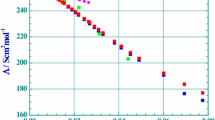
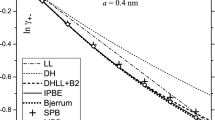
Abstract
Conductivities of symmetrical and unsymmetrical electrolytes of 2:2, 3:3, 1:2, 2:1 and 1:3 types in ethanol–water and the 1,4-dioxane–water mixtures were analyzed using the Quint-Viallard conductivity equation and taking into account the ion association effect. The molar limiting conductances and the ion association constants were reexamined for various multivalent electrolytes. One non-aqueous system, methanol–ethylene glycol mixtures, was also considered. The limiting conductances were also examined in the framework of universal curves of limiting conductances and the excess Walden products introduced by the author. These new concepts in the analysis of conductance data allow the estimation of values of limiting conductances of electrolytes or ions, to give an indication about the quality of the conductivity measurements and the type of interactions expected in the systems. It was found that for any type of electrolyte only one universal curve of limiting conductances exists. In the water-rich mixtures, attractive interactions (structure-making effects) are expected when electrolytes are added to mixtures with ethanol or with 1,4-dioxane. In contrast, in ethylene glycol–methanol-rich mixtures repulsive interactions (structure-breaking effects) are more likely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, W.H., Wheaton, R.J.: Conductance of symmetrical. unsymmetrical and mixed electrolytes. Part 1.—Relaxation terms. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. II 74, 743–766 (1978)
Lee, W.H., Wheaton, R.J.: Conductance of symmetrical. unsymmetrical and mixed electrolytes. Part 2.—Hydrodynamic terms and complete conductance equation. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. II 74, 1456–1482 (1978)
Quint, J., Viallard, A.: Relaxation field for the general case of electrolyte mixtures. J. Solution Chem. 7, 137–153 (1978)
Quint, J., Viallard, A.: The electrophoretic effect for the case of electrolyte mixtures. J. Solution Chem. 7, 525–531 (1978)
Quint, J., Viallard, A.: Electrical conductance of electrolyte mixtures of any type. J. Solution Chem. 7, 533–548 (1978)
Quint, J.: Contribution a l’étude de la conductibilité électrique de mélanges d’électrolytes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Clermont-Ferrand, April (1976)
Apelblat, A.: Limiting conductances of electrolytes and the Walden product in mixed solvents in a phenomenological approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 7032–7044 (2008)
Niazi, M.S.K., Hussain, M.: Conductivities and ionic association of copper(II) and manganese(II) sulfates in ethanol + water at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 39, 48–49 (1994)
Kielland, J.: Individual activity coefficients of ions in aqueous solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 59, 1675–1678 (1937)
Barthel, J.M.G., Krienke, H., Kunz, W.: Physical Chemistry of Electrolyte Solutions. Modern Aspects. Springer, Darmstadt (1998)
Bateman, R.L., Ewing, D.T.: The electrical conductance of strontium chloride and strontium bromide in ethanol–water mixtures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 70, 2137–2140 (1948)
Than, A., Amis, E.S.: The equivalent conductance of electrolytes in mixed solvent. XI. The equivalent conductance (Λ) of magnesium chloride in the water-ethanol system. Z. Phys. Chem. 58, 196–205 (1968)
Srour, R.K., McDonald, L.M.: Ionic conductivity of selected 2:1 electrolytes in mixed aqueous–organic solvents at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 53, 335–342 (2008)
James, J.C.: The electrolytic dissociation of zinc sulphate, copper sulphate, and zinc malonate in mixed solvents. J. Chem. Soc. 153–157 (1951)
Szimizu, K., Tsuchihashi, N., Ikemoto, K.: Effect of pressure on electrolytic conductance of cupric sulfate in ethanol–water mixtures. Sci. Eng. Rev. Doshisha Univ. 22, 7–12 (1981)
Vivo, A., Esteso, M.A., Llorente, M.L., Dominguez, B.: Conductividades en medios aqua–etanol. IV. Conductividad limito del MgSO4 a 25 °C. An. Quim. 77, 209–213 (1981)
Vivo, A., Esteso, M.A., Llorente, M.L.: Conductividades en medios aqua-etanol. III. Conductividad limito del Na2SO4 a 25 °C. An. Quim. 77, 204–208 (1981)
James, J.C.: The electrolytic dissociation of lanthanum ferricyanide in mixed solvents. J. Chem. Soc. 1094–1097 (1950)
Amis, E.S., Casteel, J.F.: The equivalent conductance of electrolytes in mixed solvent. XII. Magnesium sulfate in water–ethanol solvents. J. Electrochem. Soc. 117, 213–218 (1970)
Kay, R.L., Broadwater, T.L.: Solvent structure in aqueous mixtures. III. Ionic conductances in ethanol–water mixtures at 10 and 25 °C. J. Solution Chem. 5, 57–76 (1976)
Dunsmore, H.S., Kelly, T.R., Nancollas, G.H.: Electrochemical studies in the rare earth series. Part 3. Conductances of some 3-3 electrolytes in water and dioxane + water. Trans. Faraday Soc. 59, 2606–2611 (1963)
Dunsmore, H.S., James, J.C.: The electrolytic dissociation of magnesium sulphate and lanthanum ferricyanide in mixed solvents. J. Chem. Soc. 2925–2930 (1951)
Atkinson, G., Hallada, C.J.: Ion association in polyvalent symmetrical electrolytes. IV. The conductance of MnSO4 and MnBDS in dioxane–water mixtures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 84, 721–724 (1962)
Masterton, W.L., Bierly, T.: Ion association in 2:2 complex ion electrolytes: [Co(NH3)5NO2]SO4 in water–dioxane mixtures. J. Solution Chem. 5, 721–731 (1976)
Bešter-Rogač, M., Hauptman, N., Barthel, J.: Conductometric study of ion association of divalent symmetric electrolytes. II. MgSO4 in water + 1,4-dioxane mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 131–132, 29–35 (2007)
Atkinson, G.: Ion association in polyvalent symmetrical electrolytes. I. Conductances of several rare earth hexacyanocobaltates(III) in dioxane–water mixtures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82, 818–820 (1960)
Hafez, A.M., Osman, M.M., El-Kholy, M.M.: Electrical conductance of some transition metal complexes in both water and dioxane–water mixtures at 25 °C. Electrochim. Acta 30, 541–549 (1985)
Kay, R.L., Broadwater, T.L.: Solvent structure in aqueous mixtures. I. Ionic mobilities in dioxane–water mixtures at 25 °C. Electrochim. Acta 16, 667–678 (1971)
Fratiello, A., Kay, R.L.: Transference numbers for KCl in ethanol–water and dioxane–water mixtures at 25 °C. J. Solution Chem. 3, 857–864 (1974)
Perif, M., Perif, J., Chemla, M.: Mesure des nombres de transport des ions Cs+ et Br− en milieu eau–dioxanne a l’aide de radiotraceurs. Electrochim. Acta 21, 739–744 (1976)
Apelblat, A.: A new look on the representation of electrical conductivities in mixed solvents. The universal curves of limiting conductances of electrolytes and the modified and the excess Walden products. Acta Chim. Slov. 56, 1–17 (2009)
Doe, H., Kitagawa, T.: Conductometric study of cobalt(II), nickel(II), copper(II), and zinc(II) perchlprates in methanol–ethylene glycol mixtures. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 58, 2975–2980 (1985)
Doe, H., Ohe, H., Matoba, H., Ishimura, A., Kitagawa, T.: Conductometric study of calcium(II), strontium(II), and barium(II) perchlorates in methanol–ethylene glycol mixtures. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 63, 2785–2789 (1985)
Roy, M.N., Pradhan, P., Dewan, R.: Study on ion-solvent interactions of alkali metal salts in pure methanol and its binary mixtures with ethane-1,2-diol by a conductometric technique. Fluid Phase Equilib. 282, 51–57 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apelblat, A. Representation of Electrical Conductances for Polyvalent Electrolytes by the Quint-Viallard Conductivity Equation. Universal Curves of Limiting Conductances and Walden Products of Electrolytes in Mixed Solvents. Part 5. Symmetrical 2:2, 3:3 and Unsymmetrical 1:2, 2:1 and 1:3 Type Electrolytes. J Solution Chem 40, 1544–1562 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-011-9741-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-011-9741-z