Abstract
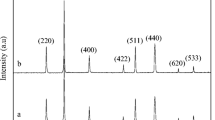
In this research, BiFeO3 nanoparticles were synthesized by sol-gel auto-combustion method with and without the addition of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) surfactant. The effect of different amounts of CTAB addition (0, 1.5, 3, and 6 wt.%) on phase constituents, microstructure, and magnetic properties of the synthesized samples were evaluated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), and vibration sample magnetometer (VSM). Also, BiFeO3 nanoparticles were used for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) as a typical dye pollutant under UV irradiation. XRD results showed the formation of BiFeO3 mainly with some minute impurity phases such as Bi2O3 and γ-Fe2O3. Proper amounts of CTAB addition (1.5 wt.%) considerably eliminates Bi2O3 and γ-Fe2O3 residuals in the combustion product. FESEM micrographs show particle size reduction and also more uniform particle size distribution when using 0.75 wt.% of CTAB addition. In the presence of the BiFeO3, the UV irradiation for 120 min resulted in 26% degradation of MB, in a sample with 0.75 wt.% CTAB. The synthesized nanoparticles of BiFeO3 in the sample with 0.75 wt.% CTAB after calcination at 650 ∘C showed a weak ferromagnetism behavior with saturation magnetization of 0.54 emu/g. iHC values of the samples are in the range of 200 to 238 Oe, depending on the crystallite size and phase constituents of the samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, J.H., Ke, H., Jia, D.C., Wang, W., Zhou, Y.: Low-temperature synthesis of BiFeO3 nanopowders via a sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 472, 473–477 (2009)
Xu, J.M., Wang, G.M., Wang, H.X., Ding, D.F., He, Y.: Synthesis and weak ferromagnetism of Dy-doped BiFeO3 powders. Mater. Lett. 63, 855–857 (2009)
McDonnell, K.A., Wadnerkar, N., English, N.J., Rahman, M., Dowling, D.: Photo-active and optical properties of bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3): an experimental and theoretical study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 572, 78–84 (2013)
Chen, C., Cheng, J., Yu, S., Che, L., Meng, Z.: Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite bismuth ferrite crystallites. J. Cryst. Growth 291, 135–139 (2006)
Li, S., Lin, Y.H., Zhang, B.P., Nan, C.W., Wang, Y.: Photocatalytic and magnetic behaviors observed in nanostructured BiFeO3 particles. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 056105 (2009)
Zhou, J.P., Yang, R.L., Xiao, R.J., Chen, X.M., Deng, C.Y.: Structure and phase transition of BiFeO3 cubic micro-particles prepared by hydrothermal method. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 3630–3636 (2012)
Shabani, S., Mirkazemi, S.M., Masoudpanah, S.M., Taheri Dolat Abadi, P.: Synthesis and characterization of pure single phase BiFeO3 nanoparticles by the glyoxylate precursor method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 2795–2801 (2014)
Yang, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, G., Wei, X., Ren, Z., Shen, G., Han, G.: Phase and morphology evolution of bismuth ferrites via hydrothermal reaction route. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 1694–1699 (2013)
Vanga, P.R., Mangalaraja, R.V., Ashok, M.: Structural, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of La and alkaline co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 40, 796–802 (2015)
Zhang, X., Lv, J., Bourgeois, L., Cui, J., Wu, Y., Wang, H., Webley, P.A.: Formation and photocatalytic properties of bismuth ferrite submicrocrystals with tunable morphologies. New J. Chem. 35, 937–941 (2011)
Vanga, P.R., Mangalaraja, R.V., Ashok, M.: Effect of co-doping on the optical, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of the Gd modified BiFeO3. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 27, 5699–5706 (2016)
Ke, H., Wang, W., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Jia, D., Lu, Z., Zhou, Y.: Factors controlling pure-phase multiferroic BiFeO3 powders synthesized by chemical co-precipitation. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 2192–2197 (2011)
Das, N., Majumdar, R., Sen, A., Maiti, H.S.: Nanosized bismuth ferrite powder prepared through sonochemical and microemulsion techniques. Mater. Lett. 61(10), 2100–2104 (2007)
Masoudpanah, S.M., Mirkazemi, S.M., Shabani, S., Taheri Dolat Abadi, P.: The effect of the ethyleneglycol to metal nitrate molar ratio on the phase evolution, morphology and magnetic properties of single phase BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 41, 9642–9646 (2015)
Ghosh, S., Dasgupta, S., Sen, A., Sekhar, H.: Low-temperature synthesis of nanosized bismuth ferrite by soft chemical route. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88, 1349 (2005)
Godara, S., Sinhaa, N., Raya, G., Kumar, B.: Combined structural, electrical, magnetic and optical characterization of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by auto-combustion route. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2, 416–421 (2014)
Ramdas, B., Khomane, A.S., Prakash, K., Ramesha, M.: Sathiya: CTAB-assisted sol–gel synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 and its performance as anode material for Li-ion batteries. Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 1139–1142 (2011)
Mirkazemi, S.M., Alamolhoda, S., Ghiami, Z.: Microstructure and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 nano-sized powders prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion method with CTAB surfactant. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 1543–1549 (2015)
Carvalho, T.T., Tavares, P.B.: Synthesis and thermodynamic stability of multiferroic BiFeO3. Mater. Lett. 62, 3984–3986 (2008)
Silambarasan, P., Vairavel, M., Ramesh Kumar, G., Gokul Raj, S.: Effect of fuel on phase formation of nanocrystalline bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3). Mater. Today: Proceedings 2, 1923–1926 (2015)
Zhao, Y., Miao, J., Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Xu, X.G., Jiang, Y.: Ultra-thin BiFeO3 nanowires prepared by a sol–gel combustion method: an investigation of its multiferroic and optical properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23, 180–184 (2012)
Upadhyay, R.K., Pan, S., Barman, A., Mc Laughlin, J.A., SinhaRoy, S.: Oil swollen surfactant gel based synthesis of metal oxides nanoparticles: an attractive alternative for the conventional sol gel synthesis. Ceram. Int. 42, 12119–12128 (2016)
Hardy, A., Gielis, S., Van den Rul, H., D’Haen, J., Van Bael, M.K., Mullens, J.: Effects of precursor chemistry and thermal treatment conditions on obtaining phase pure bismuth ferrite from aqueous gel precursors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 3007–3013 (2009)
George, M., Johna, A.M., Naira, S.S., Joy, P.A., Anantharaman, M.R.: Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 190–195 (2006)
Sivakumar, P., Ramesh, R., Ramanand, A., Ponnusamy, S., Muthamizhchelvan, C.: Synthesis, studies and growth mechanism of ferromagnetic NiFe2O4 nanosheet. Appl. S.rf. Sci. 258, 6648–6652 (2012)
Ghosh, S., Dasgupta, S., Sen, A., Maiti, H.S.: Effect of fuel on phase formation of nanocrystalline bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3). Mater. Res. Bull. 40, 2073–2079 (2005)
Medernach, J.W., Snyder, R.L.: Low-temperature synthesis of nanosized bismuth ferrite by soft chemical route. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 61, 494–497 (1978)
Wang, Z., Li, X., Feng, Z.: The effect of CTAB on the citrate sol-gel process for the synthesis of sodium beta-alumina nano-powders. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 32, 1310–1314 (2011)
Ghobeiti Hasab, M., Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A., Badiei, A.: Comparison of the effects of cationic, anionic and nonionic surfactants on the properties of Sr-hexaferrite nanopowder synthesized by a sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, e13–e15 (2007)
Liu, J.L., Chen, X.L., Wang, S.Y., Yan, L.M., Zhang, M.: Synthesis and properties of strontium hexa-ferrite ultrafine powders via a CTAB-assisted co-precipitation method. Rare Met. 36, 666–670 (2017)
Jia, D.C., Xu, J.H., Ke, H., Wang, W., Zhou, Y.: Structure and multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 3099–3103 (2009)
Pillai, V., Shah, D.O.: Synthesis of high-coercivity cobalt ferrite particles using water in-oil microemulsions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 163, 243–248 (1996)
Jain, S.R., Adiga, K.C., PaiVernecker, V.R.: A new approach to thermochemical calculations of condensed fuel-oxidizer mixtures. Combust. Flame 40, 71–79 (1981)
Alamolhoda, S., Mirkazemi, S.M., Shahjooyi, T., Benvidi, N.: Effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) amount on phase constituents and magnetic properties of nano-sized NiFe2O4 powders synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 638, 121–126 (2015)
Zhong, J., Li, J., Xiao, Z., Hu, W., Zhou, X., Zheng, X.: Improved photocatalytic performance of ZnO prepared by sol–gel method with the assistance of CTAB. Mater. Lett. 91, 301–303 (2013)
Yin, S., Shinozaki, M., Sato, T.: Synthesis and characterization of wire-like and near-spherical Eu2O3-doped Y2O3 phosphors by solvothermal reaction. J. Lumin 126, 427–433 (2007)
Rajendran, R., Muralidharan, R., Gopalakrishnan, R.S., Chellamuthu, M., Ponnusamy, S.U., Manikandan, E.: Controllable synthesis of single-crystalline Fe3O4 nanorice by a one-pot, surfactant-assisted hydrothermal method and its properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 5384–5389 (2011)
Zhang, L., He, R., Gu, H.C.: Synthesis and kinetic shape and size evolution of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 41, 260–267 (2006)
Puntes, V.F., Zanchet, D., Erdonmez, C.K., Paul Alivisatos, A.: Synthesis of hcp-Co nanodisks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 12874–12880 (2002)
Kumar, A., Rai, R.C., Podraza, N.J., Denev, S., Ramirez, M., Chu, Y.H., Martin, L.W., Ihlefeld, J., Heeg, T., Schubert, J., Schlom, D.G., Orenstein, J., Ramesh, R., Collins, R.W., Musfeldt, J.L., Gopalan, V.: Linear and nonlinear optical properties of BiFeO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 121915 (2008)
Yang, J., Li, X., Zhou, J., Tang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, Y.: Factors controlling pure-phase magnetic BiFeO3 powders synthesized by solution combustion synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 9271–9277 (2011)
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to Magnetic Materials, 2nd edn. IEEE Press & Wiley, New Jersey (2009)
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1978)
Zhang, M., Yang, H., Xian, T., Wei, Z.Q., Jiang, J.L., Feng, Y.C., Liu, X.Q.: Polyacrylamide gel synthesis and photocatalytic performance of Bi2Fe4O9 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 809–812 (2011)
Arya, G.S., Negi, N.S.: Effect of In and Mn co-doping on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 095004 (2013)
Stoner, E.C., Wohlfarth, E.P.: A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 27, 3475–3518 (1991)
Xiang, J., Zhou, G., Shen, X., Chu, Y., Guo, Y.: Effect of Bi2O3 addition on structure and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanofibers. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 62, 186–192 (2012)
Irfan, S., Rizwan, S., Shen, Y., Li, L., Asfandiyar, Butt, S., Nan, C.W.: The gadolinium (Gd3+) and tin (Sn4+) co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles as new solar light active photocatalyst. Sci. Rep. 7, 42493 (2017)
Soltani, T., Entezari, M.H.: Photolysis and photocatalysis of methylene blue by ferrite bismuth nanoparticles under sunlight irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A:Chem. 377, 197–203 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, P., Alamolhoda, S. & Mirkazemi, S.M. Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide (CTAB) Surfactant-Assisted Synthesis of BiFeO3 Nanoparticles by Sol-Gel Auto-Combustion Method. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 3307–3314 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4596-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4596-9