Abstract
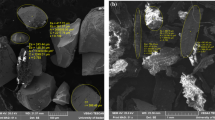
Adsorbents based on sludge flocs derived from wastewater have been widely developed in recent years. Herein, one of the adsorbents (PFloc) was obtained from water produced from oil without further treatment and was eluted via polysilicate aluminium to produce another adsorbent, MPFloc. The physiochemical characteristics of MPFloc and PFloc were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, contact angle measurements, scanning electron microsocpy, thermogravimetric analysis and zeta-potential techniques. The adsorption performance parameters of MPFloc and PFloc were assessed using Congo red (CR). The effect of dosage and settling time on CR adsorption was investigated. The adsorption capacities of adsorbents reached 1924.4 mg and 854.3 mg g−1 (generally below 100 mg g−1), respectively, because of their large quantities of –OH, better dispersion in CR solution, strong positive charge and cross-linked structure. The dynamic adsorption modes of the adsorption data were studied, which indicated that the adsorption process follows a pseudo-second-order model. Moreover, the adsorption isotherms of PFloc and MPFloc were in agreement with the Freundlich and Langmuir models, respectively. The waste utilization and superb adsorption capacity of MPFloc and PFloc provide new insight into the preparation of adsorbents.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.Z.M. Badruddoza, G.S.S. Hazel, K. Hidajat, M.S. Uddin, Synthesis of carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin conjugated magnetic nano-adsorbent for removal of methylene blue. Colloids Surf. A 367(1–3), 85–95 (2010)
F. Cheng et al., Sludge carbonization and activation: from hazardous waste to functional materials for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4(4), 4574–4586 (2016)
E. Chibowski, Surface free energy of a solid from contact angle hysteresis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 103(2), 149–172 (2003)
P. Devi, A.K. Saroha, Utilization of sludge based adsorbents for the removal of various pollutants: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 578, 16–33 (2016)
S. Fan et al., Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived biochar: adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5(1), 601–611 (2017)
M. Foroughi-dahr, M. Esmaieli, H. Abolghasemi, A. Shojamoradi, E. Sadeghi Pouya, Continuous adsorption study of congo red using tea waste in a fixed-bed column. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(18), 8437–8446 (2015)
V. Gupta, I. Ali, T. Saleh, A. Nayak, S. Agarwal, Chemical treatment technologies for waste-water recycling-an overview. RSC Adv. 2(16), 6380–6388 (2012)
Y.S. Ho, G. Mckay, Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34(5), 451–465 (1999)
H. Hou, R. Zhou, P. Wu, L. Wu, Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution with hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite. Chem. Eng. J. 211–212, 336–342 (2012)
R.S. Hsu, W.H. Chang, J.J. Lin, Nanohybrids of magnetic iron-oxide particles in hydrophobic organoclays for oil recovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2(5), 1349 (2010)
B.I. Langmuir, The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Chem. Phys. 40(12), 1361–1403 (2015)
A.G. Leyva, J. Marrero, P. Smichowski, D. Cicerone, Sorption of antimony onto hydroxyapatite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 35(18), 3669–3675 (2001)
J. Li et al., Magnetic polydopamine decorated with Mg–Al LDH nanoflakes as a novel bio-based adsorbent for simultaneous removal of potentially toxic metals and anionic dyes. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(5), 1737–1746 (2016)
I.D. Mall, V.C. Srivastava, N.K. Agarwal, I.M. Mishra, Removal of congo red from aqueous solution by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon: kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Chemosphere 61(4), 492–501 (2005)
M. Mekhloufi, A. Zehhaf, A. Benyoucef, C. Quijada, E. Morallon, Removal of 8-quinolinecarboxylic acid pesticide from aqueous solution by adsorption on activated montmorillonites. Environ. Monit. Assess. 185(12), 10365–10375 (2013)
T. Ngulube, J.R. Gumbo, V. Masindi, A. Maity, An update on synthetic dyes adsorption onto clay based minerals: a state-of-art review. J. Environ. Manag. 191, 35–57 (2017)
E. Pajootan, M. Arami, N.M. Mahmoodi, Binary system dye removal by electrocoagulation from synthetic and real colored wastewaters. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 43(2), 282–290 (2012)
D. Rui, L. Xiaoheng, Thermogravimetric analysis of bebtonites hardened by sodium silicate. Oilfield Chem. 15(4), 293–296 (1998)
F. Tseng, C. Huang, C. Chieng, H. Huang, C. Liu, Size effect on surface tension and contact angle between protein solution and silicon compound, PC, and PMMA substrates. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 6(1), 31–53 (2002)
L. Wang, J. Li, Y. Wang, L. Zhao, Preparation of nanocrystalline Fe 3-x LaxO4 ferrite and their adsorption capability for Congo red. J. Hazard. Mater. 196, 342–349 (2011)
L. Wang, J. Li, Y. Wang, L. Zhao, Q. Jiang, Adsorption capability for Congo red on nanocrystalline MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) spinel ferrites. Chem. Eng. J. 181–182, 72–79 (2012)
X.S. Wang, J.P. Chen, Biosorption of Congo red from aqueous solution using wheat bran and rice bran: batch studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 44(6), 1452–1466 (2009)
Y. Wei et al., Characterisation and coagulation performance of an inorganic coagulant—poly-magnesium-silicate-chloride in treatment of simulated dyeing wastewater. Colloids Surf. A 470, 137–141 (2015)
X. Xu, S.-l.. Yu, W. Shi, Z.-q.. Jiang, C. Wu, Effect of acid medium on the coagulation efficiency of polysilicate-ferric (PSF)—a new kind of inorganic polymer coagulant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 66(3), 486–491 (2009)
A. Zehhaf et al., Lead ion adsorption from aqueous solutions in modified Algerian montmorillonites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 110(3), 1069–1077 (2011)
A. Zehhaf, A. Benyoucef, C. Quijada, S. Taleb, E. Morallón, Algerian natural montmorillonites for arsenic(III) removal in aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12(2), 595–602 (2013)
Y. Zhang et al., Superior adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2 core-shell microspheres for removal of Congo red from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 219, 88–94 (2016)
X.M. Zheng, W.M. Lu, D.Z. Sun, Enthalpy and entropy criterion for the molecular recognize of some organic compounds with beta cyclodextrin. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 17(4), (2001)
H.Y. Zhu et al., Adsorption removal of Congo red onto magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 173(2), 494–502 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support and technical support provided by Southwest Petroleum University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, D., Zhang, T. & Zhang, F. Superb Capacity of Magnetic Sludge-Floc-Based Adsorbents for Congo Red: Synthesis and Adsorption Studies. J Inorg Organomet Polym 28, 990–1000 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0732-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0732-4