Abstract
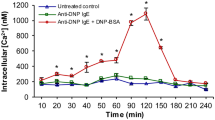
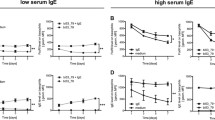
Activation of mast cells through either FcɛRI or FcγRI leads to release of mediators contributing to the inflammatory response. One of the biologic characteristics of mast cells in allergic pathology is that these cells have the capacity to recover and regranulate after aggregation of FcɛRI. We have previously demonstrated that the pro-survival protein A1/Bfl-1 is required for mast cells to survive IgE-mediated activation. In the present study, we have investigated whether human mast cells show similar induction of bfl-1 and activation-induced survival after aggregation of FcγRI. Human cord blood-derived mast cells were activated by aggregation of either FcɛRI or FcγRI, and activation-induced survival and induction of bfl-1 was measured. We found that aggregation of FcγRI-induced expression of bf-1 and caused a comparable activation-induced mast cell survival as FcɛRI does. These data suggests that activation through Fc-receptors contribute to mast cell survival during antibody-dependent mast cell mediated inflammatory responses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams CMM, Galli SJ. The diverse potential effector and immunoregulatory roles of mast cells in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000;105:847–9.
Turner H, Kinet J-P. Signalling through the high-affinity IgE receptor FceRI. Nature 1999;402(Suppl):B24–B30.
Okayama Y, Kirshenbaum AS, Metcalfe DD. Expression of a functional high-affinity IgG receptor, Fc gamma RI, on human mast cells: up-regulation by IFN-gamma. J Immunol 2000;164:4332–9.
Okayama Y, Hagaman DD, Metcalfe DD. A comparison of mediators released or generated by IFN-gamma-treated human mast cells following aggregation of Fc gamma RI or Fc epsilon RI. J Immunol 2001;166:4705–12.
Kawakami T, Galli SJ. Regulation of mast-cell and basophil function and survival by IgE. Nature Rev Immunol 2002;2:773–6.
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA, Piliponsky AM, Williams CM, Tsai M. Mast cells as “tunable” effector and immunoregulatory cells: Recent advances. Annu Rev Immunol 2005;23:749–86.
Xiang Z, Ahmed AA, Möller C, Nakayama K-I, Hatakeyama S, Nilsson G. Essential role of the pro-survival bc-2 homolog A1 in mast cell survival following allergic activation. J Exp Med 2001;194:1561–9.
Yoshikawa H, Nakajima Y, Tasaka K. Glucocorticoid suppresses autocrine survival of mast cells by inhibiting IL-4 production and ICAM-1 expression. J Immunol 1999;162:6162–70.
Kitaura J, Xiao W, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Kawakami Y, Lowell CA, Kawakami T. Early divergence of Fc epsilon receptor I signals for receptor up-regulation and internalization from degranulation, cytokine production, and survival. J Immunol 2004;173:4317–23.
Kobayasi T, Asboe-Hansen G. Degranulation and regranulation of human mast cells. Acta Derm Venerol 1969;49:369–81.
Burwen SJ. Recycling of mast cells following degranulation in vitro: an ultrastructural studiy. Tissue Cell 1982;14:125–34.
Dvorak AM, Schleimer RP, Lichtenstein LM. Morphologic mast cell cycles. Cell Immunol 1987;105:199–204.
Xiang Z, Block M, Löfman C, Nilsson G. IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation and recovery monitored by time-lapse photography. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;108:116–21.
Xiang Z, Möller C, Nilsson G. IgE-receptor activation induces survival and bfl-1 expression in human mast cells but not basophils. Allergy 2006;61:1040–6.
Fischer M, Harvima IT, Carvalho RFS, Möller C, Naukkarinen A, Enblad G, et al. Mast cell CD30 ligand is up-regulated in cutaneous inflammation and mediates degranulation-independent chemokine secretion. J Clin Invest 2006;116:2748–56.
Dastych J, Hardison MC, Metcalfe DD. Aggregation of low affinity IgG receptors induces mast cell adherence to fibronectin. Requirement for the common FcR g-chain. J Immunol 1997;158:1803–9.
Iemura A, Tsai M, Ando A, Wershil BK, Galli SJ. The c-kit ligand, stem cell factor, promotes mast cell survival by suppressing apoptosis. Am J Pathol 1994;144:321–8.
Finotto S, Mekori YA, Metcalfe DD. Glucocorticoids decrease tissue mast cell number by reducing the production of the c-kit ligand, stem cell factor, by resident cells—In vitro and in vivo evidence in murine systems. J Clin Invest 1997;99:1721–8.
Benhamou M, Bonnerot C, Fridman WH, Daeron M. Molecular heterogeneity of murine mast cell Fcg receptors. J Immunol 1990;144:3071–7.
Barker JN. The pathophysiology of psoriasis. Lancet 1991;338:227–30.
Tkaczyk C, Okayama Y, Wollhiser MR, Hagaman DD, Gilfillan AM, Metcalfe DD. Activation of human mast cells through the high affinity IgG receptor. Mol Immunol 2001;38:1289–93.
Grumont RJ, Rourke IJ, Gerondakis S. Rel-dependent induction of A1 transcription is required to protect B cells from antigen receptor ligation-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999;13:400–11.
Tomayko MM, Punt JA, Bolcavage JM, Levy SL, Allman DM, Cancro MP. Expression of the Bcl-2 family member A1 is developmentally regulated in T cells. Int Immunol 1999;11:1753–61.
Karsan A, Yee E, Kaushansky K, Harlan JM. Cloning of a human Bcl-2 homologue: inflammatory cytokines induce human A1 in cultured endothelial cells. Blood 1996;87:3089–96.
Lin EY, Orlofsky A, Wang HG, Reed JC, Prystowsky MB. A1, a Bcl-2 family member, prolongs cell survival and permits myeloid differentiation. Blood 1996;87:983–92.
Möller C, Karlberg M, Åbrink M, Nakayama KI, Motoyama N, Nilsson G. Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL are indispensible for the late phase of mast cell development from mouse embryonic stem cells. Exp Hematol 2007;35:385–93.
Moller C, Xiang Z, Nilsson G. Activation of mast cells by immunoglobulin E-receptor cross-linkage, but not through adenosine receptors, induces A1 expression and promotes survival. Clin Exp Allergy 2003;33:1135–40.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Mrs Agnetha Beinhoff for the mast cell cultures. This work was supported by the Swedish Research Council-Medicine, the Swedish Cancer Society, The Swedish Allergy and Cancer Foundation, the King Gustaf V:s 80-years Foundation, the Ollie and Elof Ericsson Foundation, Ellen, Walter, and Lennart Hesselmans foundation for scientific research, Consul Th C Berghs foundation, Karolinska Institutet, and Innoventus Project AB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlberg, M., Xiang, Z. & Nilsson, G. FcγRI-Mediated Activation of Human Mast Cells Promotes Survival and Induction of the Pro-survival Gene Bfl-1. J Clin Immunol 28, 250–255 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9153-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9153-4