Abstract
The mathematical modeling is used to study the dynamics of solution deionization by sorption on aerogel electrodes. The matter transport by solution flow, diffusion, and sorption in pores are simulated. Several models are proposed to describe the phenomenon with different degree of approximation. Problems arising in numerical computing and ways to solve them are described. It is shown that at low solution concentrations and a small pore size the effect of electro-sorption is not reduced to the formation of a double electric layer on the pore surface, which uptakes ions from the solution. In addition to the formation of this layer distributed ionic charge is accumulated all over the pore space. The dependence of the effective diffusion coefficient inside the porous electrode on the ion concentration is found. Examples of calculating the deionization process at one-cycle and multi-cycle sorption are given.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
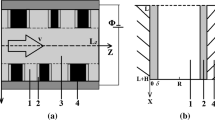
- Lz :
-
Channel length (m)
- H :
-
The thickness of porous-material layer (m)
- L :
-
The distance between layers, channel width (m)
- \(\eta \) :
-
Sorbent porosity (dimensionless)
- z :
-
The coordinate along the channel, \(0\le z\le Lz\) (m)
- x :
-
The coordinate across the channel, \(-\,H\le x\le L+H\) (m)
- r :
-
Radial coordinate in a pore, \(0\le r\le R\) (m)
- t :
-
Time, \(t\ge 0\) (s)
- T :
-
Time interval within which voltage is applied to the capacitor (s)
- \(R_{0}\) :
-
Pore radius (m)
- \(r_{hyd}\) :
-
The radius of ion hydrate envelope,
 (m)
(m) - \(\Phi \) :
-
The voltage applied to the capacitor (v)
- \(\varphi \) :
-
The local value of the potential measured relative the center of the channel (v)
- \(u=\frac{\phi q}{kT}\) :
-
Normalized local potential, \(u_0 -\frac{\Phi q}{2kT}\) (dimensionless)
- v :
-
Flow rate in the channel \(( \mathrm {m \, s^{-1}})\)
- C :
-
Electrolyte concentration in the channel \((\mathrm {mol\,L^{-1}})\)
- \(C_\pm \) :
-
Concentrations of ions of appropriate signs \((\mathrm {mol\,L^{-1}})\)
- \(j_\pm \) :
-
Fluxes of ions of different signs, \(j=(j_+ +j_- )/2 \quad (\mathrm {mol\,m^{-2}\,s^{-1}})\)
- \(C_0\) :
-
Electrolyte concentration at channel entry and at the initial moment \((\mathrm {mol\,L^{-1}})\)
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient \(( \mathrm {m^{2}\, s^{-1}})\)
- \(\overline{C} (x,z,t)\) :
-
Mean concentration in a pore cross-section \((\mathrm {mol\,L^{-1}})\)
- V(R):
-
The relative volume occupied by pores of radius R (dimensionless)
- \(D_{ex}\, \mathrm{and}\, D_{in}\) :
-
Diffusion coefficients in the channel and sorbent \(( \mathrm {m^{2}\,s^{-1}})\)
References
M.A. Anderson, A.L. Cudero, J. Palma, Electrochim. Acta 55, 3845–3856 (2010)
O.N. Demirer, R.M. Naylor, C.A. Rios Perez, E. Wilkes, C. Hidrovo, Desalination 314, 130–138 (2013)
M.E. Suss, S. Porada, X. Sun, P.M. Biesheuvel, J. Yoon, V. Presser, Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 2296–2319 (2015)
Y. Oren, Desalination 228, 10–29 (2008)
G. Rasines, P. Lavela, C. Macías, M. Haro, C.O. Ania, J.L. Tirado, J. Electroanal. Chem. 671, 92–98 (2012)
A. Faisal, Al Marzooqi, A. Amal, Al Ghaferi, I. Saadat, N. Hilal, Desalination 342, 3–15 (2014)
D. Marmanis, A. Christoforidis, K. Ouzounis, K. Dermentzis, Global NEST J. 16(4), 609–615 (2014)
D.A.B. Iozzo, M. Tong, G. Wu, E.P. Furlani, J. Phys. Chem. C 119(45), 25235–25242 (2015)
K.L. Yang, T.Y. Ying, J. Sátira, Langmuir 17, 1961–1969 (2001)
C.A. Rios Perez, O.N. Demirer, R.L. Clifton, R.M. Naylor, C.H. Hidrovo, J. Electrochem. Soc. 160(3), E13–E21 (2013)
D.B. Robinson, C.A.M. Wu, B.W. Jacobs, J. Electrochem. Soc. 157(8), A912–A918 (2010)
K. Honda, M. Yoshimura, K. Kawakita, A. Fujishima, Y. Sakamoto, K. Yasui, N. Nishio, H. Masudac, J. Electrochem. Soc. 151(4), A532–A541 (2004)
N.C. Hoyt, J.S. Wainright, R.F. Savinell, J. Electrochem. Soc. 162(4), A652–A657 (2015)
C. Niu, E.K. Sichel, R. Hoch, D. Moy, H. Tennet, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70(11), 1480–1482 (1997)
A. Hemmatifar, M. Stadermann, J.G. Santiago, J. Phys. Chem. C 119(44), 24681–24694 (2015)
M.E. Sussz, Electrochem. Soc. 164(9), E270–E275 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tikhonov, N.A. Mathematical modeling of solution deionization by sorption on aerogel electrodes. J Math Chem 56, 700–712 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-017-0825-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-017-0825-x




 (m)
(m)