Abstract
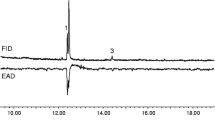
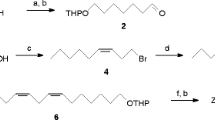
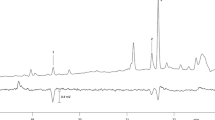
The spherical mealybug Nipaecoccus viridis is a pest of several major crops including soybeans, grapes and citrus varieties. Sessile virgin females of N. viridis release two volatiles, 2,2,3,4–tetramethyl–3–cyclopentene–1–methanol (γ–necrodol) and γ–necrodyl isobutyrate, on a circadian rhythm with peak at 17:00 (11 hr of photophase) as determined by automated, sequential solid phase micro extraction with gas chromatography−mass spectrometry analysis. The females increased the released amounts with age by about seven–fold from 5 to 6 d to 10–12 d of age. trans–3,4,5,5–Tetramethyl–2–cyclopentene–1–methanol (trans–α–necrodol) and trans–α–necrodyl acetate, found in essential oil of Spanish lavender, Lavandula luisieri, were rearranged to γ–necrodol and then used to synthesize γ–necrodyl isobutyrate. GC–MS and NMR data confirmed the identifications. In a petri dish bioassay, N. viridis males were significantly attracted to filter paper discs impregnated with γ–necrodyl isobutyrate but not to γ–necrodol or controls. A mixture of the two compounds was not more attractive than γ–necrodyl isobutyrate alone. Similar results were obtained with trapping flying adults, suggesting that the sex pheromone consists only of γ–necrodyl isobutyrate. This compound has not been reported previously in insects. Conversion of α–necrodol in lavender essential oil simplifies the synthesis of the sex pheromone and should allow its use in management of this cosmopolitan invasive pest.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmann J, Tapia J, Bravo M, Zaviezo T, Flores MF (2019) Synthesis of citrophilus mealybug sex pheromone using chrysanthemol extracted from pyrethrum (Tanacetum cinerariifolium). Nat Prod Res 33:303–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1446136
Eisner T, Meinwald J (1982) Defensive spray mechanism of a silphid beetle (Necrodes surinamensis). Psyche 89:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1155/1982/41643
El–Sayed AM (2019) The Pherobase: database of pheromones and Semiochemicals. http://www.pherobase.com. Accessed 28 February 2019
Figadere BA, McElfresh JS, Borchardt D, Daane KM, Bentley W, Millar JG (2007) trans–α–Necrodyl isobutyrate, the sex pheromone of the grape mealybug, Pseudococcus maritimus. Tetrahedron Lett 48:8434–8437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.09.155
Garcia--Vallejo MI, Garcia--Vallejo MC, Sanz J, Bernabe M, Velasco--Negueruela A (1994) Necrodanes derivatives in Lavandula luisieri, new compounds to the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 36:43–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)97009-2
Gerson U, Applebaum S (2015) Plant pests of the Middle East. http://www.agri.huji.ac.il/mepests/entry/Pseudococcidae. Accessed 28 February 2019
Griffiths K, Derksen A (2010) 2009–2010 CAPS Surveys for Nipaecoccus viridis (Newstead) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) in South Florida. Division of Plant Industry, Florida Dept. Agric. Consumer Serv. Gainsvile, Florida
Jacobs RT, Feutrill GI, Meinwald J (1990) Defense mechanisms of arthropods. 84. Synthesis of (−)–α–necrodol and (−)–β–necrodol: novel cyclopentanoid terpenes from a carrion beetle. J Org Chem 55:4051–4062. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00300a021
Levi--Zada A, Fefer D, Anshelevitch L, Litovsky A, Bengtsson M, Gindin G, Soroker V (2011) Identification of the sex pheromone of the lesser date moth, Batrachedra amydraula, using sequential SPME auto–sampling. Tetrahedron Lett 52:4550–4553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2011.06.091
Levi–Zada A, Fefer D, David M, Eliyahu M, Franco JC, Protasov A, Dunkelblum E, Mendel Z (2014) Diel periodicity of pheromone release by females of Planococcus citri and Planococcus ficus and the temporal flight activity of their conspecific males. Naturwissenschaften 101:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-014-1206-y
Mendel Z, Jasrotia P, Protasov A, Kol–Maimon H, Levi–Zada A, Franco JC (2012) Responses of second–instar male nymphs of four mealybug species (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) to conspecific and heterospecific female sex pheromones. J Insect Behav 25:504–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-012-9317-9
Pamingle H, Snowden RL, Schulte–Elte KH (1991) 52. Stereoselective conversion of campholene to necrodane–type monoterpenes. Novel access to (−)–(R,R)– and (R,S)–α–necrodol and the enantiomeric γ–necrodols. Helv Chim Acta 74:543–548. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19910740310
Sharaf NW, Meyerdirk DE (1987) A review on the biology, ecology and control of Nipaecoccus viridis (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae), vol 66. Miscellaneous Publications of the Entomological Society of America, pp 1–18
Sugie H, Teshiba M, Narai Y, Tsutsumi T, Sawamura N, Tabata J, Hiradate S (2008) Identification of a sex pheromone component of the Japanese mealybug, Planococcus kraunhiae (Kuwana). Appl Entomol Zool 43:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1303/aez.2008.369
Tabata J, Ichiki RT (2017) (1S,3R)–cis–Chrysanthemyl tiglate: sex pheromone of the striped mealybug, Ferrisia virgata. J Chem Ecol 43:745–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-017-0879-z
Tabata J, Teshiba M, Shimizu N, Sugie H (2015) Mealybug mating disruption by a sex pheromone derived from lavender essential oil. J Essent Oil Res 27:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2015.1007219
Unelius CR, El–Sayed AM, Twidle A, Bunn B, Flores MF, Zaviezo T, Bell V, Bergmann J (2011) Absolute configuration of the citrophilous mealybug sex pheromone. J Chem Ecol 37:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-010-9904-1
Zou Y, Daane KM, Bentley WJ, Millar JG (2010) Synthesis and bioassay of racemic and chiral trans–α–necrodyl isobutyrate, the sex pheromone of the grape mealybug Pseudococcus maritimus. J Agric Food Chem 58:4977–4982. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf904452v
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Jun Tabata of NARO (Ibaraki, Japan), Dr. Christian Chapuis of Firmenich (Switzerland) and Dr. Azucena González Coloma, of Instituto de Ciencias Agrarias (ICA) (Madrid, Spain), for generous sharing of their standards with us. Thanks to Dr. Lyuda Groysman, Israeli Ministry of Health, for HR–MS analyses; Dr. Tali Scherf, Weizmann Institute, for NMR analyses and Mrs. Reut Madar, Volcani Center, for technical assistance. Thanks to Dr. Ezra Dunkelblum and Dr. John A. Byers for helpful reviews of the manuscript. This research was funded by Chief Scientist, Israeli Ministry of Agriculture, grant #20–02–0071.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 807 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levi-Zada, A., Steiner, S., Fefer, D. et al. Identification of the Sex Pheromone of the Spherical Mealybug Nipaecoccus viridis. J Chem Ecol 45, 455–463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-019-01075-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-019-01075-3