Abstract
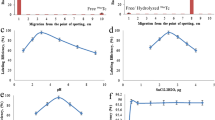
The labeling of garenoxacin (GXN) with technetium-99m (99mTc) using different concentrations of GXN, sodium pertechnetate (Na99mTcO4), stannous chloride dihydrate (SnCl2·2H2O) at different pH was investigated and evaluated in terms of in-vitro stability in saline, serum, binding with multi-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MDRSA) and penicillin-resistant Streptococci (PRSC) and its biodistribution in artificially MDRSA and PRSC infected rats. 99mTc–GXN complex with 97.45 ± 0.18% radiochemical stability was prepared by mixing 3 mg of GXN with 3 mCi of Na99mTcO4 in the presence of 150 μL of SnCl2·2H2O (1 μg/μL in 0.01 N HCl) at a pH 5.6. The radiochemical stability of the complex was evaluated in normal saline up to 240 min of reconstitution. It was observed that the complex showed maximum RCP values after 30 min of the reconstitution and remained more than 90% up to 240 min. The complex showed radiochemical stability in normal saline at 37 °C up to 16 h with a 17.80% de-tagging. The complex showed saturated in-vitro binding with living MDRSA and PRSC as compared to the insignificant binding with heat killed MDRSA and PRSC. Biodistribution behavior of the complex was assessed in artificially infected with living and heat killed MDRSA and PRSC rats. It was observed that the accumulation of the complex in the infected (live MDRSA and PRSC) tissue of the rats was almost five fold than in the inflamed and normal tissue. The high radiochemical stability in normal saline at room temperature, promising in-vitro stability in serum at 37 °C, saturated in-vitro binding with living MDRSA and PRSC, specific biodistribution behavior and high infected (target) to normal (non-target) tissue and low inflamed (non-target) to normal (non-target) tissue ratios we recommend 99mTc–GXN complex for in-vivo localization of infection caused by MDRSA and PRSC effective stains.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallagher H, Ramsay SC, Barnes J, Maggs J, Cassidy N, Ketheesan N (2006) Neutrophil labeling with [99mTc]-technetium stannous colloid is complement receptor 3-mediated and increases the neutrophil priming response to lipopolysaccharide. Nucl Med Biol 33:433
Stumpe KDM, Dazzi H, Schaffner A, Schulthess GK (2000) Infection imaging using whole-body FDG-PET. Eur J Nucl Med 27:822
Chattopadhyay S, Das SS, Chandra S, De K, Mishra M, Sarkar BR, Sinha S, Ganguly S (2010) Synthesis and evaluation of 99mTc-moxifloxacin, a potential infection specific imaging agent. Appl Radiat Isot 68:314
Motaleb MA (2007) Preparation of 99mTc–cefoperazone complex, a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 272:167
Motaleb MA (2007) Preparation and biodistribution of 99mTc–lomefloxacin and 99mTc–olfloxacin complex. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 272:95
Zhang J, Guo H, Zhang S, Lin Y, Wang X (2008) Synthesis and biodistribution of a novel 99mTcN complex of ciprofloxacin dithiocarbamate as a potential agent for infection imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:51
Roohi S, Mushtaq A, Jehangir M, Ashfaq MS (2006) Synthesis, quality control and biodistribution of 99mTc-Kanamycin. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267:561
Oh SJ, Ryu J, Shin JW, Yoon EJ, Ha H, Cheon JH, Lee HK (2002) Synthesis of 99mTc-ciprofloxacin by different methods and its biodistribution. Appl Radiat Isot 57:193
EL-Gany EA, EL-Kolaly MT, Amine AM, EL-Sayed AS, Abdel-Gelil F (2005) Synthesis of 99mTc-pefloxacin: a new targeting agent for infectious foci. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 266:131
Motaleb MA (2009) Preparation, quality control and stability of 99mTc–sparafloxacin complex, a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. J Label Compd Radiopharm 52:415
Xia J, Wang Y, Yu J, Li S, Tang L, Zheng M, Liu X, Li G, Cheng D, Liang S, Yin D (2008) Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo behavior of 188Re(I)–tricarbonyl complexes for the future functionalization of biomolecules. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 275:325
Zhang J, Wang X, Jin C (2007) Synthesis and biodistribution of the 99mTc(CO)3–DEDT complex as a potential new radiopharmaceutical for brain imaging. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 272:91
Djokic DD, Jankovic DL, Stamenkovic LL, Pirmettis I (2004) Chemical and biological evaluation of 99mTc (CO)3 and 99mTc complexes of some IDA derivatives. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 260:471
Xia J, Long S, Yu J, Wang Y, Cao Z (2009) Pyridyl derivatives provide new pathways for labeling protein with fac-[188Re(CO)3(H2O)3]+. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 281:493
Zhang JB, Wang XB, Jin C (2006) Synthesis of 99mTc(CO)3-NOET via [99mTc(OH2)3(CO)3]+ precursor and comparative biological studies with 99mTcN-NOET. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 269:227
Qaiser SS, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Synthesis, biodistribution and evaluation of 99mTc-sitafloxacin kit: a novel infection imaging agent. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 284:189
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis of 99mTc-nitrifuratonin a novel radiotracer for in vivo imaging of Escherichia coli infection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-010-0697-z
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis and biodistribution of 99mTc-rifampicin: a novel radiotracer for in vivo infection imaging. Appl Radiat Isot 68:2255
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) 99mTc-novobiocin: a novel radiotracer for infection imaging. Radiochim Acta (in press)
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis, biodistribution and scintigraphy of the 99mTc–teicoplanin complex in artificially infected animal models. J Label Compd Radiopharm (in press)
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis and biological evaluation of 99mTcN-sitafloxacin dithiocarbamate as potential radiotracer for Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-010-0833-9
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis and biodistribution of 99mTcN–garenoxacin dithiocarbamate complex a potential infection imaging agent. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-010-0871-3
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis and biological evolution of 99mTc(CO)3–sitafloxacin dithiocarbamate complex: a promising Staphylococcus aureus infection radiotracer. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-010-0880-2
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) 99mTc(CO)3-garenoxacin dithiocarbamate synthesis and biological evolution in rats infected with multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus and penicillin-resistant Streptococci. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi: 10.1007/s10967-010-0892-y
Sader HS, Fritsche TR, Jones RN (2007) In vitro activity of garenoxacin tested against a worldwide collection of ciprofloxacin-susceptible and ciprofloxacin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae strains (1999–2004). Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 58:27
Roblin PM, Reznik T, Hammerschlag MR (2003) In vitro activity of garenoxacin against recent clinical isolates of Chlamydia pneumoniae. Int J Antimicrob Agents 21:578
Welling MM, Paulusma-Annema A, Batler HS, Pauwels EKJ, Nibbering PH (2000) Technetium-99m labelled antimicrobial peptides discriminate between bacterial infections and sterile inflammations. Eur J Nucl Med 27:292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, S.Q., Khan, A.U. & Khan, M.R. Synthesis, biological evaluation and biodistribution of the 99mTc–Garenoxacin complex in artificially infected rats. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288, 207–213 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0896-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0896-7