Abstract
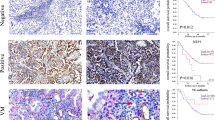
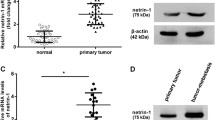
Lung cancer, the most concerning malignancy worldwide and one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths. Growing evidence indicates that Angiomotin (Amot)-p130 plays an important role in types of cancer, including breast cancer and gastric cancer. Moreover, evidence suggested that the low Amot-p130 expression correlates with the poor prognosis of lung cancer patients, however, the role and mechanism of Amot-p130 in lung cancer is still unclear. In this study, we showed that Amot-p130 expression was reduced in lung cancer tissues, compared with the adjacent para-carcinoma tissues. In addition, we observed that the reduced expression of Amot-p130 was associated with vasculogenic mimicry (VM) channels formation in lung cancer tissues. Amot-p130 expression was differently expression in lung cancer cell line H446, H1688 and H2227 compared with the normal human lung cells HFL1. To clarify the role of Amot-p130 in lung cancer, we constructed the Amot-p130 expressing H446 cells and Amot-p130 silencing H1299 cells. We confirmed that Amot-p130 overexpression inhibited the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells, whereas its silence promoted cell migration and invasion. Interestingly, we also found that Amot-p130 overexpression suppressed VM tube formation in H446 cells, while its knockdown promoted VM tube formation in H2227 cells. Further studies suggested that Amot-p130 plays roles in M tube formation of lung cancer cell V are independent on smad2/3 signaling pathway. Finally, inoculation of Amot-p130 expressing H446 cells and Amot-p130 silencing H1299 cells into nude mice suppressed tumor growth, when compared with the control group. Based on these results, Amot-p130 serves as a possible diagnostic and therapeutic target in lung cancer patients, and may be an effective mediator of VM formation in lung cancer.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09896-2
References
Adler J, Heller B, Bringman L, Ranahan W, Cocklin R, Goebl M, Oh M, Lim H, Ingham R, Wells C (2013) Amot130 adapts atrophin-1 interacting protein 4 to inhibit yes-associated protein signaling and cell growth. J Biol Chem 288(21):15181–15193
Bratt A, Wilson WJ, Troyanovsky B, Aase K, Kessler R, Van Meir EG, Holmgren L (2002) Angiomotin belongs to a novel protein family with conserved coiled-coil and PDZ binding domains. Gene 298(1):69–77
Brunner P, Hastar N, Kaehler C, Burdzinski W, Jatzlau J, Knaus P (2020) AMOT130 drives BMP-SMAD signaling at the apical membrane in polarized cells. Mol Biol Cell 31(2):118–130
Cao Z, Bao M, Miele L, Sarkar FH, Wang Z, Zhou Q (2013) Tumour vasculogenic mimicry is associated with poor prognosis of human cancer patients: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 49(18):3914–3923
Ernkvist M, Aase K, Ukomadu C, Wohlschlegel J, Blackman R, Veitonmäki N, Bratt A, Dutta A, Holmgren L (2006) p130-angiomotin associates to actin and controls endothelial cell shape. FEBS J 273(9):2000–2011
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A, Spitznagel EL, Piccirillo J (2006) Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 24(28):4539–4544
Hsu Y, Hung J, Chou S, Huang M, Tsai M, Lin Y, Chiang S, Ho Y, Wu C, Kuo P (2015a) Angiomotin decreases lung cancer progression by sequestering oncogenic YAP/TAZ and decreasing Cyr61 expression. Oncogene 34(31):4056–4068
Hsu YL, Hung JY, Chou SH, Huang MS, Tsai MJ, Lin YS, Chiang SY, Ho YW, Wu CY, Kuo PL (2015b) Angiomotin decreases lung cancer progression by sequestering oncogenic YAP/TAZ and decreasing Cyr61 expression. Oncogene 34(31):4056–4068
Jang SH, Cho HD, Lee JH, Lee HJ, Hong SA, Cho J, Kim HJ, Oh MH (2017) Reduced angiomotin p130 expression correlates with poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol 70(7):625–630
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Hardy KM, Seftor RE, Hendrix MJ (2012) Molecular pathways: vasculogenic mimicry in tumor cells: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res 18(10):2726–2732
Lazzari C, Gregorc V, Bulotta A, Dottore A, Altavilla G, Santarpia M (2018) Temozolomide in combination with either veliparib or placebo in patients with relapsed-sensitive or refractory small-cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 7(Suppl 4):S329–s333
Lv M, Shen Y, Yang J, Li S, Wang B, Chen Z, Li P, Liu P, Yang J (2017) Angiomotin family members: oncogenes or tumor suppressors? Int J Biol Sci 13(6):772–781
O'Brien ME, Ciuleanu TE, Tsekov H, Shparyk Y, Cuceviá B, Juhasz G, Thatcher N, Ross GA, Dane GC, Crofts T (2006) Phase III trial comparing supportive care alone with supportive care with oral topotecan in patients with relapsed small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(34):5441–5447
Ranahan W, Han Z, Smith-Kinnaman W, Nabinger S, Heller B, Herbert B, Chan R, Wells C (2011) The adaptor protein AMOT promotes the proliferation of mammary epithelial cells via the prolonged activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases. Cancer Res 71(6):2203–2211
Ren K, Yao N, Wang G, Tian L, Ma J, Shi X, Zhang L, Zhang J, Zhou X, Zhou G, Wu S, Sun X (2014) Vasculogenic mimicry: a new prognostic sign of human osteosarcoma. Human Pathol 45(10):2120–2129
Ren K, Zhang J, Gu X, Wu S, Shi X, Ni Y, Chen Y, Lu J, Gao Z, Wang C, Yao N (2018) Migration-inducing gene-7 independently predicts poor prognosis of human osteosarcoma and is associated with vasculogenic mimicry. Exp Cell Res 369(1):80–89
Roudier E, Chapados N, Decary S, Gineste C, Le Bel C, Lavoie JM, Bergeron R, Birot O (2009) Angiomotin p80/p130 ratio: a new indicator of exercise-induced angiogenic activity in skeletal muscles from obese and non-obese rats? J Physiol 587(Pt 16):4105–4119
Santarpia M, Daffinà MG, Karachaliou N, González-Cao M, Lazzari C, Altavilla G, Rosell R (2016) Targeted drugs in small-cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5(1):51–70
Santos FN, de Castria TB, Cruz MR, Riera R (2015) Chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the elderly population. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015(10):Cd010463
Seftor RE, Hess AR, Seftor EA, Kirschmann DA, Hardy KM, Margaryan NV, Hendrix MJ (2012) Tumor cell vasculogenic mimicry: from controversy to therapeutic promise. Am J Pathol 181(4):1115–1125
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67(1):7–30
Troyanovsky B, Levchenko T, Månsson G, Matvijenko O, Holmgren L (2001) Angiomotin: an angiostatin binding protein that regulates endothelial cell migration and tube formation. J Cell Biol 152(6):1247–1254
Wang Y, Justilien V, Brennan KI, Jamieson L, Murray NR, Fields AP (2017) PKCι regulates nuclear YAP1 localization and ovarian cancer tumorigenesis. Oncogene 36(4):534–545
Wang Y, Li Z, Xu P, Huang L, Tong J, Huang H, Meng A (2011) Angiomotin-like2 gene (amotl2) is required for migration and proliferation of endothelial cells during angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 286(47):41095–41104
Wu X, Zhang F, Xiong X, Lu C, Lian N, Lu Y, Zheng S (2015) Tetramethylpyrazine reduces inflammation in liver fibrosis and inhibits inflammatory cytokine expression in hepatic stellate cells by modulating NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. IUBMB Life 67(4):312–321
Yang J, Zhang X, Chen Z, Shen Y, Wang F, Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu P, Yang J (2019) Angiomotin-p130 inhibits β-catenin stability by competing with Axin for binding to tankyrase in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 10(3):179
Yang JP, Liao YD, Mai DM, Xie P, Qiang YY, Zheng LS, Wang MY, Mei Y, Meng DF, Xu L, Cao L, Yang Q, Yang XX, Wang WB, Peng LX, Huang BJ, Qian CN (2016) Tumor vasculogenic mimicry predicts poor prognosis in cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Angiogenesis 19(2):191–200
Yi C, Shen Z, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Dawany N, Troutman S, Showe L, Liu Q, Shimono A, Sudol M, Holmgren L, Stanger B, Kissil J (2013) The p130 isoform of angiomotin is required for Yap-mediated hepatic epithelial cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Sci Signal 6(291):ra77
Zeng H, Ortiz A, Shen P, Cheng C, Lee Y, Yu G, Lin S, Creighton C, Yu-Lee L, Lin S (2017) Angiomotin regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation by signaling through the hippo-YAP pathway. Oncotarget 8(6):10145–10160
Zhang H, Sun J, Ju W, Li B, Lou Y, Zhang G, Liang G, Luo X (2019) Apatinib suppresses breast cancer cells proliferation and invasion via angiomotin inhibition. Am J Transl Res 11(7):4460–4469
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Key Research and Development Project of Shaanxi Province (No. 2021SF-041) and Xi’an Science and Technology Project (No. 201805102YX10SF36(3)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuan Wang designed this manuscript. Dan Li wrote this manuscript. Dan Li, Yanwei Shen and Hui Ren performed experiments. Jin Yang analyzed the data. Li Wang revised the language of the manuscript; all the authors approved the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Shen, Y., Ren, H. et al. Angiomotin-p130 inhibits vasculogenic mimicry formation of small cell lung cancer independently of Smad2/3 signal pathway. J Bioenerg Biomembr 53, 295–305 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09891-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09891-7