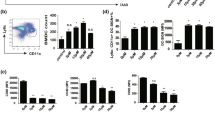
Pertussis toxin (PTX) is an exotoxin produced by Bordetella pertussis. It is known to exert adjuvant activities inducing Th1-launched immune responses. In this study, we show that PTX can selectively block the expression of CD1a isoform during the differentiation of human monocytes into dendritic cells. In fact, dendritic cells differentiated from monocytes in the presence of PTX do not express CD1a on their surface, unlike CD1b and CD1c isoforms, which are normally regulated. The impaired CD1a expression on cell membrane depends, at least partially, on decreased mRNA transcription and does not affect cellular capability to respond to other maturation stimuli. Since CD1a+ dendritic cells are involved in the early steps of primary immune response, the interference of PTX in the CD1a expression may be relevant for its employment as adjuvant.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tuomanen E, Weiss A: Characterization of two adhesins of Bordetella pertussis for human ciliated respiratory-epithelial cells. J Infect Dis 152(1):118–125, 1985
Van't Wout J, Burnette WN, Mar VL, Rozdzinski E, Wright SD, Tuomanen EI: Role of carbohydrate recognition domains of pertussis toxin in adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human macrophages. Infect Immun 60:3303–3308, 1992
Shive CL, Hofstetter H, Arredondo L, Shaw C, Forsthuber TG: The enhanced antigen-specific production of cytokines induced by pertussis toxin is due to clonal expansion of T cells and not to altered effector functions of long-term memory cells. Eur J Immunol 30:2422–2431, 2000
Hou W, Wu Y, Sun S, Shi M, Sun Y, Yang C, Pei G, Gu Y, Zhong C, Sun B: Pertussis toxin enhances Th1 responses by stimulation of dendritic cells. J Immunol 170:1728–1736, 2003.
He J, Gurunatham S, Iwasaki A, Ash-Shaheed B, Kelsall B: Primary role for G proteins signalling in the regulation of interleukin 12 production and the induction of T helper cell type 1 responses. J Exp Med 191:1605–1610, 2000
Robbinson D, Cockle S, Singh B, Strejan GH: Native but not genetically inactivated, pertussis toxin protects mice against experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Cell Immunol 168:165–173, 1996
Sewell WS, Munoz JJ, Vadas MA: Enhancement of the intensity, persistence and passive transfer of delayed type hypersensitivity lesions by pertussigen in mice. J Exp Med 157:2087–2096, 1983
Shumilla JA, Lacaille V, Hornell TMC, Huang J, Narasimhan S, Relman DA, Mellins ED: Bordetella pertussis infection of primary human monocytes alters HLA-DR expression. Infect Immun 72:1450–1462, 2004
Banchereau J, Steinman R: Dendritic cells and the control of the immunity. Nature 392:245–252, 1998
Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F: Regulation of T cell immunity by dendritic cells. Cell 106:263–266, 2001
Brigl M, Brenner MB: CD1: Antigen presentation and T cell function. Annu Rev Immunol 22:817–890, 2004
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N: Single-step method of RNA isolation by Guanidium thiocyanate phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159, 1987
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408, 2001
Wakatsuki A, Borrow P, Rigley K, Beverley PC: Cell-surface bound pertussis toxin induces polyclonal T cell responses with high levels of interferon-gamma in the absence of interleukin-12. Eur J Immunol 33:1859–1867, 2003
Sander B, Skannsen-Saphir U, Damm O, Hakansson L, Anderson J, Andersson U: Sequential production of Th1 and Th2 cytokines in response to live bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Immunology 86:512–518, 1995
Delneste Y, Charbonnier P, Herbault N, Magistrelli G, Caron G, Bonnefoy JY, Jeannine P: Interferon-gamma switches monocyte differentiation from dendritic cells to macrophages. Blood 101:143–150, 2003
Porcelli SA: The CD1 family: A third lineage of antigen presenting molecules. Adv Immunol 59:1–98, 1995
Porcelli SA, Modlin RL: The CD1 system: antigen presenting molecules for T cell recognition of lipids and glycolipids. Annu Rev Immunol 17:297–329, 1999
Schaible UE, Kaufmann SH: CD1 and CD1-restricted T cells in infections with intracellular bacteria. Trends Microbiol 8:419–425, 2000.
Sieling PA, Ochos MT, Jullieu D, Leslie DS, Sabet S, Rasat JP, Burdick AE, Rea TH, Brenner MB, Porcelli SA, Modlin RL: Evidence for human CD4 T cells in CD1-restricted repertoire: Derivation of mycobacteria-reactive T cells from leprosy lesions. J Immunol 164:4790–4796, 2000
Coventry B, Heinzel S: CD1a in human cancers: A new role for an old molecule. Trends Immunol 25:242–248, 2004
Sallusto P, Lanzavecchia A: Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and down regulated by tumor necrosis factor-α. J Exp Med 179:1109–1118, 1994
Zhou LJ, Tedder TF: CD14+ blood monocytes can differentiate into functionally mature CD83+ dendritic cells. PNAS 93:2588–2592, 1996
Lyakh LA, Koski GK, Telford W, Gress RE, Cohen PA, Rice NR: Bacterial lipopolysaccharide, TNF-α and calcium ionophore under serum-free conditions promote rapid dendritic cell-like differentiation in CD14+ monocytes through distinct pathways that activate NK-kB. J Immunol 165:3647–3655, 2000
Navarro Péguet J, Sportouch M, Popa I, Berthier O, Schmitt D, Portoukalian J: Gangliosides from human melanoma tumors impair dendritic cell differentiation from monocytes and induce their apoptosis. J Immunol 170:3488–3494, 2003
Chang CC, Wright A, Punnonen J: Monocyte-derived CD1a+ and CD1a− Dendritic cell subsets differ in their cytokine production profiles, susceptibility to transfection, and capacities to direct Th cell differentiation. J Immunol 165:3584–3591, 2000
Martino A, Sacchi A, Sanarico N, Spadaro F, Ramoni C, Ciaramella A, Pucillo LP, Colizzi V, Vendetti S: Dendritic cells derived from BCG-infected precursors induce Th2-like immune response. J Leukoc Biol 76:827–834, 2004
Cappello F, Rappa F, Anzalone R, La Rocca G, Zummo G: CD1a expression by Barrett's metaplasia of gastric type may help to predict its evolution towards cancer. Br J Cancer 92:888–890, 2005
La Rocca G, Anzalone R, Bucchieri F, Farina F, Cappello F, Zummo G: CD1a and antitumour immune response. Immunol Lett 95:1–4, 2004
Silk JD, Hermans IF, Gileadi U, Chong TW, Shepherd D, Salio M, Mathew B, Schmidt RR, Lunt SJ, Williams KJ, Stratford U, Harris AL, Cerandolo V: Utilizing the adjuvant properties of CD1d-dependent NK T cells in T cell-mediated immunotherapy. J Clin Invest 114:1800–1811, 2004
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. Fabrizio Poccia for the help in the realization of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Equally contributing authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martino, A., Volpe, E., Auricchio, G. et al. Influence of Pertussis toxin on CD1a Isoform Expression in Human Dendritic Cells. J Clin Immunol 26, 153–159 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9009-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9009-3