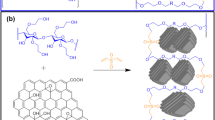
Abstract
In the current study, poly(p-aminophenol) (PpAP), with starch and graphene oxide (GO), was successfully synthesised by oxidative polymerisation from p-aminophenol monomer in an aqueous alkaline medium using ammonium persulfate (APS) as an oxidising agent. The synthesised polymers were characterised using UV–Vis spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller and zeta potential techniques. These techniques confirmed the presence of site-selective interaction between the conjugated PpAP chain and π-bonded surface, and thus the H-bonding of starch and GO. Further, the enhanced dye removal efficiency was ascribed to the improved morphology and the pore volume created by the entangled PpAP/Starch/GO. The influences of experimental conditions, such as the polymer composite content, dye concentration, time, pH of the bath solution, and temperature on cationic dye adsorption, were investigated. The adsorption data were fixed to the Langmuir isotherm (R2 in the range between 0.997 and 0.9995) and showed a pseudo-second order (R2 = in the range of 0.996 to 0.9996) kinetic model. Moreover, the polymer ternary composite was able to remove a large proportion (96.7%) of the cationic dye from water at pH 7. The thermodynamic investigation found that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic. In addition, the synthesised adsorbent showed good reusability at six cycles. The data acquired suggest that the PpAP/Starch/GO composite can be effectively applied and reused as an inexpensive adsorbent material for removal of MB dye from water.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar R, Sharma RK, Singh AP (2019) Synthesis and characterization of cellulose based graft copolymers with binary vinyl monomers for efficient removal of cationic dyes and Pb (II) ions. J Polym Res 26:135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1790-9
Mohammed MQ, Ismail HK, Alesary HF, Barton S (2022) Use of a Schiff base-modified conducting polymer electrode for electrochemical assay of Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions by square wave voltammetry. Chem Pap 76:715–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01882-7
Mustafa FS, Güran M, Gazi M (2020) Effective removal of dyes from aqueous solutions using a novel antibacterial polymeric adsorbent. J Polym Res 27:247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02227-w
Yasin SA, Zeebaree SYS, Sharaf Zeebaree AY, Haji Zebari OI, Saeed IA (2021) The efficient removal of methylene blue dye using CuO/PET nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. Catalysts 11:241. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020241
Gupta VK (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal–a review. J Environ manage 90:2313–2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017
Jain H, Garg MC (2021) Fabrication of polymeric nanocomposite forward osmosis membranes for water desalination—A review. Environ Technol Innov 23:101561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101561
Senguttuvan S, Senthilkumar P, Janaki V, Kamala-Kannan S (2021) Significance of conducting polyaniline based composites for the removal of dyes and heavy metals from aqueous solution and wastewaters-A review. Chemosphere 267:129201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129201
Thorat MN, Jagtap A, Dastager SG (2021) Fabrication of bacterial nanocellulose/polyethyleneimine (PEI-BC) based cationic adsorbent for efficient removal of anionic dyes. J Polym Res 28:354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02702-y
Ardani MR, Pang AL, Pal U, Zheng R, Arsad A, Hamzah AA, Ahmadipour M (2022) Ultrasonic-assisted polyaniline-multiwall carbon nanotube photocatalyst for efficient photodegradation of organic pollutants. J Water Process Eng 46:102557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102557
Koohi P, Rahbar-kelishami A, Shayesteh H (2021) Efficient removal of congo red dye using Fe3O4/NiO nanocomposite: Synthesis and characterization. Environ Technol Innov 23:101559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101559
Reghioua A, Barkat D, Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Khan MR (2021) Synthesis of Schiff’s base magnetic crosslinked chitosan-glyoxal/ZnO/Fe3O4 nanoparticles for enhanced adsorption of organic dye: Modeling and mechanism study. Sustain Chem Pharm 20:100379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2021.100379
Gil A, Assis F, Albeniz S, Korili S (2011) Removal of dyes from wastewaters by adsorption on pillared clays. Chem Eng J 168:1032–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.078
Tony M (2020) Zeolite-based adsorbent from alum sludge residue for textile wastewater treatment. Int J Environ Science Technol 17:2485–2498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02646-8
Elwakeel KZ (2009) Removal of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solutions using magnetic chitosan resins. J Hazard Mater 167:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.051
Minitha C, Lalitha M, Jeyachandran Y, Senthilkumar L, Rajendra KRT (2017) Adsorption behaviour of reduced graphene oxide towards cationic and anionic dyes: Co-action of electrostatic and π–π interactions. Mater Chem Phys 194:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.03.048
Shang L, Bian T, Zhang B, Zhang D, Wu LZ, Tung CH, Yin Y, Zhang T (2014) Graphene-supported ultrafine metal nanoparticles encapsulated by mesoporous silica: robust catalysts for oxidation and reduction reactions. Angew Chem 126:254–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201306863
Li Y, Du Q, Liu T, Sun J, Wang Y, Wu S, Wang Z, Xia Y, Xia L (2013) Methylene blue adsorption on graphene oxide/calcium alginate composites. Carbohydr polym 95:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.094
Vellaichamy B, Periakaruppan P, Nagulan B (2017) Reduction of Cr6+ from wastewater using a novel in situ-synthesized PANI/MnO2/TiO2 nanocomposite: renewable, selective, stable, and synergistic catalysis. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 5:9313–9324. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02324
Alesary HF, Ismail HK, Mohammed MQ, Mohammed HN, Abbas ZK, Barton S (2021) A comparative study of the effect of organic dopant ions on the electrochemical and chemical synthesis of the conducting polymers polyaniline, poly (o-toluidine) and poly (o-methoxyaniline). Chem Pap 75:5087–5101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01477-8
Ismail HK, Alesary HF, Mohammed MQ (2019) Synthesis and characterisation of polyaniline and/or MoO2/graphite composites from deep eutectic solvents via chemical polymerisation. J Polym Res 26:65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1732-6
Sjahro N, Yunus R, Abdullah LC, Rashid SA, Asis AJ, Akhlisah Z (2021) Recent advances in the application of cellulose derivatives for removal of contaminants from aquatic environments. Cellulose 28:7521–7557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03985-6
Mallakpour S, Ezhieh AN (2017) Preparation and characterization of chitosan-poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite films embedded with functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube. Carbohydr polym 166:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.086
Zare EN, Motahari A, Sillanpää M (2018) Nanoadsorbents based on conducting polymer nanocomposites with main focus on polyaniline and its derivatives for removal of heavy metal ions/dyes: a review. Environ Res 162:173–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.12.025
Janaki V, Vijayaraghavan K, Oh BT, Lee KJ, Muthuchelian K, Ramasamy A, Kamala-Kannan S (2012) Starch/polyaniline nanocomposite for enhanced removal of reactive dyes from synthetic effluent. Carbohydr Polym 90:1437–1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.012
Gomes RF, de Azevedo ACN, Pereira AG, Muniz EC, Fajardo AR, Rodrigues FH (2015) Fast dye removal from water by starch-based nanocomposites. J Colloid Interface Sci 454:200–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.05.026
Cheng R, Xiang B, Li Y, Zhang M (2011) Application of dithiocarbamate-modified starch for dyes removal from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 188:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.104
Saberi A, Alipour E, Sadeghi M (2019) Superabsorbent magnetic Fe3O4-based starch-poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogel for efficient removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from water. J Polym Res 26:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1917-z
Haroon M, Ullah R, Mehmood S, Haq F (2021) Synthesis and characterization of starch-g-polymethyl methacrylate and their properties as adsorbents for removing Rhodamine 6G from water. J Polym Res 28:330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02692-x
Wang H, Duan M, Guo Y, Wang C, Shi Z, Liu J, Lv J (2018) Graphene oxide edge grafting of polyaniline nanocomposite: an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue and methyl orange. Water Sci Technol 77:2751–2760. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.250
Gheydari M, Dorraji MS, Fazli M, Rasoulifard M, Almaie S, Daneshvar H, Ashjari HR (2021) Preparation of open-cell polyurethane nanocomposite foam with Ag3PO4 and GO: antibacterial and adsorption characteristics. J Polym Res 28:69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02432-1
Zhang J, Azam MS, Shi C, Huang J, Yan B, Liu Q, Zeng H (2015) Poly (acrylic acid) functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite for removal of methylene blue. RSC Adv 5:32272–32282. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01815C
Ali M, Husain Q, Sultana S, Ahmad M (2018) Immobilization of peroxidase on polypyrrole-cellulose-graphene oxide nanocomposite via non-covalent interactions for the degradation of Reactive Blue 4 dye. Chemosphere 202:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.073
Abd Ali L, Ismail HK, Alesary HF, Aboul-Enein H (2021) A nanocomposite based on polyaniline, nickel and manganese oxides for dye removal from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:2031–2050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02961-0
Hummers WS Jr, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80:1339–1339. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01539a017
Kar P, Pradhan NC, Adhikari B (2008) A novel route for the synthesis of processable conducting poly (m-aminophenol). Mater Chem Phys 111:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.03.012
Kojidi MH, Aliakbar A (2019) Synthesis of graphene oxide-based poly (p-aminophenol) composite and its application in solid phase extraction of trace amount of Ni (II) from aquatic samples. Environ Monit Assess 191:145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7282-x
Verma SK, Choudhury A, Kar P (2015) Interaction of multi-walled carbon nanotube with poly (m-aminophenol) in their processable conducting nanocomposite. Physica Status Solidi (a) 212:2044–2052. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201431910
Usman A, Hussain Z, Riaz A, Khan AN (2016) Enhanced mechanical, thermal and antimicrobial properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide/starch/silver nanocomposites films. Carbohydr Polym 153:592–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.026
Thenmozhi G, Arockiasamy P, Santhi RJ (2014) Isomers of poly aminophenol: chemical synthesis, characterization, and its corrosion protection aspect on mild steel in 1 M HCl. Int J Electrochem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/961617
Kong Y, Zhou Y, Shan X, Jiang Y, Yao C (2011) Electropolymerization of m-aminophenol on expanded graphite and its electrochemical properties. Synth Met 161:2301–2305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2011.08.038
Li R, Liu C, Ma J (2011) Studies on the properties of graphene oxide-reinforced starch biocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 84:631–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.041
Ovchinnikov OV, Evtukhova AV, Kondratenko TS, Smirnov MS, Khokhlov VY, Erina OV (2016) Manifestation of intermolecular interactions in FTIR spectra of methylene blue molecules. Vib Spectrosc 86:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2016.06.016
Alver E, Metin AÜ, Brouers F (2020) Methylene blue adsorption on magnetic alginate/rice husk bio-composite. Int J Biol Macromol 154:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.330
Sousa HR, Silva LS, Sousa PAA, Sousa RRM, Fonseca MG, Osajima JA, Silva-Filho EC (2019) Evaluation of methylene blue removal by plasma activated palygorskites. J Mater Res Technol 8:5432–5442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.09.011
Pourjavadi A, Nazari M, Kabiri B, Hosseini SH, Bennett C (2016) Preparation of porous graphene oxide/hydrogel nanocomposites and their ability for efficient adsorption of methylene blue. RSC Adv 6:10430–10437. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA21629J
Duman O, Polat TG, Diker CÖ, Tunç S (2020) Agar/κ-carrageenan composite hydrogel adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue from water. Int J Biol Macromol 160:823–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.191
Lee LY, Gan S, Tan MSY, Lim SS, Lee XJ, Lam YF (2016) Effective removal of acid blue 113 dye using overripe cucumis sativus peel as an eco-friendly biosorbent from agricultural residue. J Clean Prod 113:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.016
Sharma K, Dalai AK, Vyas RK (2018) Removal of synthetic dyes from multicomponent industrial wastewaters. Rev Chem Eng 34:107–134. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2016-0042
Cui L, Wang Y, Gao L, Hu L, Yan L, Wei Q, Du B (2015) EDTA functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for removal of Pb (II), Hg (II) and Cu (II) in water treatment: adsorption mechanism and separation property. Chem Eng J 281:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.043
Yu KL, Lee XJ, Ong HC, Chen WH, Chang JS, Lin CS, Show PL, Ling TC (2021) Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic congo red dyes using wet-torrefied microalgal biochar: Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism modeling. Environ Pollut 272:115986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115986
Kumar PS, Ramalingam S, Senthamarai C, Niranjanaa M, Vijayalakshmi P, Sivanesan S (2010) Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 261:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.05.032
Hameed B, Krishni R, Sata S (2009) A novel agricultural waste adsorbent for the removal of cationic dye from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 162:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.036
Srivastava VC, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2006) Characterization of mesoporous rice husk ash (RHA) and adsorption kinetics of metal ions from aqueous solution onto RHA. J Hazard Mater 134:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.052
Wang S, Zhai YY, Gao Q, Luo WJ, Xia H, Zhou CG (2014) Highly efficient removal of acid red 18 from aqueous solution by magnetically retrievable chitosan/carbon nanotube: batch study, isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. J Chem Eng Data 59:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1021/je400700c
Singh SK, Townsend TG, Mazyck D, Boyer TH (2012) Equilibrium and intra-particle diffusion of stabilized landfill leachate onto micro-and meso-porous activated carbon. Water Res 46:491–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.007
Crini G, Peindy HN, Gimbert F, Robert C (2007) Removal of CI Basic Green 4 (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep Purif Technol 53:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.018
Lagergren SK (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven Vetenskapsakad Handingarl 24:1–39
McKay G, Ho Y, Ng J (1999) Biosorption of copper from waste waters: a review. Sep Purif Methods 28:87–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602549909351645
Elovich SY, Zhabrova G (1939) Mechanism of the catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene on nickel. I. Kinetics of the process. J Phys Chem 13:1761.
Weber WJ Jr, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–59. https://doi.org/10.1061/JSEDAI.0000430
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02268a002
Freundlich H (1907) Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z Phys Chem 57(1):385–470. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1907-5723
Tempkin M, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys Chim USSR 12(1):327
Ali I, Alharbi OM, Alothman ZA, Badjah AY, Alwarthan A (2018) Artificial neural network modelling of amido black dye sorption on iron composite nano material: kinetics and thermodynamics studies. J Mol Liq 250:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.163
Maruthapandi M, Kumar VB, Luong JH, Gedanken A (2018) Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies of methylene blue adsorption on polyaniline and polypyrrole macro–nanoparticles synthesized by C-Dot-Initiated polymerization. ACS Omega 3(7):7196–7203. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00478
Li B, Guo J, Lv K, Fan J (2019) Adsorption of methylene blue and Cd (II) onto maleylated modified hydrochar from water. Environ Pollut 254:113014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113014
Cheng J, Zhan C, Wu J, Cui Z, Si J, Wang Q, Peng X, Turng LS (2020) Highly efficient removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous solution using cellulose acetate nanofibrous membranes modified by polydopamine. ACS Omega 5:5389–5400. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04425
Dao MU, Le HS, Hoang HY, Tran VA, Doan VD, Le TTN, Sirotkin A (2021) Natural core-shell structure activated carbon beads derived from Litsea glutinosa seeds for removal of methylene blue: Facile preparation, characterization, and adsorption properties. Environ Res 198:110481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110481
Kuang Y, Zhang X, Zhou S (2020) Adsorption of methylene blue in water onto activated carbon by surfactant modification. Water 12:587. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020587
Zhu W, Jiang X, Jiang K, Liu F, You F, Yao C (2021) Fabrication of reusable carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene oxide composite aerogel with large surface area for adsorption of methylene blue. Nanomaterials 11:1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061609
Pasichnyk M, Václavíková M, Melnyk I (2021) Fabrication of polystyrene-acrylic/ZnO nanocomposite films for effective removal of methylene blue dye from water. J Polym Res 28:56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02418-z
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Mastuli MS (2020) Acid-factionalized biomass material for methylene blue dye removal: a comprehensive adsorption and mechanism study. J Taibah Univ Sci 14:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2020.1736767
Minisy IM, Salahuddin NA, Ayad MM (2021) Adsorption of methylene blue onto chitosan–montmorillonite/polyaniline nanocomposite. Appl Clay Scie 203:105993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2021.105993
Çatlıoğlu F, Akay S, Turunç E, Gözmen B, Anastopoulos I, Kayan B, Kalderis D (2021) Preparation and application of Fe-modified banana peel in the adsorption of methylene blue: process optimization using response surface methodology. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100517
Haider S, Binagag FF, Haider A, Al-Masry WA (2014) Electrospun oxime-grafted-polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane and its application to the adsorption of dyes. J Polym Res 21:371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0371-1
Zhang T, Zhang W, Xi H, Li Q, Shen M, Ying G, Zhang J (2021) Polydopamine functionalized cellulose-MXene composite aerogel with superior adsorption of methylene blue. Cellulose 28:4281–4293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03737-6
Zidan T, Yehia A, Abdelhamid AE (2021) Crosslinked poly (methacrylic acid)/organoclay nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization and methylene blue adsorption from aquatic environments. J Polym Res 28(8):306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02665-0
Zeebaree SYS, Zeebaree AYS, Zebari OIH, Zebari AYS (2021) Sustainable fabrication, optical properties and rapid performance of bio-engineered copper nanoparticles in removal of toxic methylene blue dye in an aqueous medium. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry 4:100103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100103
Nekouei F, Kargarzadeh H, Nekouei S, Keshtpour F, Makhlouf ASH (2017) Efficient method for determination of methylene blue dye in water samples based on a combined dispersive solid phase and cloud point extraction using Cu (OH)2 nanoflakes: central composite design optimization. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:1079–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-0026-7
Hassan SS, Nafady A, Solangi AR, Kalhoro MS, Abro MI, Sherazi STH (2015) Ultra-trace level electrochemical sensor for methylene blue dye based on nafion stabilized ibuprofen derived gold nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B Chem 208:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.11.021
Liu X, An S, Wang Y, Yang Q, Zhang L (2015) Rapid selective separation and recovery of a specific target dye from mixture consisted of different dyes by magnetic Ca-ferrites nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 262:517–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.002
Xiao Z, Zhou J, Fan L, Li Y, He Y, Wang Y et al (2021) Controllable Preparation of Cu-MOF-Coated Carboxyl Filter Paper for Simultaneous Removal of Organic Dye and Metal Ions. Ind Eng Chem Res 60(19):7311–7319. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.1c00140
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Universities of Koya and Kerbala for providing the required materials and instruments for this work. The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Mark Watkins (University of Leicester) for helping and proofreading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, H.K., Ali, L.I.A., Alesary, H.F. et al. Synthesis of a poly(p-aminophenol)/starch/graphene oxide ternary nanocomposite for removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. J Polym Res 29, 159 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03013-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03013-6