for copper ions from ethanol. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 398:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2012.01.030
Manu V, Mody HM, Bajaj HC, Jasra RV(2009) Adsorption of Cu2+ on amino functionalized silica gel with different loading Ind Eng Chem Res 48:8954–8960. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie900273v
Pissetti FL, De Araújo PL, Silvaa FAB, Poirier GY (2015) Synthesis of poly(dimethylsiloxane) networks functionalized with imidazole or benzimidazole for copper(II) removal from water. J Braz Chem Soc 26:266–272. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20140264
Peng X, Xu F, Zhang W et al. (2014) Magnetic Fe3O4 @ silica-xanthan gum composites for aqueous removal and recovery of Pb2+. Colloids Surf a-Physicochem Eng Asp 443:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.10.062
Yamaura M, Fungaro DA (2013) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic adsorbent prepared by magnetite nanoparticles and zeolite from coal fly ash. J Mater Sci 48:5093–5101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7297-6
Sobhanardakani S, Zandipak R (2015) 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine functionalized sodium dodecyl sulfate-coated magnetite nanoparticles for effective removal of Cd(II) and Ni(II) ions from water samples. Environ Monit Assess 187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4635-y
Azari A, Kakavandi B, Rezaei R, Ahmadi E (2015) Rapid and efficient magnetically removal of heavy metals by magnetite-activated carbon composite: a statistical design approach. J Porous Mater 22:1083–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-9983-z
Reddy DHK, Lee SM (2013) Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 201–202:68–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.10.002
Pissetti FL, Magosso Ha, Yoshida IVP et al. (2007) n-Propylpyridinium chloride-modified poly(dimethylsiloxane) elastomeric networks: preparation, characterization, and study of metal chloride adsorption from ethanol solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 314:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.05.040
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K Sven Vetenskapsakad Handl 24:1–39
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Lopes ECN, Dos Anjos FSC, Vieira EFS, Cestari AR (2003) An alternative Avrami equation to evaluate kinetic parameters of the interaction of Hg(II) with thin chitosan membranes. J Colloid Interface Sci 263:542–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00326-6
Elovich SY, Zhabrova GM (1939) Mechanism of the catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene on nickel. I. Kinetics of the process. J Phys Chem 13:1761–1775
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Chem Phys 57:385–471
Sips R (1948) Combined form of Langmuir and Freundlich equations. J Chem Phys 16:490–495. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746922
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024–1024. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150576a611
Royer B, Cardoso NF, Lima EC et al. (2009) Applications of Brazilian pine-fruit shell in natural and carbonized forms as adsorbents to removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions-Kinetic and equilibrium study. J Hazard Mater 164:1213–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.028
Ncibi MC (2008) Applicability of some statistical tools to predict optimum adsorption isotherm after linear and non-linear regression analysis. J Hazard Mater 153:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.08.038
Pissetti FL, Yoshida IVP, Gushikem Y, Kholin YV (2008) Metal ions adsorption from ethanol solutions on ethylenediamine-modified poly(dimethylsiloxane) elastomeric network. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 328:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.06.016
Silva FAB, Pissetti FL (2014) Adsorption of cadmium ions on thiol or sulfonic-functionalized poly(dimethylsiloxane) networks. J Colloid Interface Sci 416:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.10.039
Jadav GL, Aswal VK, Singh PS (2015) In-situ preparation of polydimethylsiloxane membrane with long hydrophobic alkyl chain for application in separation of dissolved volatile organics from wastewater. J Memb Sci 492:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.05.050
Barczak M, Oszust M, Michalak K et al. (2014) Functionalized SBA-15 organosilicas as sorbents of mercury(II), cadmium(II) and copper(II). Glas. Phys Chem 40:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1087659614010040
Kim JM, Wolf F, Baier SK (2015) Effect of varying mixing ratio of PDMS on the consistency of the soft-contact Stribeck curve for glycerol solutions. Tribol Int 89:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.12.010
Shen S-C, Ng WK, Chia L et al. (2011) Sonochemical synthesis of (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane-modified monodispersed silica nanoparticles for protein immobilization. Mater Res Bull 46:1665–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATERRESBULL.2011.06.004
Lin Y, Chen H, Lin K et al. (2011) Application of magnetic particles modified with amino groups to adsorb copper ions in aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 23:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60371-3
Hozhabr Araghi S, Entezari MH (2015) Amino-functionalized silica magnetite nanoparticles for the simultaneous removal of pollutants from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 333:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.211
Infante-Castillo R, Rivera-Montalvo LA, Hernández-Rivera SP (2008) Theoretical DFT, vibrational and NMR studies of benzimidazole and alkyl derivatives. J Mol Struct 877:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2007.07.012
Ma Z, Guan Y, Liu H (2005) Synthesis and characterization of micron-sized monodisperse superparamagnetic polymer particles with amino groups. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 43:3433–3439. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.20803
Farjadian F, Ghasemi S, Mohammadi-Samani S (2016) Hydroxyl-modified magnetite nanoparticles as novel carrier for delivery of methotrexate. Int J Pharm 504:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.03.022
Yazdani F, Fattahi B, Azizi N (2016) Synthesis of functionalized magnetite nanoparticles to use as liver targeting MRI contrast agent. J Magn Magn Mater 406:207–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.01.026
Silva FAB, Chagas-Silva FA, Florenzano FH, Pissetti FL (2016) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) and Poly[vinyltrimethoxysilane-co-2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate] based cross-linked organic-inorganic hybrid adsorbent for copper(II) removal from aqueous solutions J Braz Chem Soc 00:1–11. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20160110
Li S, Qin F, Qin P et al. (2013) Preparation of PDMS membrane using water as solvent for pervaporation separation of butanol–water mixture. Green Chem 15. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3GC40291F
Naeimi M, Karkhaneh A, Barzin J et al. (2013) Novel PDMS-based membranes: sodium chloride and glucose permeability. J Appl Polym Sci 000:0. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.37709
Darwish MSA, Stibor I (2015) Preparation and characterization of magnetite e PDMS composites by magnetic induction heating. Mater Chem Phys 164:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.08.038
De Souza Neto FN, Araújo OA, Guilherme LR et al. (2015) Particles that slide over the water surface: Synthesis and characterization of iron oxides particles coated with PDMS, with hydrophobic and magnetic properties. Mater Chem Phys 162:100e–105e. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.05.014
Qu R, Wang M, Sun C et al. (2008) Chemical modification of silica-gel with hydroxyl- or amino-terminated polyamine for adsorption of Au(III). Appl Surf Sci 255:3361–3370. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2008.09.055
Redondo SUA, Radovanovic E, Torriani IL, Yoshida IVP (2001) Polycyclic silicone membranes. Synthesis, characterization and permeability evaluation. Polymer 42:1319–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00520-6
Srivastava VC, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2006) Characterization of mesoporous rice husk ash (RHA) and adsorption kinetics of metal ions from aqueous solution onto RHA. J Hazard Mater 134:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.052
Guo W, Chen R, Liu Y et al. (2013) Preparation of ion-imprinted mesoporous silica SBA-15 functionalized with triglycine for selective adsorption of Co(II). Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 436:693–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.08.011
Peng W, Xie Z, Cheng G et al. (2015) Amino-functionalized adsorbent prepared by means of Cu(II) imprinted method and its selective removal of copper from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 294:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.046
Mahaninia MH, Rahimian P, Kaghazchi T (2015) Modified activated carbons with amino groups and their copper adsorption properties in aqueous solution. Chin J Chem Eng 23:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.11.004
Montazer-Rahmati MM, Rabbani P, Abdolali A, Keshtkar AR (2011) Kinetics and equilibrium studies on biosorption of cadmium, lead, and nickel ions from aqueous solutions by intact and chemically modified brown algae. J Hazard Mater 185:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.047
Adamczuk A, Kołodyńska D (2015) Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies on removal of chromium, copper, zinc and arsenic from aqueous solutions onto fly ash coated by chitosan. Chem Eng J 274:200–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.088
Ali RM, Hamad HA, Hussein MM, Malash GF (2016) Potential of using green adsorbent of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions: adsorption kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic, mechanism and economic analysis. Ecol Eng 91:317–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.03.015
Zhang H, Xu M, Wang H et al. (2013) Adsorption of copper by aminopropyl functionalized mesoporous delta manganese dioxide from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 435:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2012.12.037
Lei D, Zheng Q, Wang Y, Wang H (2015) Preparation and evaluation of aminopropyl-functionalized manganese-loaded SBA-15 for copper removal from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci (China) 28:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.06.045
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Papageorgiou SK, Katsaros FK, Kouvelos EP et al. (2006) Heavy metal sorption by calcium alginate beads from Laminaria digitata. J Hazard Mater 137:1765–1772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.017
Ren Y, Abbood HA, He F et al. (2013) Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chem Eng J 226:300–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.059
Xin X, Wei Q, Yang J et al. (2012) Highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions by amine-functionalized mesoporous Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 184:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.016
Li H, Xiao DL, He H et al. (2013) Adsorption behavior and adsorption mechanism of Cu(II) ions on amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China (Engl Ed 23:2657–2665. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62782-X
Yong-mei H, Man C, Zhong-bo H (2010) Effective removal of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 184:392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.048
Ge F, Li M, Ye H, Zhao B (2012) Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 211–212:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.013
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to CAPES for the master’s degree fellowship granted to MRB, as well as to CNPq for financial support. We also thank the CME-UFRGS for use of the scanning electron microscopy facilities and Leliz T. Arenas for the SEM images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Rezende Bonesio, M., Pissetti, F.L. Magnetite particles covered by amino-functionalized poly(dimethylsiloxane) network for copper(II) adsorption from aqueous solution. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 94, 154–164 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05154-5