Abstract
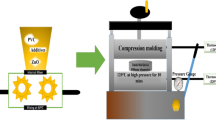
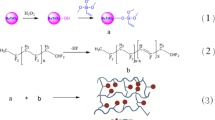
Nanodielectrics based on metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) exhibit significant improvement in dielectric performances. This study was carried out to examine the dielectric properties of Poly vinyl chloride (PVC) with the introduction of zinc oxide (ZnO) NPs synthesized by simple sol gel method. The microstructure and surface morphology of the synthesized ZnO NPs were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field emission scanning microscopy (FE-SEM). The formation of the wurtzite-type ZnO was verified from XRD with average crystallite sizes around 35 nm. PVC/ZnO-NPs nanocomposites were prepared by the solution-cast technique with two different procedures of NPs addition. The dielectric properties of PVC/ZnO nanocomposites were studied by measuring the DC dielectric strength with constant 1 kV/s ramp and the dielectric response as function of frequency from 500 Hz to 1 MHz. A significant enhancement in breakdown strength has been observed with addition of ZnO NPs. The breakdown strength values reached up to 45 % (for PVC/0.14 vol% ZnO) more than obtained for the pristine PVC sample. The effect of dispersibility of NPs due to the used procedures of addition on the DC dielectric strength was studied and confirmed by FE-SEM. The dependency of the real part of permittivity (ε ′) on filler concentration was observed and confirmed the obtained results from DC dielectric strength.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanaka T, Montanari GC, Mulhaupt R (2004) Polymer nanocomposites as dielectrics and electrical insulation- perspectives for processing technologies, material characterization and future applications. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 11:763–784
Mansour SA (2013) Study of thermal stabilization for polystyrene/carbon nanocomposites via TG/DSC techniques. J Therm Anal Calorim 112:579–583
Kurimoto M, Okubo H, Kato K, Hanai M, Hoshina Y, Takei M, Hayakawa N (2010) Dielectric properties of epoxy/alumina nanocomposite influenced by control of micrometric agglomerates. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 17:662–670
Tian F, Lei Q, Wang X, Wang Y (2012) Investigation of electrical properties of LDPE/ZnO nanocomposite dielectrics. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 19:763–769
Velayutham TS, Abd Majid WH, Gan WC, Zak A, Gan SN (2012) Theoretical and experimental approach on dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles and polyurethane/ZnO nanocomposites. J Appl Phys 112:054106
Singha S, Thomas MJ (2009) Influence of filler loading on dielectric properties of Epoxy-ZnO nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 16:531–542
Tanaka T (2005) Dielectric nanocomposites with insulating properties. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 12:914–927
Tanaka T, Matsunawa A, Ohki Y, Kozako M, Kohtoh M, Okabe S (2006) Treeing phenomenon in epoxy/alumina nanocomposite and interpretation by a multi-core model. IEEJ Trans Fund Mater 126:1128–1135
Jonscher AK, Lacoste R (1984) On a cumulative model of dielectric breakdown in solids. IEEE Trans Electr Insul 19:567–577
Scherrer P (1918) Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr Ges Wiss Göttingen 26:98
Langford JI, Wilson AJC (1987) Scherrer after sixty years: A survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J Appl Cryst 11:102
Varlec A, Mansour SA, Di Luccio T, Borriello C, Bruno A, Jelenc J, Visic B, Remskar X (2013) Microscopic and spectroscopic investigation of MoS2 nanotubes/P3HT nanocomposites. Phys Status Solidi A 210:2335–2340
Theodosiou K, Vitellas I, Gialas I, Agoris DP (2004) Polymer films degradation and breakdown in high voltage AC fields. J Electr Eng 55:225–231
Shah KS, Jain RC, Shrinet V, Singh AK, Bharambe DP (2009) High density polyethylene (HDPE) clay nanocomposite for dielectric applications. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 16:853–861
Danikas MG, Tanaka T (2009) Nanocomposites―A Review of electrical Treeing and breakdown. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 25:19–25
Mansour SA, Yahia IS, Yakuphanoglu F (2010) The electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of C.I. Basic Violet 10. Dyes Pigments 87:144–148
Mansour SA, Yahia IS, Sakr GB (2010) Electrical conductivity and dielectric relaxation behavior of fluorescein sodium salt (FSS). Solid State Commun 150:1386–1391
Couderc H, David E (2014) Study of water diffusion in PE-SiO 2 nanocomposites by dielectric spectroscopy. Trans Electr Electron Mater 15:291–296
David E, Sami A, Fréchette MF (2011) Dielectric response of polyethylene loaded with nanoparticules of Si02. Proc Int’l Conf Insulated Power Cables JiCable, paper C.5.5
Tuncer E, Sauers I, James DR, Ellis AR, Paranthaman MP, Aytug T, Sathyamurthy S, More KL, Li J, Goyal A (2007) Electrical properties of epoxy resin based nano-composites. Nanotechnology 18:025703 (1)-(6)
Ciuprina F, Plesa I, Notingher PV, Tudorache T, Panaitescu D (2008) Dielectric properties of nanodielectrics with inorganic fillers. Proc of the Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation Dielectric Phenomena:682–685
Singha S, Thomas MJ (2008) Dielectric properties of epoxy resin nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 15:12–23
Nelson JK, Hu Y (2005) Nanocomposite dielectrics—properties and implications. J Phys D 38:213–222
Bistac S, Vallat MF, Schultz J (1999) Study of ethylene copolymers films by dielectric spectroscopy: influence of the polymer thickness on the glass-transition temperature. Prog Org Coat 37:49–56
Roy M, Nelson JK, Reed CW, MacCrone RK, Keefe RJ, Zenger W, Schadler LS (2005) Polymer nanocomposite dielectrics - the role of the interface. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 12:629–642
Huang X, Xie L, Yang K, Wu C, Jiang P, Li S, Wu S, Tatsumi KI, Tanaka T (2014) Role of interface in highly filled epoxy/BaTiO3 nanocomposites. part I-Correlation between nanoparticle surface chemistry and nanocomposite dielectric property. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 21:467–479
Huang X, Zheng Y, Jiang P, Yin Y (2010) Influence of nanoparticle surface treatment on the electrical properties of cycloaliphatic epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 17:635–643
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansour, S.A., Elsad, R.A. & Izzularab, M.A. Dielectric properties enhancement of PVC nanodielectrics based on synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. J Polym Res 23, 85 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-0978-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-0978-5