Abstract
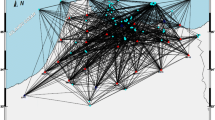
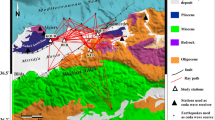
We analyzed the local earthquakes waveform recorded on a broadband seismic network in the northwestern Himalayan Region to compute lapse time and frequency dependence of coda Q (Q c). The observed Q c values increase with increasing lapse time at all frequency bands. The increase in Q c values with lapse time is attributed to an increase in Q c with depth. This implies that attenuation decreases with increasing depth. The approximate radius of medium contributing to coda generation varies from 55 to 130 km. By comparing the Q c values with those from other regions of the world, we find that they are similar to those obtained from tectonically active regions. The estimated Q c values show a frequency-dependent relationship, Q c = Q 0 f n, where Q 0 is Q c at 1 Hz and n represents degree of frequency dependence. They represent the level of heterogeneity and tectonic activity in an area. Our results show that northwest Himalayas are highly heterogeneous and tectonically very active. Q 0 increases from 113 ± 7 to 243 ± 10 and n decreases from 1.01 ± 0.05 to 0.85 ± 0.03 when lapse time increases from 30 to 70 s. As larger time window sees the effect of deeper part of the Earth, it is concluded that Q 0 increases and n decreases with increasing depth; i.e., heterogeneity decreases with depth in the study area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki K (1969) Analysis of the seismic coda of local earthquakes as scattered waves. J Geophys Res 74:615–631
Aki K (1980) Attenuation of shear waves in the lithosphere for frequencies from 0.05 to 25 Hz. Phys Earth Planet Inter 21:50–60
Aki K, Chouet B (1975) Origin of the coda waves: source attenuation and scattering effects. J Geophys Res 80:3322–3342
Akinci A, Taktak AG, Ergintav S (1994) Attenuation of coda waves in Western Anatolia. Phys. Earth Planet Inter 87:155–165
Gao LS, Lee LC, Biswas NN, Aki K (1983) Comparison of the single and multiple scattering on coda waves for local earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 73:377–389
Gupta SC, Singh VN, Kumar A (1995) Attenuation of coda waves in the Gharwal Himalaya, India. Phys Earth Planet Inter 87:247–253
Gupta SC, Kumar A, Singh VN, Basu S (1996) Lapse-time dependence of Qc in the Garhwal Himalaya. Bull Indian Soc Earthq Technol 33:147–159
Ibanez JM, Pezzo ED, De Miguel F, Herriaz M, Alguacie G, Morales J (1990) Depth dependent seismic attenuation in the Granada zone (Southern Spain). Bull Seismol Soc Am 80:1232–1244
Jin A, Aki K (1986) Temporal change in Coda-Q before the Tangshan earthquake of 1976 and the Haicheng earthquake of 1975. J Geophys Res 91:665–673
Kanao M, Ito K (1991) Attenuation of S-waves and coda waves in the inner zone of Southern Japan. Disaster Prev Res Inst Kyoto Univ Bull 41:31–51
Kopnichev YF (1977) The role of multiple scattering in the formation of seismogram’s tail. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Fiz Zemli 13:394–398 (in Russian)
Kvamme LB, Havskov J (1989) Q in Southern Norway. Bull Seismol Soc Am 79:1575–1588
Mandal P, Rastogi BK (1998) A frequency dependent relation of coda Q c for Koyna–Warna Region, India. Pure Appl Geophys 153:163–177
Molnar P (1988) A review of geophysical constraints on the deep structure of the Tibetan plateau, the Himalaya and the Karakoram and their tectonic implications. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 326:33–88
Nishigami K, Iio Y, Gurbuz C, Pinar A, Aybey N, Ucer SB, Honkura Y, I Sikara AM (1990) Microseismic activity and spatial distribution of coda-Q in the western most part of the North Anatolian fault zone Turkey. Disaster Prev Res Inst Kyoto Univ Bull 40:41–56
Pulli JJ (1984) Attenuation of Coda waves in New England. Bull Seismol Soc Am 74:1149–1166
Pulli JJ, Aki K (1981) Attenuation of seismic waves in the lithosphere: comparison of active and stable areas. In: Beavers JE (ed.) Earthquakes and Earthquake Engineering: The Eastern United States (pp 129–141). Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor, MI
Rai SS, Priestley K, Gaur VK, Singh MP, Searle MP (2006) Configuration of the Indian Moho beneath the NW Himalaya and Ladakh. Geophys Res Lett (in press)
Rautian TG, Khalturin VI (1978) The use of the coda for the determination of the earthquake source spectrum. Bull Seismol Soc Am 68:923–948
Reha S (1984) Q determined from local earthquakes in the South Carolina coastal plain. Bull Seismol Soc Am 74:2257–2268
Roecker SW, Tucker B, King J, Hatzfield D (1982) Estimates of Q in Central Asia as a function of frequency and depth using the Coda of locally recorded earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 72:129–149
Sato H (1977) Energy propagation including scattering effects: single isotropic scattering. J Phys Earth 25:27–41
Tsujiura M (1978) Spectral analysis of coda waves from local earthquake. Bull Earthq Res Inst 53:1–48
Van-Eck T (1988) Attenuation of coda waves in the Dead Sea region. Bull Seismol Soc Am 82:770–779
Woodgold CRD (1994) Coda Q in the Charlevoix, Quebec region: lapse-time dependence and spatial and temporal comparison. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84:1123–1131
Yin A, Harrison TM (2000) Geological evolution of the Himalayan–Tibetan orogen. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 28:211–280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, S., Tyagi, C. Lapse time and frequency-dependent attenuation characteristics of coda waves in the Northwestern Himalayas. J Seismol 11, 149–158 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-006-9042-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-006-9042-y