Abstract
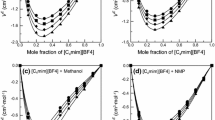
We report here the systematic study of the effect of concentration on the physical properties of aqueous solutions of the room-temperature ionic liquid [BMIM][BF4]. The measurements of density, ρ, refractive index △n, viscosity η, specific conductivity κ and surface tension, γ, were made over the whole concentration range. The equivalent conductance Λ m was calculated. The observed linear variations of density and refractive index with the molar concentration are established as those of an ideal solution. The surface tension varied most rapidly in the dilute region whereas the viscosity changed much more rapidly in the concentrated region. Two regions with different composition dependences were found after the analyses of the relationship between the conductivity and the concentration of [BMIM][BF4]. A proposed model for a structural change in the mixtures was described. The physical origin of the observed concentration dependence of these properties is discussed. The physical properties of the solutions vary with changes of association between anions and cations and the interaction between [BMIM][BF4] and water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rogers, R.D., Sedden, K.R.: Ionic liquids-solvents of the future. Science 302, 792–793 (2003)
Hurley, F.H., Wier, T.P.: Electrodeposition of metals from fused quaternary ammonium salts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 98, 203–206 (1951)
Welton, T.: Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 99, 2071–2082 (1999)
Chiappe, C., Pieraccini, D.: Ionic liquids: solvent properties and organic reactivity. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 18, 275–297 (2005)
Kubisa, P.: Application of ionic liquids as solvents for polymerization processes. Prog. Polymer. Sci. 29, 3–12 (2004)
Carlin, R.T., Osteryoung, R.A., Wilkes, J.S., Rovang, J.: Studies of titanium(IV) chloride in a strongly Lewis acidic molten salt: Electrochemistry and titanium NMR and electronic spectroscopy. Inorg. Chem. 29, 3003–3009 (1990)
Huddleston, J.G., Willauer, H.D., Swatloski, R.P., Visser, A.E., Rogers, R.D.: Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for ‘clean’ liquid-liquid extraction. Chem. Commun. 1765–1766 (1998)
Poole, C.F.: Chromatographic and spectroscopic methods for the determination of solvent properties of room temperature ionic liquids. J. Chromatogr. A. 1037, 49–82 (2004)
Najdanovic-Visak, V., Esperanca, J.M.S.S., Rebelo, L.P.N., Nunes da Ponte, M., Guedes, H.J.R., Seddon, K.R., Szydlowski, J.: Phase behaviour of room temperature ionic liquid solutions: An unusually large co-solvent effect in (water + ethanol). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 4, 1701–1703 (2002)
Rebelo, L.P.N., Najdanovic-Visak, V., Visak, Z.P., Nunes da Ponte, M., Szydlowski, J., Cerdeirina, C.A., Troncoso, J., Romani, L., Esperanca, J.M.S.S., Guedes, J.R.H., de Sousa, H.C.: A detailed thermodynamic analysis of [C4mim][BF4] + water as a case study to model ionic liquid aqueous solutions. Green Chem. 6, 369–381 (2004)
Swatloski, R.P., Spear, S.K., Holbrey J.D., Rogers, R.D.: Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 4974–4795 (2002)
Huddleston, J.G., Visser, A.E., Reichert, W.M., Willauer, H.D., Broker, G.A., Rogers, R.D.: Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem. 3, 156–164 (2001)
Wu, X., Liu, Z., Huang, S., Wang, W.: Molecular dynamics simulation of room-temperature ionic liquid mixture of [bmim][BF4] and acetonitrile by a refined force field. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 7, 2771–2779 (2005)
Seddon, K.R., Stark, A., Torres, M.-J.: Influence of chloride, water, and organic solvents on the physical properties of ionic liquids. Pure Appl. Chem. 72, 2275–2287 (2000)
Perry, R.L., Jones, K.M., Scott, W.D., Liao, Q., Hussey, C.L.: Densities, viscosities, and conductivities of mixtures of selected organic cosolvents with the Lewis basic aluminum chloride + 1-methy-3-ethylimidazolium chloride molten salt. J. Chem. Eng. Data 40, 615–619 (1995)
Abraham, M., Abraham, M.C.: Electrolytic conductance and viscosity of some mixed nitrate-water systems from fused salts to dilute solutions. Electrochim. Acta 31, 821–829 (1986)
Sirieix-Plenet, J., Gaillon, L., Letellier, P.: Behaviour of a binary solvent mixture constituted by an amphiphilic ionic liquid, 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide and water potentiometic and conductimetic studies. Talanta 63, 979–986 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Zhao, T., Zhang, Y. et al. The Physical Properties of Aqueous Solutions of the Ionic Liquid [BMIM][BF4]. J Solution Chem 35, 1337–1346 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-006-9064-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-006-9064-7