Abstract
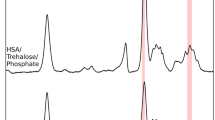
The aim of this study was the investigation of static magnetic field effects on haemoglobin secondary structure and the bioprotective effectiveness of two disaccharides, sucrose and trehalose. Samples of haemoglobin aqueous solutions, in the absence and in the presence of sucrose and trehalose, were exposed to a uniform magnetic field at 200 mT, which is the exposure limit established by the ICNIRP recommendation for occupational exposure. Spectral analysis by FTIR spectroscopy after 3 and 7 h of exposure revealed a decrease in the amide A vibration band for haemoglobin in bi-distilled water solution. Analogue exposures did not produce any appreciable change of amide A for haemoglobin in sucrose and trehalose solutions. Otherwise, no relative increase of \(\upbeta \)-sheet contents in amide I and II regions was detected for haemoglobin aqueous solutions, leading us to exclude the hypothesis that static magnetic fields can induce the formation of aggregates in the protein. In addition, a decrease in CH3 stretching linkages occurred for haemoglobin in bi-distilled water solution after exposure, which was not observed for haemoglobin in sucrose and trehalose aqueous solutions, providing further evidence of a bioprotective compensatory mechanism of such disaccharides.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belton, P.S., Gil, A.M.: IR and Raman spectroscopic studies of the interaction of trehalose with hen egg white lysozyme. Biopolymers 34, 957–961 (1994)
Crowe, L.M., Reid, D.S., Crowe, J.H.: Is trehalose special for preserving dry biomaterials? Biophys. J. 71, 2087–2093 (1996)
Green, J.L., Angell, C.A.: Phase relation and vitrification in saccharide-water solutions and the trehalose anomaly. J. Phys. Chem. 93, 2880–2882 (1989)
Timasheff, S.N.: Protein hydration, thermodynamic binding, and preferential hydration. Biochemistry 41, 13473–13482 (2002)
Hédoux, A., Ionov, R., Willart, J.F., Lerbret, A., Affouard, F., Guinet, Y., Descamps, M., Prevost, D., Paccou, L., Danéde, F.: Evidence of a two-stage thermal denaturation process in lysozyme: a Raman scattering and differential scanning calorimetry investigation. J. Chem. Phys. 124, 14703 (2006)
Hédoux, A., Willart, J.F., Ionov, R., Affouard, F., Guinet, Y., Paccou, L., Lerbret, A., Descamps, M.: Analysis of sugar bioprotective mechanisms on the thermal denaturation of lysozyme from Raman scattering and differential scanning calorimetry investigations. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 22886–228893 (2006)
Hédoux, A., Affouard, F., Descamps, M., Guinet, Y., Paccou, L.: Microscopic description of protein thermostabilization mechanisms with disaccharides from Raman spectroscopy investigations. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 19, 205142 (2007)
Hédoux, A., Willart, J.F., Paccou, L., Guinet, Y., Affouard, F., Lerbret, A., Descamps, M.: Thermostabilization mechanism of bovine serum albumin by trehalose. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 6119–6126 (2009)
Strickley, R.G., Anderson, B.D.: Solid-state stability of human insulin. II. Effect of water on reactive intermediate partitioning in lyophiles from pH 2-5 solutions: stabilization against covalent dimer formation. J. Pharm. Sci. 86, 645–653 (1997)
Kaushik, J.K., Bhat, R.: J. Biol. Chem. 278, 26458 (2003)
Magazù, S., Migliardo, F., Vadalà, M., Mondelli, C.: Correlation between bioprotective effectiveness and dynamic properties of trehalose–water, maltose–water and sucrose–water mixtures. Carbohydr. Res. 340(18), 2796–2801 (2005)
Crowe, J.H., Carpenter, J.F., Crowe, L.M.: The role of vitrification in anhydrobiosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 60, 73–103 (1998)
Donnamaria, M.C., Howard, E.I., Grigera, J.R.: Interaction of water with α,α-trehalose in solution: molecular dynamics simulation approach. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 90, 2731–2735 (1994)
Magazù, S., Migliardo, F., Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.: Inelastic neutron scattering study on bioprotectant systems. J. R. Soc. Interf. 2(5), 527–532 (2005)
Magazù, S., Maisano, G., Migliardo, P., Villari, V.: Experimental simulation of macromolecules in trehalose aqueous solutions: a photon correlation spectroscopy study. J. Chem. Phys. 111(19), 9086–9092 (1999)
Affouard, F., Bordat, P., Descamps, M., Lerbret, A., Magazù, S., Migliardo, F., Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J., Telling, M.F.T.: A combined neutron scattering and simulation study on bioprotectant systems. Chem. Phys. 317(2–3), 258–266 (2005)
Magazù, S., Migliardo, F., Telling, M.T.F.: α,α-trehalose–water solutions. VIII. Study of the diffusive dynamics of water by high-resolution quasi elastic neutron scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(2), 1020–1025 (2006)
Chadwick, P., Lowes, F.: Magnetic fields on British trains. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 42(5), 331–335 (1998)
Dietrich, F.M., Jacobs, W.L.: Survey and assessment of electric and magnetic field public exposure in the transportation environment. US Department of Transportation, Federal Railroad Administration 1999 (Report No PB99-130908)
Muc, A.M.: Electromagnetic Fields Associated with Transportation Systems. Health Canada, Toronto (2001)
NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health—National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, US Department of Energy): Questions and Answers—EMF in the Work-Place. Electric and Magnetic Fields Associated with the Use of Electric Power. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, Washinton, DC (1996)
WHO (World Health Organization): Framework for Developing Health-Based EMF Standards. World Health Organization, Geneva (2006)
International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP): Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 74, 494–522 (1998)
Jung, C.: Insight into protein structure and protein-ligand recognition by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Mol. Recognit. 13, 325–351 (2000)
Byler, D.M., Susi, H.: Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymer 25, 469-487 (1986)
Surewicz, W.K., Mantsch, H.H.: New insight into protein secondary structure from resolution-enhanced infrared spectra. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 952, 115-130 (1988)
Dong, A., Caughey, W.S.: Infrared methods for study of hemoglobin reaction and structures. Methods Enzymol. 232, 139-175 (1994)
Zamfirescu, M., Rusu, I., Sajin, G., Sajin, M., Kovacs, E.: Efecte biologice ale radiaţiilor electromagnetice de radiofrecvenţă şi microunde, Editura Medicală, Bucureşti (2000)
Tsui, S.L., Lee, A.K., Lui, S.K., Poon, R.T., Fan, S.T.: Acute intraoperative hemolysis and hemoglobinuria during radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 50, 526–529 (2003)
Kim, Y.A., Elemesov, R.E., Akoev, V.R., Abdrasilov, B.S.: Study of erythrocyte hemolysis on exposure to strong 2.45 GHz electromagnetic radiation. Biophysics 50(1), S44–S50 (2005)
Smith, B.M., Franzen, S.: Single-pass attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the analysis of proteins in H2O solution. Anal. Chem. 74, 4076–4080 (2002)
Susi, H., Byler, D.M.: Resolution-enhanced Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 130, 290-311 (1986)
Yang, W.-J., Griffiths, P.R., Byler, D.M., Susi, H.: Protein conformation by infrared spectroscopy: resolution enhancement by Fourier self deconvolution. Appl. Spectrosc. 39(2), 282–287 (1985)
Krimm, S., Bandekar, J.: Vibrational spectroscopy and conformation of peptides, polypeptides, and proteins. Adv. Protein Chem. 38, 181-364 (1986)
Kato, K., Matsui, T., Tanaka, S.: Quantitative estimation of alpha-helix coil content in bovine serum albumin by Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 41(5), 861–865 (1987)
Sarver, R.W., Krueger, W.C.: Protein secondary structure from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: a data base analysis. Anal. Biochem. 194, 89-100 (1991)
Ismail, A.A., Mantch, H.H., Wong, P.T.T.: Aggregation of chymotrypsinogen: portrait by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1121, 183–188 (1992)
Lefevre, T., Subirade, M.: Molecular differences in the formation and structure of fine-stranded and particulate \(\upbeta \)-lactglobulin gels. Biopolymers 54, 578–586 (2000)
Magazù, S., Calabrò, E., Campo, S.: FTIR spectroscopy studies on the bioprotective effectiveness of trehalose on human haemoglobin aqueous solutions under 50 Hz electromagnetic field exposure. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 12144–12149 (2010)
West, W. (ed.): Chemical Applications of Spectroscopy. Interscience Publishers, Inc., New York (1956)
McQuade, D.T., McKay, S.L., Powell, D.R., Gellman, S.H.J.: Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 8528 (1997)
Lee, S.H., Mirkin, N.G., Krimm, S.: Biopolymers 49, 195 (1999)
Chen, J., Park, J., Hochstrasser, R.M.: J. Phys. Chem. A 107, 10660 (2003)
Park, J., Hochstrasser, R.M.: Chem. Phys. 323, 78 (2006)
Miyazawa, T.: The characteristic band of secondary amides at 3100 cm_1. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 4, 168–172 (1960)
Krimm, S., Dwivedi, A.M.: Vibrational analysis of peptides, polypeptides and proteins. XII-Fermi resonance analysis of the unperturbed ND stretching fundamental in polypeptides. J. Raman Spectrosc. 12, 133–137 (1982)
Stuart, B.: Biological Applications of Infrared Spectroscopy. Analytical Chemistry of Open Learning. Wiley, Chichester 115 (1997)
Dumas, P., Miller, L.: The use of synchrotron infrared microspectroscopy in biological and biomedical investigations. Vib. Spec. 32, 3–21 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magazù, S., Calabrò, E., Campo, S. et al. New insights into bioprotective effectiveness of disaccharides: an FTIR study of human haemoglobin aqueous solutions exposed to static magnetic fields. J Biol Phys 38, 61–74 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-010-9209-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-010-9209-1