Abstract
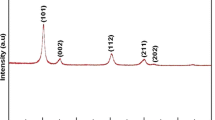
Magnesium hydroxide and magnesium oxide nanostructures have been prepared by microwave/hydrothermal technique using magnesium metal in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The applied power of the microwave was 700 W for 10 min at 145 °C. The method produced Mg(OH)2 powder as a base material for MgO by calcinations at 550 °C for 2 h. X-ray diffraction data confirms the microwave production of Mg(OH)2 and (MgO) through the agreement with the standard JCDPS cards. Scanning electron microscopy shows nanoplates morphology for Mg(OH)2 and large-scale nanoplates with a hexagonal shape for MgO. The fundamental direct optical band gap of Mg(OH)2 equals 5.8 eV while for MgO equals 5.2 eV from the analysis of diffused reflectance data. MgO has higher dielectric constant than Mg(OH)2 at the higher frequencies. AC electrical conductivity increases with increasing the applied frequency for both materials. The microwave-hydrothermal technique shows a promising method for production of magnesium compounds from magnesium metal which can be used in different aspects such as catalysis, wastewater treatment, pharmaceutical and coated materials.

SEM images of MgO nano-plates







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao CNR, Kulkarni GU, Thomas PJ, Edwards PP (2000) Chem Soc Rev 29:27–35
Lv J, Qiu L, Qu B (2004) Nanotechnology 15:1576–1578
Yan L, Zhuang J, Sun X, Deng Z, Li Y (2002) Mater Chem Phys 76(2):119–122
Ma RZ, Bando Y (2003) Chem Phys Lett 370:770
Selvama NCS, Kumara RT, Kennedyb LJ, Vijaya JJ (2011) J Alloy Compd 509:9809–9815
Kumar A, Kumar J (2008) J Phys Chem Solids 69:2764
Fang F, Hu B, Wang L, Lu R, Yang C (2008) Front. Chem. China 3:193–197
Ding Y, Zhang G, Wu H, Hai B, Wang L, Qian Y (2001) Chem Mater 13:435
Niu H, Yang Q, Tang K, Xie Y (2006) J Nanopart Res 8:881
Geng B, Zhang L, Meng G, Xie T, Peng X, Lin Y (2003) J Cryst Growth 259:291–295
Shall ME, Slack W, Vann W, Kane D, Hanley D (1998) J Phys Chem 98:3067
Subramania A, Kumar GV, Priya ARS, Vasudevan T (2007) Nanotechnology 18:225601
Matthews JS, Just O, Johnson BO, Rees WS (2000) J Chem Vap Depos 6:129
Aslan K, Geddes CD (2008) Plasmonics 3:89
Al-Gaashani R, Radiman S, Al-Douri Y, Tabet N, Daud AR (2012) J Alloy Comp 521:71–76
Shah MA, Qurashi A (2009) J Alloy Comp 482:548–551
Li XC, Xiao W, He GH, Zheng WJ, Yu NS, Tan M (2012) Colloids Surf A 408:79–86
Bhatte KD, Sawant DN, Deshmukh KM, Bhanage BM (2012) Particuology 10:384–387
Callister WD (1997) Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction. Wiley, New York
Zahran HY, Yahia IS (2015) Appl Phys 119:1397–1403
Yousefi S, Ghasemi B, Tajally M, Asghari A (2017) J Alloy Compd 711:521–529
Sathyamoorthy R, Mageshwari K, Mali SS, Priyadharshini S, Patil PS (2013) Effect of organic capping agent on the photocatalytic activity of MgO nanoflakes obtained by thermal decomposition route. Ceram Int 39:323–330
Weckhuysen BM, Schoonheydt RA (1999) Catal Today 49:441–451
Yakuphanoglu F, Mehrotra R, Gupta A, Munoz M (2009) J Appl Polym Sci 114:794
Hafez M, Yahia IS, Taha S (2014) Spectrochim Acta A 127:521–529
Bindhu MR, Umadevi M, Kavin Micheal M, Arasu MV, Abdullah Al-Dhabi N (2016) Structural, morphological and optical properties of MgO nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. Mater Lett 166:19–22
Mbarki R, Hamzaoui AH, M’nif A (2015) Dielectric properties and electrical conductivity of MgO synthesized by chemical precipitation and sol-gel method. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 69:10402
Sierra-Fernandez A, Gomez-Villalba LS, Milosevic O, Fort R, Rabanal ME (2014) Synthesis and morpho-structural characterization of nanostructured magnesium hydroxide obtained by a hydrothermal method. Ceram Int 40:12285–12292
Hadia NMA, Mohamed HAH (2015) Characteristics and optical properties of MgO nanowires synthesized by solvothermal method. Mater Sci Semicond Process 29:238–244
Prashantha SC, Lakshminarasappa BN, Nagabhushana BM (2011) J Alloy Comp 509:10185–10189
Brodie G, Jacob MV, Farrell P (2016) Microwave and Radio-Frequency Technologies in Agriculture: An Introduction for Agriculturalists and Engineers, Walter de Gruyter Open Ltd. Warschau/Berlin
Bouzidi A, Yahia IS, El-Sadek MSA (2017) Dyes Pigments 146:66–72
Huang Z, Zhou W, Tang X, Luo Fa, Zhu J (2012) Int J Appl Ceram Technol 9(2):413–420
Qing YC, Zhou WC, Jia S, Luo F, Zhu DM (2010) Appl Phys A 100:1177–1181
Mansour ShA, Yahia IS, Yakuphanoglu F (2010) Dyes Pigm 87:144–148
Yaghmour SJ (2010) Eur Phys J Appl Phys 49:10402
Mbarki R, Mnif A, Hamzaoui AH (2015) Mater Sci Semicond Process 29:300–306
Jonscher AK (1977) Nature 267:673–679
Shukla N, Kumar V, Dwivedi DK (2016) J Non-Oxide Glass 8:47–57
Elliot SR (1978) Solid State Comm 27:749
Wahab LA, Zayed HA, Farrag AA (2012) Arab J Nucl Sci Appl 45:290–305
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to The Research Center for Advanced Material Science (RCAMS) at King Khalid University, with grant number (RCAMS-1-17-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Highlights
-
Magnesium hydroxide and magnesium oxide nanostructures have been prepared by microwave/hydrothermal technique.
-
SEM shows nano-plates morphology for Mg(OH)2 and large-scale nano-plates with a hexagonal shape for MgO.
-
The direct optical band gap of Mg(OH)2 equals =5.012 eV while for MgO equals 4.844 eV from the analysis of diffused reflectance data.
-
MgO has higher dielectric constant than Mg(OH)2 at the higher frequencies.
-
Magnesium compounds can be used as catalysis, wastewater treatment, pharmaceutical and coated materials.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahran, H.Y., Shneouda, S.S., Yahia, I.S. et al. Facile and rapid synthesis of nanoplates Mg(OH)2 and MgO via Microwave technique from metal source: structural, optical and dielectric properties. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 86, 104–111 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4613-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4613-2