Abstract
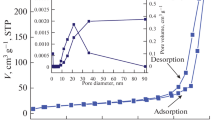
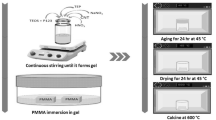
Two glasses of the CaO-MgO-P2O5-SiO2 system with different MgO contents (0 and 10 mol%, respectively) have been synthesized by sol–gel method. The degradation of glass samples was evaluated through the weight loss in the tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane and hydrochloric acid (Tris–HCl) buffer solution, and the in vitro bioactivity was assessed by determining the changes in surface morphology and composition after soaking in a simulated body fluid. Formation of the apatite-like layer on glasses surface was studied by means of X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared, scanning electron microscopy. Results indicate that, with the partial substitution of MgO for CaO in glass composition, the glass degradation decrease and the formation of apatite-like layer is delayed. Furthermore, it is observed that the glass bioactivity is relative to its dissolution, and the effects of MgO on glass degradability and bioactivity may be attributed to the influence of ionic field strength and distinct bonding configuration of glass.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hench LL (1999) Mater Sci Forum 293:37
Vitale-Brovarone C, Vernè E, Bosetti M, Appendino P, Cannas M (2005) J Mater Sci Mater Med 16:909
Balamurugan A, Sockalingum G, Michel J, Fauré J, Banchet V, Wortham L, Bouthors S, Laurent-Maquin D, Balossier G (2006) Mater Lett 60:3752
Fathi MH, Doostmohammadi A (2009) J Mater Process Tech 209:1385
Pereira MM, Clark AE, Hench LL (1994) J Biomed Mater Res 28:693
Hench LL (1998) J Am Ceram Soc 81:1705
Zhong JP, Greenspan DC (2000) J Biomed Mater Res (Appl Biomater) 53:694
Sepulveda P, Jones JR, Hench LL (2002) J Biomed Mater Res 61:301
Wu CT, Ramaswamy Y, Chang J, Woods J, Chen YQ, Zreiqat H (2008) J Biomed Mater Res (Appl Biomater) 87:346
Wu CT, Chang J, Wang JY, Ni SY, Zhai WY (2005) Biomaterials 26:2925
Kokubo T, Kushitani H, Sakka S, Kitsugi T, Yamamuro T (1990) J Biomed Mater Res 24:721
Ohtsuki C, Kokubo T, Yamamuro T (1992) J Non-Cryst Solids 143:84
Li P, Ohtsuki C, Kokubo T, Nakanishi K, Soga N, Nakamura T, Yamamuro T (1993) J Mater Sci Mater Med 4:127
Martínez A, Izquierdo-Barba I, Vallet-Regí M (2000) Chem Mater 12:3080
Vallet-Regí M, Ragel CV, Salinas AJ (2003) Eur J Inorg Chem 6:1029
Brink M, Turunen T, Happonen RP, Yli-Urpo A (1997) J Biomed Mater Res 37:114
Branda F, Arcobello-Varlese F, Costantini A, Luciani G (2002) Biomaterials 23:711
Ducheyne P, Radin S, King L (1993) J Biomed Mater Res 27:25
Ducheyne P, Radin SJ (1993) J Biomed Mater Res 27:35
Kibalcyc W, Christoffersen J, Christoffersen MR, Zielenkiewicz A, Zielenkiewicz W (1990) J Cryst Growth 106:355
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Department of Science and Technology of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2006GG3203006) and Department of Science and Technology of Jinan, Shandong Province (Grant No. 051070), P. R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Chen, C.Z., Wang, D.G. et al. In vitro degradability and bioactivity of mesoporous CaO-MgO-P2O5-SiO2 glasses synthesized by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 54, 69–76 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2159-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2159-z