Abstract
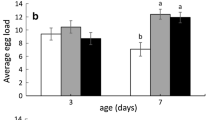
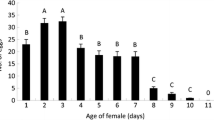
Bracon vulgaris is a larval ectoparasitoid of the boll weevil, Anthonomus grandis, a key cotton pest We investigated the influence of parasitoid age, photoperiod and host availability on B. vulgaris parasitism. Five- and 10-day-old parasitoids were exposed to A. grandis densities of three, six, 12 and 24 larvae per female. Five-day-old females showed higher parasitism rates (F = 21.55, P < 0.0001), with a positive increase in parasitism rate up to 12 larvae, parasitizing an average (±SE) of 1.3 (±0.12), 3.4 (±0.35) and 4.4 (±0.45) larvae (at the densities of 3, 6 and 12 larvae, respectively), dropping to 1.4 (±0.17) when 24 larvae were offered. Next, the period of most parasitism activity during the photophase was determined by exposing five-day-old B. vulgaris females to different durations of light exposure (1, 3, 6, 8 and 10 h) after 12 h darkness. Results showed that the shortest time to host location occurred 8 h after light exposure, when parasitoids were most active searching for the host. A sequence of seven behavioral acts leading to successful parasitism was identified and the transitions between successive behavioral acts were quantified and depicted in an ethogram. The longest duration act was oviposition (or host acceptance), a complex behavior with several distinct phases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed T, Zhang T, He K, Bai S, Wang Z (2013) Sense organs on the ovipositor of Macrocentrus cingulum brischke (hymenoptera: braconidae); their probable role in stinging, oviposition and host selection process. J Asia Pacific Entomol 16:343–348. doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2013.04.015
Alves AP, Serikawa RH (2006) Controle químico de pragas do algodoeiro. Rev Bras Ol Fibros 10:1197–1209
Alves TJSA, Wanderley-Teixeira V, Teixeira AAC, Silva-Torres CSA, Malaquias JB, Pereira BF, Cunha FM (2014) Parasitoid-host interaction: sensory structures involved in the parasitism behavior of Bracon vulgaris (hymenoptera: braconidae). Anim Biol 64:365–381. doi:10.1163/15707563-00002452
Araújo LHA, Guerra AA, Herrera EA (2000) Contenido de los nutrientes básicos en Catolaccus grandis Burks criados sobre larvas del picudo del algodon. Pesqu Agropecu Bras 35:1701–1707
Azzouz H, Giordanengo P, Wackers FL, Kaiser L (2004) Effects of feeding frequency and sugar concentration on behavior and longevity of the adult aphid parasitoid Aphidius ervi (haliday) (hymenoptera: braconidae). Biol Control 31:445–452. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2004.07.013
Bezemer TM, Mills NJ (2003) Clutch size decisions of a gregarious parasitoid under laboratory and field conditions. Animal Behav 66:1119–1128
Brown PE, Anderson M (1998) Morphology and ultrastructure of sense organs on the ovipositor of Trybliographa rapae, a parasitoid of the cabbage root fly. J Insect Physiol 44:1017–1025
Busoli AC, Pereira FF, Lopéz VAG, Soares JJ, Melo RS, Almeida CA (2004) Preferência alimentar do bicudo-do-algodoeiro por frutos de diferentes cultivares e idades. Pesqu Agropecu Bras 39:101–104
Carvalho SL, Fernandes WD, Habib MEM, Patel PN (2002) Preferência de Bracon vulgaris e adequações de alguns hospedeiros em condições de laboratório. Rev Agric 77:39–56
Carvalho SL, Fernandes WD, Patel PN, Habib MEM (2000) Respostas comparativas de Bracon vulgaris ashmead (hymenoptera: braconidae) a diferentes macerados de plantas de algodão, em dois modos de exposição. Rev Agric 75:41–53
Chen WL, Leopold RA, Harris MO (2006) Parasitism of the glassy-winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca coagulata (homoptera: cicadellidae): functional response and superparasitism by Gonatocerus ashmeadi (hymenoptera: mymaridae). Biol Control 37:119–129. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2005.10.011
Cooperband MF, Matthews RW, Vinson SB (2003) Factors affecting the reproductive biology of Melittobia digitata and failure to meet the sex ratio predictions of Hamilton’s local mate competition theory. Entomol Exp Appl 109:1–12
Del-Claro K, Santos JC, Souza Jr AD (2002) Etograma da formiga arborícola Cephalotes pusillus (Klug, 1824) (formicidae: myrmicinae). Rev Etol 4:31–40
Dossi FAC, Cônsoli FL (2010) Desenvolvimento ovariano e influência da cópula na maturação dos ovários de Diaphorina citri kuwayama (hemiptera: psyllidae). Neotrop Entomol 39:414–419
Dweck HKM (2009) Antennal sensory receptors of Pteromalus puparum female (hymenoptera: pteromalidae), a gregarious pupal endoparasitoid of Pieris rapae. Micron 40:769–774. doi:10.1016/j.micron.2009.07.012
Dweck HKM, Gadallah NS, Darwish E (2008) Structure and sensory equipment of the ovipositor of Habrobracon hebetor (say) (hymenoptera: braconidae). Micron 39:1255–1261. doi:10.1016/j.micron.2008.03.012
Faria CA, Torres JB, Farias AMI (2000) Resposta funcional de Trichogramma pretiosum riley (hymenoptera: trichogrammatidae) parasitando ovos de Tuta absoluta (meyrick) (Lepidoptera: gelechiidae): efeito da idade do hospedeiro. An Soc Entomol Brasil 29:85–93
Faria CA, Torres JB, Fernandes AMV, Farias AMI (2008) Parasitism of Tuta absoluta in tomato plants by Trichogramma pretiosum riley in response to host density and plant structures. Cienc Rural 38:1504–1509
Ferreira SWJ, Barros R, Torres JB (2003) Exigências térmicas e estimativa do número de gerações de Oomyzus sokolowskii (kurdjumov) (hymenoptera: eulophidae), Para regiões produtoras de crucíferas em Pernambuco. Neot Entomol 32:407–411
Fonseca PRB, Lima Jr IS, Soria MF, Kodama C, Degrande PE (2011) Inseticidas neonicotinóides no controle do bicudo-do-algodoeiro Anthonomus grandis (boheman, 1843) (coleoptera: curculionidae) e a falha de controle do endosulfan. Arq Inst Biol 78:545–551
Goodman LA (1968) The analysis of cross-classified data: independence, quasi independence, and interactions in contingency tables with or without missing entries. J Amer Statist Assoc 63:1091–1131
Grigolli JFJ, Souza LA, Fraga DF, Funichello M, Busoli AC (2013) Within plant distribution of Anthonomus grandis (coleoptera: curculionidae) feeding and oviposition damages in cotton cultivars. Ciênc Agrotec 36:78–84
Gunduz EA, Gulel A (2005) Investigation of fecundity and sex ratio in the parasitoid Bracon hebetor say (hymenoptera: braconidae) in relation to parasitoid age. Turk J Zool 29:291–294
Haccou P, Meelis E (1992) Statistical analysis of behavioral data: an approach based on time-structures models. Oxford University Press, U.K.
Harbinson JL, Legaspi JC, Fabritius SL, Saldana RR, Legaspi Jr BC, Enkegaard A (2001) Effects of age and host number on reproductive biology of Allorhogas pyralophagus (hymenoptera: braconidae) attacking the Mexican rice borer (Lepidoptera: pyralidae). Environ Entomol 30:129–135
Hohmann CL, Luck RF (2004) Effect of host availability and egg load in Trichogramma platneri nagarkatti (hymenoptera: trichogrammatidae) and its consequences on progeny quality. Braz Arch Biol Technol 47:413–422
Honda T, Kainoh Y (1998) Age-related fecundity and learning ability of the egg-larval parasitoid Ascogaster reticulatus Watanabe (hymenoptera: braconidae). Biol Control 13:177–181
Jervis MA, Ellers J, Harvey JA (2008) Resource acquisition, allocation, and utilization in parasitoid reproductive strategies. Annu Rev Entomol 53:361–385. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.53.103106.093433
Kovac H, Stabentheiner A, Schmaranzer S (2009) Thermoregulation of water foraging wasps (Vespula vulgaris and Polistes dominulus). J Insect Physiol 55:959–966. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.06.012
Lewis CN, Whitfield JB (1999) Braconid wasp (hymenoptera: braconidae) diversity in forest plots under different silvicultural methods. Environ Entomol 28:986–997
Li X, Lu D, Liu X, Zhang Q, Zhou X (2011) Ultrastructural characterization of olfactory sensilla and immunolocalization of odorant binding and chemosensory proteins from an ectoparasitoid Scleroderma guani (hymenoptera: bethylidae). Int J Biol Sci 7:848–868
Makundi RH, Sariah JE (2005) A functional response of braconid parasitoids of the bean stem maggot, Ophiomyia spencerella (diptera, agromyzidae), in beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Tanzania. J Pl Dis Prot 112:478–484
Matadha D, Hamilton GC, Lashomb JH, Zhang J (2005) Ovipositional preferences and functional response of parasitoids of euonymus scale, Unaspis euonymi (Comstock) and San Jose scale, Quadraspidiotus perniciosus (Comstock) (homoptera: diaspididae). Biol Control 32:337–347. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2004.12.005
Mehrnejad MR, Copland MJW (2006) Host-stage selection and oviposition behavior of Psyllaephagus pistaciae, parasitoid of the common pistachio psylla Agonoscena pistaciae. Biol Control 36:139–146. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2005.07.005
Mills NJ, Kuhlmann U (2004) Oviposition behavior of Trichogramma platneri nagarkatti and Trichogramma pretiosum riley (hymenoptera: trichogrammatidae) in patches of single and clustered host eggs. Biol Control 30:42–51. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2003.09.011
Moreau SJM, Vinchon S, Cherqui A, Prévost G (2009) Components of Asobara venoms and their effects on hosts. Adv Insect Physiol 70:217–232. doi:10.1016/S0065-308X(09)70008-9
Ne’non JP, Kacem N, Le Lannic J (1997) Structure, sensory equipment, and secretions of the ovipositor in a giant species of hymenoptera: Megarhyssa atrata F. (ichneumonidae: pimplinae). Can Entomol 129:789–799
Neves RCS, Showler AT, Pinto ES, Bastos CS, Torres JB (2013) Reducing boll weevil populations by clipping terminal buds and removing abscised fruiting bodies. Entomol Exp Appl 146:276–285. doi:10.1111/eea.12026
Pereira FP, Zanuncio JC, Serrão JE, Oliveira HO, Fávero K, Grance ELV (2009) Progênie de Palmistichus elaeisis delvare & LaSalle (hymenoptera: eulophidae) parasitando pupas de Bombyx mori L. (Lepidoptera: bombycidae) de diferentes idades. Neotrop Entomol 38:660–664
Quicke DLJ (1997) Parasitic wasps. Chapman & Hall, Cambridge
Ramalho FS, Wanderley PA (1996) Ecology and management of cotton boll weevil in South America cotton. Am Entomol 42:41–47
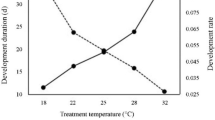
Ramalho FS, Wanderley PA, Malaquias JB, Souza JVS, Rodrigues KCV, Zanuncio JC (2009) Effect of temperature on the reproduction of Bracon vulgaris ashmead (hymenoptera: braconidae), a parasitoid of the cotton boll weevil. Entomol News 120:476–487. doi:10.3157/021.120.0503
Ramalho FS, Silva AMC, Zanuncio JC, Serrão JE (2007) Competition between Catolaccus grandis (hymenoptera:pteromalidae) and Bracon vulgaris (hymenoptera: braconidae), parasitoids of the boll weevil. Braz Arch Biol Technol 50:371–378
Rukmowati-Brotodjojo RR, Walter GH (2006) Oviposition and reproductive performance of a generalist parasitoid (Trichogramma pretiosum) exposed to host species that differ in their physical characteristics. Biol Control 39:300–312. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2006.08.011
Sampaio MV, Bueno VHP, Pérez-Maluf R (2001) Parasitismo de Aphidius colemani viereck (hymenoptera: aphidiidae) em diferentes densidades de Myzus persicae (sulzer) (hemiptera: aphididae). Neotrop Entomol 30:81–87
Santos RC, Marcellino LH, Monnerat RG, Gander ES (2003) Mechanical damage in cotton buds caused by the boll weevil. Pesqu Agropecu Bras 38:1351–1356
Santos RL, Neves RCS, Colares F, Torres JB (2013) Parasitoides do bicudo Anthonomus grandis e predadores residentes em algodoeiro pulverizado com caulim. Semina 34: 3463–3474. doi: 10.5433/1679-0359.2013v34n6Supl1p3463.
SAS Institute (2001) SAS/STAT User’s guide, version 8.02, TS level 2MO. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC.
Shah AZ, Blackwell A, Hubbard SF (2012) Ultramorphology of the ovipositor of Venturia canescens (gravenhorst) and possible mechanisms for oviposition. Int J Agric Biol 14:908–914
Silva-Torres CSA, Barros R, Torres JB (2009a) Efeito da idade, fotoperíodo e disponibilidade de hospedeiro no comportamento de parasitismo de Oomyzus sokolowskii kurdjumov (hymenoptera: eulophidae). Neotrop Entomol 38:512–519. doi:10.1590/S1519-566X2009000400013
Silva-Torres CSA, Ramos Filho IT, Torres JB, Barros R (2009b) Superparasitism and host size effects in Oomyzus sokolowskii, a parasitoid of diamondback moth. Entomol Exp Appl 133:65–73. doi:10.1111/j.1570-7458.2009.00903.x
Silva-Torres CSA, Torres JB, Barros R, Pallini A (2010) Parasitismo de traça-das-crucíferas por Oomyzus sokolowskii. Pesq Agropec Bras 45:638–645
Sinzato DMS, Prezoto F (2000) Aspectos comportamentais de fêmeas dominantes e subordinadas de Polistes versicolor Olivier, 1791 (hymenoptera: vespidae) em colônias na fase de fundação. Rev Etologia 2:121–127
Torres JB (2008) Controle de pragas do algodoeiro: expectativas de mudanças. Ciênc Agríc 8:37–49
Tunçbilek AS, Ayvaz A (2003) Influences of host age, sex ratio, population density, and photoperiod on parasitism by Trichogramma evanescens westw. (hymenoptera: trichogrammatidae). J Pest Sci 76:176–180
Varaldi J, Foillet P, Boulétreau M, Fleury F (2005) Superparasitism acceptance and patch-leaving mechanisms in parasitoids: a comparison between two sympatric wasps. Anim Behav 69:1227–1234. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2004.09.012
Wang X, Yang Z, Gould JR (2010) Sensilla on the antennae, legs and ovipositor of Spathius agrili yang (hymenoptera: braconidae), a parasitoid of the emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis fairmaire (coleoptera: buprestidae). Micros Res Tech 73:560–571
Xiaoyi W, Zhongqi Y (2008) Behavioral mechanisms of parasitic wasps for searching concealed insect hosts. Acta Ecol Sin 28:1257–1269
Yamamoto ME, Volpato GL (2007) Comportamento animal. Editora UFRN, Natal
Zara FJ, Balestieri JBP (2000) Behavioural catalogue of Polistes versicolor Oliver (vespidae: polistinae) post-emergence colonies. Naturalia 25:301–319
Acknowledgments
We thank Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) Foundation for providing grants to the first and second author, respectively. We also acknowledge Embrapa-Algodão for partially supporting the development this research and R.R. Costa for the preparation of ethogram figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alves, T.J.S., Silva-Torres, C.S.A., Wanderley-Teixeira, V. et al. Behavioral Studies of the Parasitoid Bracon vulgaris Ashmead (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J Insect Behav 28, 604–617 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-015-9529-x
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-015-9529-x