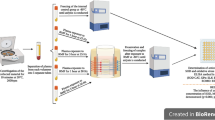
Abstract—Red blood cells of rats were exposed to the earth’s magnetic field and an attenuated magnetic field in the presence of tert-butyl hydroperoxide to induce oxidative stress. Spectral analysis within the wavelength range of 500–700 nm was used to estimate the concentration of three forms of hemoglobin: oxyhemoglobin, methemoglobin, and hemichrome, released during erythrocyte hemolysis. The concentration of reactive oxygen species was determined in samples by spin trapping using electron paramagnetic resonance. It was found that after 4 h of incubation at high tert-butyl hydroperoxide concentrations (>700 μM), red blood cells that were exposed to an attenuated magnetic field released considerably more (p < 0.05) hemoglobin, mostly methemoglobin. After 24 h of incubation at low tert-butyl hydroperoxide concentrations (≤350 μM), erythrocytes that were exposed to the earth’s magnetic field released relatively more (p < 0.001) hemoglobin, with methemoglobin as a major form of total hemoglobin. Red blood cells exposed to the attenuated magnetic field generated more oxygen radicals than cells exposed to the earth’s magnetic field. Under certain oxidative stress conditions, the attenuated magnetic field can impair the functional state of red blood cells and provoke cell death. However, low concentrations of reactive oxygen species can neutralize attenuated magnetic field effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. C. Finlay, S. Maus, C. D. Beggan, et al., Geophys. J. Int. 183 (3), 1216 (2010).
F. Steinhilber, J. A. Abreu, J. Beer, et al., J. Geophys. Res. 115, 1 (2010).
M. S. Berguig, M. Hamoudi, and J. L. Lemoueel, Arab. J. Geosci. 6 (4), 1063 (2011).
T. R. Watters, P. J. McGovern, and R. P. Irwin III. Annu. Rev. Earth Planetary Sci. 35, 621 (2007).
J. Ouyang and H. Li, J. Life Sci. Res. 4 (2), 14 (2017).
A. P. Dubrov, The Geomagnetic Field and Life: Geomagnetobiology (Plenum, New York, 1978).
N. A. Belyavskaya, Adv. Space Res. 34, 1566 (2004).
B. Jia and P. Shang, Space Med. Med. Eng. 22, 308 (2009).
S. V. Surma, G. B. Belostotskaya, B. F. Shchegolev, et al., Bioelectromagnetics 35 (8), 537 (2014).
C. F. Martino, H. Perea, U. Hopfner, et al., Bioelectromagnetics 31, 296 (2010).
I. Y. Belyaev, Y. D. Alipov, and M. Harms-Ringdahl, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1336, 465 (1997).
I. S. Eldashev, B. F. Shchegolev, S. V. Surma, and G. B. Belostotskaya, Biophysics (Moscow) 55 (3), 765 (2010).
I. M. Spivak, M. L. Kuranova, G. R. Mavropulo-Stolyarenko, et al., Biophysics (Moscow) 61 (3), 435 (2016).
A. L. Buchachenko and R. G. Lawler, Accounts Chem. Res. 50 (4), 877 (2017).
C. F. Martino and P. R. Castello, PLoS One 6 (8), e22753 (2011).
C. F. Martino, L. Portelli, K. Mccabe, et al., Bioelectromagnetics 31, 649 (2010).
V. V. Novikov, E. V. Yablokova, and E. E. Fesenko, Biophysics (Moscow) 63 (3), 365 (2018).
T. Ritz, R. Wiltschko, P. J. Hore, et al., Biophys. J. 96, 3451 (2009).
I. A. Solov’yov and K. Schulten, Biophys. J. 96, 4804 (2009).
T. Ritz, S. Adem, and K. Schulten. Biophys. J. 78, 707 (2000).
R. J. Usselman, C. Chavarriaga, P. R. Castello, et al., Sci. Reports 6, 1 (2016).
P. H. Misra and I. Fridovich, J. Biol. Chem. 10, 6960 (1972).
C. Giulivi and E. Cadenas, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 24, 269 (1998).
E. Lang and F. Lang, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 39, 35 (2015).
I. I. Stepuro, N. A. Chaikovskauya, V. P. Vodoevich, et al., Biochemistry 62 (9), 967 (1997).
O. L. Lebedev and S. N. Kazarnowskii, Zh. Obshch. Khim. 30 (5), 1631 (1960).
T. Ide, H. Tsutsui, S. Kinugawa, et al., Circ. Res. 86 (2), 152 (2000).
H. Utsumi, E. Muto, S. Masuda, and A. Hamada, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 172, 1342 (1990).
S. V. Surma, P. A. Kuznetsov, R. S. Khrustaleva, et al., RF Patent No. 2 454 675 (June 27, 2012).
Y. Benjamini, A. M. Krieger, and D. Yekutieli. Biometrika 93, 491 (2006).
A. D. Nadeev, V. P. Zinchenko, P. V. Avdonin, et al., Toksikol. Vestn. 2, 22 (2014).
A. D. Nadeev, I. V. Kudryavtsev, M. K. Serebryakova, et al., Tsitologiya 57 (12), 909 (2015).
N. V. Goncharov, P. V. Avdonin, A. D. Nadeev, et al., Curr. Pharm. Des. 21 (9), 1134 (2015).
I. Mindukshev, I. Kudryavtsev, M. Serebriakova, et al., in Nutraceuticals: Efficacy, Safety and Toxicity, Ed. by R. C. Gupta (Academic Press/Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016), pp. 319–332.
N. Goncharov, A. Orekhov, N. Voitenko, et al., in Nutraceuticals: Efficacy, Safety and Toxicity, Ed. by R. C. Gupta (Academic Press/Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016), pp. 555–568.
B. Kalyanaraman, V. Darley-Usmar, K. J. Davies, et al., Free Radic. Biol. Med. 52 (1), 1 (2012).
V. E. Stefanov, B. F. Shchegolev, O. V. Kryachko, et al., Klet. Biol. 461 (4), 485 (2015).
A. V. Domanski, E. A. Lapshina, and I. B. Zavodnik, Biochemistry (Moscow) 70 (7), 761 (2005).
I. Sadowska-Woda, I. B. Sychta, M. Rachel, et al., Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 30 (2), 141 (2010).
Z. Liu, K. Han, Y. Lin, and X. Luo, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1570, 97 (2002).
T. N. Das, T. Dhanasekaran, Z. B. Alfassi, et al., J. Phys. Chem. A 102 (1), 280 (1998).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tert-Butyl_hydroperoxide
P. S. Rao and E. Hayon, J. Phys. Chem. A 79 (4), 397 (1975).
N. V. Goncharov, M. A. Terpilowski, A. D. Nadeev, et al., Biochemistry (Moscow), Suppl. Ser. A: Membr. Cell Biol. 12 (2) 180 (2018).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The measurements on the Elexsys E580 EPR spectrometer (BRUKER, Germany) were conducted in the Magnetic Resonance Methods of Research Resource Center of St. Petersburg State University.
Funding
The study was supported by AAAA-A18-118012290142-9 State Program and Program of Fundamental Research in State Academies, 2014–2020 (SP-14, section 63).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Translated by E. Sherstyuk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terpilovskii, M.A., Khmelevskoy, D.A., Shchegolev, B.F. et al. A Hypomagnetic Field Modulates the Susceptibility of Erythrocytes to tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide in Rats. BIOPHYSICS 64, 374–380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350919030230
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350919030230