Abstract
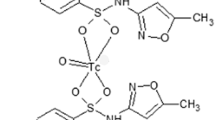
In the current investigation nemonoxacin (NMX) was radiolabeled with 99mTc in the presence of stannous chloride dihydrate as reducing agent. Factors affecting the percent labeling yield of 99mTc-Nemonoxacin (99mTc-NMX) complex were studied in details. The labeled compound was radiochemically characterized and was stable for a time up to 4 h. The complex showed in vitro saturated binding with living multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and penicillin-resistant Streptococci (PRSC). Biodistribution and imaging studies were performed. All results showed that 99mTc-NMX complex is a promising agent for MRSA and PRSC infection imaging and can differentiate between infected and sterile inflammations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shah S, Khan A, Khan M (2011) Radiosynthesis and biodistribution of 99mTcN–garenoxacin dithiocarbamate complex a potential infection imaging agent. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288:59–64
Hussien H, EL-Sheikh R, Goud A, Seddik U, Amin A (2011) Comparative study between chloramine-T and iodogen to prepare radioiodinated etodolac for inflammation imaging. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288:9–15
Shah S, Khan M (2011) Synthesis of 99mTc V:N-Pazufloxacin dithiocarbamate complex and biological evaluation in Wistar rats artificially infected with Escherichia coli. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288:511–516
Basu S, Chryssikos T, Moghadam-Kia S, Zhuang H, Torigian D, Alvai A (2009) Positron emission tomography as a diagnostic tool in infection: present role and future possibilities. Semin Nucl Med 39:36–51
Gallagher H, Ramsay S, Barnes J, Maggs J, Cassidy N, Ketheesan N (2006) Neutrophil labeling with [99mTc]-technetium stannous colloid is complement receptor 3-mediated and increases the neutrophil priming response to lipopolysaccharide. Nucl Med Biol 33:433–439
Chattopadhyay S, Das S, Chandra S, De K, Mishra M, Sarkar B, Sinha S, Ganguly S (2010) Synthesis and evaluation of 99mTc-moxifloxacin a potential infection specific imaging agent. Appl Radiat Isot 68:314–316
Zhang J, Guo H, Zhang S, Lin Y, Wang X (2008) Synthesis and biodistribution of a novel 99mTcN complex of ciprofloxacin dithiocarbamate as a potential agent for infection imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:5168–5170
Roohi S, Mushtaq A, Jehangir M, Ashfaq MS (2006) Synthesis, quality control and biodistribution of 99mTc-Kanamycin. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267:561–566
Motaleb M (2007) Preparation of 99mTc–cefoperazone complex, a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 272:167–171
Akhtar M, Imran M, Nadeem M, Shahid A (2012) Antimicrobial peptides as infection imaging agents: better than radiolabeled antibiotics. Int J Pept 2012:1–19
Rensburg D, Wu R, Perng R, Ho M, Mitha I, Chang L, King C, Bester A, Chung D, Hsu M (2010) Efficacy and safety of nemonoxacin versus levofloxacin for community-acquired pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(10):4098–4106
Lai C, Tan C, Lin S, Liao C, Chou C, Hsu H, Huang Y, Hsueh P (2009) Comparative in vitro activities of nemonoxacin, doripenem, tigecycline and 16 other antimicrobials against Nocardia brasiliensis, Nocardia asteroides and unusual Nocardia species. J Antimicrob Chemother 64:73–78
Chen Y, Liu C, Lu J, King C, Hsueh P (2009) In vitro activity of nemonoxacin (TG-873870), a novel non-fluorinated quinolone, against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, enterococci and Streptococcus pneumoniae with various resistance phenotypes in Taiwan. J Antimicrob Chemother 64:1226–1229
Adam H, Laing N, King C, Lulashnyk B, Hoban D, Zhanel G (2009) In vitro activity of nemonoxacin, a novel nonfluorinated quinolone, against 2440 clinical isolates J. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:4915–4920
Pan X, Ambler J, Mehtar S, Fisher L (1996) Involvement of topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase as ciprofloxacin targets in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:2321–2326
Huang H, Qin X (2014) Review of nemonoxacin with special focus on clinical development. Drug Des Dev Ther 8:765–774
Welling M, Paulusma-Annema A, Batler H, Pauwels E, Nibbering P (2000) 99mTechnetium labelled antimicrobial peptides discriminate between bacterial infections and sterile inflammations. Eur J Nucl Med 27(12):1865–1868
El-Ghany E, Amin A, El-Kawy O, Amin M (2007) 99mTechnetium labeling and freeze-dried kit formulation of levofloxacin ( L -Flox): a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. J Label Compd Radiopharm 50:25–31
Bandoli G, Dolmella A, Porchia M, Tisato E, Refosco P (2001) Structural overview of technetium compounds. Coord Chem Rev 214:43–90
Guo B, Wu X, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Yu J, Cao G, Zhang J (2012) Safety and clinical pharmacokinetics of nemonoxacin, a novel non-fluorinated quinolone, in healthy Chinese volunteers following single and multiple oral doses. Clin Drug Investig 32(7):475–486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Kawy, O.A., Farah, K. Radiocomplexation and biological evaluation of nemonoxacin in mice infected with multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus and penicillin-resistant Streptococci . J Radioanal Nucl Chem 306, 123–130 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4069-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4069-6