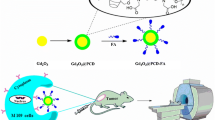
Abstract
18FDG conjugated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MNPs) were synthesized as PET-MR hybrid imaging agent. Synthesized and characterized NPs were then applied to MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. 18FDG conjugated MNPs exhibited the cell incorporation ratio up to 30 %. As well as the characterization studies, apoptotic effects were observed depending on the cellular incorporations by the time. In conclusion, synthesized structures could have a potential as hybrid imaging agent in PET-MR imaging systems besides apoptotic effect on cancer cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Unak P (2008) Imaging and therapy with radionuclide labeled magnetic nanoparticles. Braz Arch Biol Technol 51:31–37
Liang S, Wang Y, Yu J, Zhang C, Xia J, Yin D (2007) Surface modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: as a new carrier for bio-magnetically targeted therapy. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18(12):2297–2302
Ramanujan RV, Chong WT (2004) The synthesis and characterization of polymer coated iron oxide microspheres. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15(8):901–908
Alexiou C, Bergemann C, Schmid R, Hulin P, Schmidt A, Jurgons R, Arnold W, Parak FG (2002) Enrichment and biodistribution of a magnetically targeted drug carrier. Eur Cells Mater 3(2):135–137
Berry CC, Curtis SG (2003) Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:198–206
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:167–181
Saiyed ZM, Telang SD, Ramchand CN (2003) Application of magnetic techniques in the field of drug discovery and biomedicine. BioMagn Res Technol 1:1–8
Wunderlich G, Drews A, Kotzerke J (2005) A kit for labeling of [188Re] human serum albumin microspheres for therapeutic use in nuclear medicine. Appl Radiat Isot 62(6):915–918
Hafeli UO, Yu J, Farudi F, Li Y, Tapolsky G (2003) Radiolabeling of magnetic targeted carriers (MTC) with indium-111. Nucl Med Biol 30(7):761–769
Hafeli UO, Sweeney SM, Beresford BA, Humm JL, Macklis RM (1995) Effective targeting of magnetic radioactive 90Y-microspheres to tumor cells by an externally applied magnetic field. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo results. Nucl Med Biol 22(2):147–155
Felinto MCFC, Parra DF, Lugão AB, Batista MP, Higa OZ, Yamaura M, Camilo RL, Ribela MTCP, Sampaio LC (2005) Magnetic polymeric microspheres for protein adsorption. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 236(1–4):495–500
Dagdeviren K, Ünak P, Bekis R, Biber Müftüler FZ, Ertay T, Ulker O, Durak H (2007) Radioiodinated magnetic targeted carriers (I-131-MTC). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273(3):635–639
Devaraj NK, Keliher EJ, Thurber GM, Nahrendorf M, Weissleder R (2009) 18F labeled nanoparticles for in vivo PET-CT imaging. Bioconjug Chem 20:397–401
Moadel RM, Weldon RH, Katz EB (2005) Positherapy: targeted nuclear therapy of breast cancer with 18F-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose. Cancer Res 65(3):698–702
Namavari M, Padilla De Jesus O, Cheng Z (2008) Direct site-specific radiolabeling of an affibody protein with 4-[18F]fluorobenzaldehyde via oxime chemistry. Mol Imaging Biol 10(4):177–181
Babu P, Sinha S, Surolia A (2007) Sugar-quantum dot conjugates for a selective and sensitive detection of lectins. Bioconj Chem 18(1):146–151
Gillies JM, Prenant C, Chimon GN (2006) Microfluidic reactor for the radiosynthesis of PET radiotracers. Appl Radiat Isot 64(3):325–332
Altman SA, Randers L, Rao G (1993) Comparison of trypan blue dye exclusion and fluorometric assays for mammalian cell viability determinations. Biotechnol Prog 9(6):671–674
Halkes KM, Souza AC, Maljaars EP, Gerwig GJ, Kamerling JP (2005) A facile method for the preparation of gold glyconanoparticles from free oligosaccharides and their applicability in carbohydrate–protein interaction studies. Eur J Org Chem 17:3650–3659
Unak G, Ozkaya F, Medine EI, Kozgus O, Sakarya S, Bekis R, Unak P, Timur S (2012) Gold nanoparticle probes: design and in vitro applications in cancer cell culture. Colloids Surf B 90(1):217–226
Gang L, He F, Wang X, Gao F, Zhang G, Wang T, Jiang H, Wu C, Guo D, Li X, Chen B, Gu Z (2008) Novel nanocomposite of nano Fe3O4 and polylactide nanofibers for application in drug uptake and induction of cell death of leukemia cancer cells. Langmuir 24(5):2151–2156
Sun C, Lee JSH, Zhang M (2008) Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(11):1252–1265
Medine EI, Ünak P, Sakarya S, Özkaya F (2011) Investigation of in vitro efficiency of magnetic nanoparticle-conjugated 125I-uracil glucuronides in adenocarcinoma cells. J Nanopart Res 13:4703–4715
Li Z, Kawashita M, Araki N, Mitsumori M, Hiraoka M, Doi M (2010) Magnetite nanoparticles with high heating efficiencies for application in the hyperthermia of cancer. Mater Sci Eng C 30(7):990–996
Hooker JM, O’Neil JP, Romanini DW, Taylor SE, Francis MB (2008) Genome-free viral capsids as carriers for positron emission tomography radiolabels. Mol Imaging Biol 10(4):182–191
Hanley C, Layne J, Punnoose A (2008) Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 19(29):295103
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to Ege University Scientific Research Fund for the financial support with the Project Numbers 2008 NBE 08 and 2009 FEN 007. Authors also thank to Adnan Menderes University Science Technology Research and Application Center for cell culture experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozkaya, F., Unak, P., Medine, E.I. et al. 18FDG conjugated magnetic nanoparticle probes: synthesis and in vitro investigations on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295, 1789–1796 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2248-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2248-2