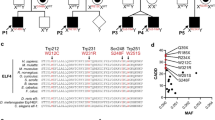
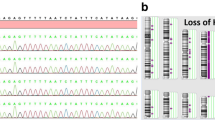
Abstract
Patients with DEX (deficiency in ELF4, X-linked) were recently reported by our team and others, and cases are very limited worldwide. Our knowledge of this new disease is currently preliminary. In this study, we described 5 more cases presenting mainly with oral ulcer, inflammatory bowel disease-like symptoms, fever of unknown origin, anemia, or systemic lupus erythematosus. Whole exome sequencing identified potential pathogenic ELF4 variants in all cases. The pathogenicity of these variants was confirmed by the detection of ELF4 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients and utilizing a simple IFN-b luciferase reporter assay, as previously reported. Our findings significantly contribute to the current understanding of DEX.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- IEIs:
-
Inborn errors of immunity
- ETS:
-
The E-twenty-six domain
- DEX:
-
Deficiency in ELF4, X-linked
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- IVIG:
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy
- NSAIDs:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- PBMCs:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- CADD:
-
Combined annotation dependent depletion
- CMBI:
-
Centre for molecular and biomolecular informatics
- MMP-9:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9
References
Tangye SG, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Cunningham-Rundles C, Franco JL, Holland SM, et al. Human inborn errors of immunity: 2022 update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert committee. J Clin Immunol. 2022;42(7):1473–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-022-01289-3.
Sun G, Qiu L, Yu L, An Y, Ding Y, Zhou L, et al. Loss of function mutation in ELF4 causes autoinflammatory and immunodeficiency disease in human. J Clin Immunol. 2022;42:798–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-022-01243-3.
Tyler PM, Bucklin ML, Zhao M, Maher TJ, Rice AJ, Ji W, et al. Human autoinflammatory disease reveals ELF4 as a transcriptional regulator of inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:1118–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-021-00984-4.
Salinas SA, Mace EM, Conte MI, Park CS, Li Y, Rosario-Sepulveda JI, et al. An ELF4 hypomorphic variant results in NK cell deficiency. JCI Insight. 2022;7(23):e155481. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.155481.
Hollenhorst PC, McIntosh LP, Graves BJ. Genomic and biochemical insights into the specificity of ETS transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:437–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.79.081507.103945.
Lacorazza HD, Miyazaki Y, di Cristofano A, Deblasio A, Hedvat C, Zhang J, et al. The ETS protein MEF plays a critical role in perforin gene expression and the development of natural killer and NK-T cells. Immunity. 2002;17:437–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00422-3.
Choi H-J, Geng Y, Cho H, Li S, Giri PK, Felio K, et al. Differential requirements for the Ets transcription factor Elf-1 in the development of NKT cells and NK cells. Blood. 2011;117:1880–7. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-09-309468.
You F, Wang P, Yang L, Yang G, Zhao YO, Qian F, et al. ELF4 is critical for induction of type i interferon and the host antiviral response. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:1237–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2756.
Yamada T, Park CS, Mamonkin M, Lacorazza HD. Transcription factor ELF4 controls the proliferation and homing of CD8+ T cells via the Krüppel-like factors KLF4 and KLF2. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:618–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1730.
Mamonkin M, Puppi M, Lacorazza HD. Transcription factor ELF4 promotes development and function of memory CD8+ T cells in Listeria monocytogenes infection. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44:715–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201343775.
Lv G, Sun G, Wu P, du X, Zeng T, Wen W, et al. Novel mutations of TYK2 leading to divergent clinical phenotypes. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2022;33(1):e13671. https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.13671.
Rentzsch P, Witten D, Cooper GM, Shendure J, Kircher M. CADD: predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D886–94. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1016.
Stewart DM, Tian L, Notarangelo LD, Nelson DL. X-linked hypogammaglobulinemia and isolated growth hormone deficiency: an update. Immunol Res. 2008;40:262–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-007-0028-9.
Ding Y, Zhou L, Xia Y, Wang W, Wang Y, Li L, et al. Reference values for peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets of healthy children in China. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142:970–973.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.04.022.
Suico MA, Shuto T, Kai H. Roles and regulations of the ETS transcription factor ELF4/MEF. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017;9:168–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjw051.
Szabo A, Rajnavolgyi E. Finding a fairy in the forest: ELF4, a novel and critical element of type I interferon responses. Cell Mol Immunol. 2014;11:218–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.1.
Hedvat CV, Yao JJ, Sokolic RA, Nimer SD. Myeloid ELF1-like factor is a potent activator of interleukin-8 expression in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:6395–400. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M307524200.
Seki Y, Suico MA, Uto A, Hisatsune A, Shuto T, Isohama Y, et al. The ETS transcription factor MEF is a candidate tumor suppressor gene on the X chromosome. Cancer Res. 2002;62(22):6579–86.
Mitchell GB, Albright BN, Caswell JL. Effect of interleukin-8 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on priming and activation of bovine neutrophils. Infect Immun. 2003;71:1643–9. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.71.4.1643-1649.2003.
Gilet A, Zou F, Boumenir M, Frippiat JP, Thornton SN, Lacolley P, et al. Aldosterone up-regulates MMP-9 and MMP-9/NGAL expression in human neutrophils through p38, ERK1/2 and PI3K pathways. Exp Cell Res. 2015;331:152–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.11.004.
Suico MA, Yoshida H, Seki Y, Uchikawa T, Lu Z, Shuto T, et al. Myeloid Elf-1-like factor, an ETS transcription factor, up-regulates lysozyme transcription in epithelial cells through interaction with promyelocytic leukemia protein. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:19091–8. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312439200.
Curina A, Termanini A, Barozzi I, Prosperini E, Simonatto M, Polletti S, et al. High constitutive activity of a broad panel of housekeeping and tissue-specific cis-regulatory elements depends on a subset of ETS proteins. Genes Dev. 2017;31:399–412. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.293134.116.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families for their cooperation. We thank the members of our laboratory for their technical assistance.
Funding
This study is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82101908), Postdoc Fund of Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (cstc2021jcyj-bshX0226), General Basic Research Project from the Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Child Development and Disorders (GBRP-202110), CQMU Program for Youth Innovation in Future Medicine (W0100), Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (SZSM201812002), Livelihood Project of Chongqing, China (cstc2018jscxmsybX0005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HQ.D, XD.Z, YM.X, L.S, ZX.W, and XR.Z conceived and supervised the project, reviewed, and revised the manuscript; G.S performed the experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; ML.W and QY.L followed the patients and collected clinical data. Others provided essential help for clinical management, follow-up of the patient, and valuable clinical expertise in reviewing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The ethics committee of Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Children’s Hospital of Fudan University, Xiangya Hospital Central South University, West China Second University Hospital and Shenzhen Children’s Hospital approved the study. Blood sample collections were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent for participation in the study was obtained from patients’ parents.
Consent for Publication
Written informed consent for publication of the study was obtained from patients’ parents.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, G., Wu, M., Lv, Q. et al. A Multicenter Cohort Study of Immune Dysregulation Disorders Caused by ELF4 Variants in China. J Clin Immunol 43, 933–939 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-023-01453-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-023-01453-3