Abstract
Both microscale and finescale measurements were conducted along 20°N and 21°N in the northern South China Sea (SCS) during July 2007. Spatial variability of turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) dissipation rate was examined, and two finescale parameterizations were assessed and compared. TKE dissipation rates along the 21°N section were found to be much higher than those along 20°N; in particular, remarkably high TKE dissipation rates existed near the Luzon Strait and around the Dongsha Plateau, which were likely caused by internal tides and internal solitary waves, respectively. The Gregg–Henyey scaling does not work well in the northern SCS, while the MacKinnon–Gregg scaling with a modified parameter matches the observations in both magnitude and variability. One explanation is that the large-scale/low-mode shear mainly comes from low-frequency internal waves such as internal tides, which are not described well by the Garrett–Munk spectrum.










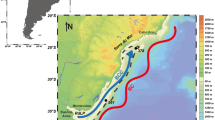
The data of temperature, salinity and velocity used in this figure were published in Yang et al. (2014)


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford MH, MacKinnon JA, Nash JD, Simmons H, Pickering A, Klymak JM, Pinkel R, Sun O, Rainville L, Musgrave R (2011) Energy flux and dissipation in Luzon Strait: two tales of two ridges. J Phys Oceanogr 41:2211–2222
Batchelor GK (1959) Small scale variation of convected quantities like temperature in a fluid. J Fluid Mech 5:113–133
Buijsman MC, Legg S, Klymak J (2012) Double-ridge internal tide interference and its effect on dissipation in Luzon Strait. J Phys Oceanogr 42:1337–1356
Carter GS, Gregg MC, Lien RC (2005) Internal waves, solitary-like waves, and mixing on the monterey bay shelf. Cont Shelf Res 25(12):1499–1520
Chaigneau A, Pizarro O, Rojas W (2008) Global climatology of near-inertial current characteristics from Lagrangian observations. Geophys Res Lett 35:L13603
Chang MH, Lien RC, Tang TY, D’Asaro EA, Yang YJ (2006) Energy flux of nonlinear internal waves in northern South China Sea. Geophys Res Lett 33:L03607. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025196
Garrett CJR, Munk WH (1972) Space-time scales of internal waves. Geophys Astrophys Fluid Dyn 2:225–264
Garrett CJR, Munk WH (1975) Space-time scales of internal waves: a progress report. J Geophys Res 80:291–297
Gill AE (1982) Atmosphere–ocean dynamics. Academic Press, San Diego, London
Gregg MC (1989) Scaling turbulent dissipation in the thermocline. J Geophys Res 94:9686–9698
Gregg MC (1999) Uncertainties and limitations in measuring ε and χT. J Atmos Ocean Technol 16:1483–1490
Gregg MC, Sanford TB, Winkel DP (2003) Reduced mixing from the breaking of internal waves in equatorial waters. Nature 422:513–515
Guan S, Zhao W, Huthnance J, Tian J, Wang J (2014) Observed upper ocean response to typhoon Megi (2010) in the Northern South China Sea. J Geophys Res Oceans 119:3134–3157. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JC009661
Jan S, Chern CS, Wang J, Chao SY (2007) Generation of diurnal K1 internal tide in the Luzon Strait and its influence on surface tide in the South China Sea. J Geophys Res 112:C06019
Klymak JM, Alford MH, Pinkel R, Lien RC, Yang YJ, Tang TY (2011) The breaking and scattering of the internal tide on a continental slope. J Phys Oceanogr 41:926–945
Kunze E, Firing E, Hummon JM, Chereskin TK, Thurnherr AM (2006) Global abyssal mixing from lowered ADCP shear and CTD strain profiles. J Phys Oceanogr 36:1553–1576
Large WG, McWilliams JC, Doney SC (1994) Oceanic vertical mixing: a review and a model with a nonlocal boundary layer parameterization. Rev Geophys 32:363–403
Liang CR, Chen GY, Shang XD (2017) Observations of the turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate in the upper central South China Sea. Ocean Dyn 67(5):597–609
Lien RC, Tang TY, Chang MH, D’Asaro EA (2005) Energy of nonlinear internal waves in the South China Sea. Geophys Res Lett 32:L05615
Liu Z, Lozovatsky I (2012) Upper pycnocline turbulence in the northern South China Sea. Chin Sci Bull 57:2302–2306
Lozovatsky I, Fernando HJS, Planella-Morato J, Liu Z, Lee JH, Jinadasa SUP (2017) Probability distribution of turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate in ocean: observations and approximations. J Geophys Res Oceans 122(10):8293–8308
Lu ZM, Chen GY, Xie XH, Xu XX, Shang XD (2009) Research on microstructural characteristics of Marine mixing in the northern south China sea. Prog Nat Sci 19(6):657–663 [in Chinese]
Lu YZ, Zhou SQ, Cen XR, Guo SX, Shang XD (2014) Salt finger and turbulent mixing in the upper layer of the central southern south china sea. Oceanol Limnol Sin 45(6):1158–1167 [in Chinese with English abstract]
MacKinnon J, Gregg M (2003) Shear and baroclinic energy flux on the summer New England shelf. J Phys Oceanogr 33:1462–1475
Mackinnon J, Gregg M (2005) Spring mixing: turbulence and internal waves during restratification on the New England shelf. J Phys Oceanogr 35:2425–2443
Mellor GL, Yamada T (1982) Developement of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev Geophys Space Phys 20:851–875
Nasmyth PW (1970) Ocean turbulence. PhD thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver
Niwa Y, Hibiya T (2004) Three-dimensional numerical simulation of M2 internal tides in the East China Sea. J Geophys Res 109:C04027
Oakey NS (1982) Determination of the rate of dissipation of turbulent energy from simultaneous temperature and velocity shear microstructure measurements. J Phys Oceanogr 12:256–271
Osborn TR (1980) Estimates of the local rate of vertical diffusion from dissipation measurements. J Phys Oceanogr 10:83–89
Osborn TR, Cox CS (1972) Oceanic fine structure. Geophys. Fluid Dyn 3:321–345
Qu T, Girton JB, Whitehead JA (2006) Deepwater overflow through Luzon Strait. J Geophys Res 111:C01002. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JC003139
Ruddick B (1983) A practical indicator of the stability of the water column to double-diffusive activity. Deep Sea Res 30(10):1105–1107
Schmitt RW, Ledwell JR, Montgomery ET, Polzin KL, Toole JM (2005) Enhanced diapycnal mixing by salt fingers in the thermocline of the tropical Atlantic. Science 308(5722):685–688
Shang XD, Liang CR, Chen GY (2017) Spatial distribution of turbulent mixing in the upper ocean of the south china sea. Ocean Sci Discuss 13(3):1–19
St. Laurent L (2008) Turbulent dissipation on the margins of the South China Sea. Geophys Res Lett 35:L23615
St. Laurent L, Simmons H, Tang TY, Wang YH (2011) Turbulent properties of internal waves in the South China Sea. Oceanography 24(4):78–87
Sun H, Wang Q (2016) Microstructure observations in the upper layer of the South China Sea. J Oceanogr 72(5):777–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-016-0371-3
Sun H, Yang Q, Zhao W, Liang X, Tian J (2016) Temporal variability of diapycnal mixing in the northern South China Sea. J Geophys Res Oceans 121:8840–8848. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JC012044
Tian J, Yang Q, Zhao W (2009) Enhanced diapycnal mixing in the South China Sea. J Phys Oceanogr 39:3191–3203. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JPO3899.1
Wang X, Peng S, Liu Z, Huang R, Qian Y, Li Y (2016) Tidal mixing in the south china sea: an internal-tide-energetics-based estimate. J Phys Oceanogr 46(1):107–124
Wang X, Liu Z, Peng S (2017) Impact of tidal mixing on water mass transformation and circulation in the South China Sea. J Phys Oceanogr 47(2):419–432
Wolk F, Yamazaki H, Seuront L, Lueck RG (2002) A new free-fall profiler for measuring biophysical microstructure. J Atmos Ocean Technol 19(5):780–793
Xie XH, Shang XD, van Haren H et al (2011) Observations of parametric subharmonic instability-induced near-inertial waves equatorward of the critical diurnal latitude. Geophys Res Lett 38:L05603
Xu J, Xie J, Chen Z, Cai S, Long X (2012) Enhanced mixing induced by internal solitary waves in the South China Sea. Cont Shelf Res 49:34–43
Yang Q, Tian J, Zhao W, Liang X, Zhou L (2014) Observations of turbulence on the shelf and slope of northern South China Sea. Deep Sea Res I 87:43–52
Yang Q, Zhao W, Liang X, Tian J (2016) Three-dimensional distribution of turbulent mixing in the south china sea. J Phys Oceanogr 46:769–788
Zhao Z, Klemas V, Zheng Q, Yan XH (2004) Remote sensing evidence for baroclinic tide origin of internal solitary waves in the northeastern South China Sea. Geophys Res Lett 31:L06302
Zhou C, Zhao W, Tian J, Yang Q, Qu T (2014) Variability of the deep water overflow in the Luzon Strait. J Phys Oceanogr 44:2972–2986
Acknowledgements
This work is jointly supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (Grant 2016YFC1401403), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 41576009), the State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Science (Project LTO1601), and the Global Change and Air–Sea Interaction Project (Grants GASI-IPOVAI-01-03 and GASI-IPOVAI-01-02). We thank the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for providing the ETOPO1 data (http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/global/global.html).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Yang, Q. & Tian, J. Microstructure measurements and finescale parameterization assessment of turbulent mixing in the northern South China Sea. J Oceanogr 74, 485–498 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-018-0474-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-018-0474-0