Abstract
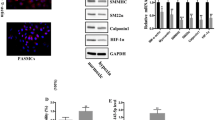
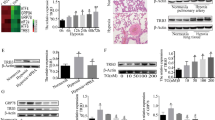
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a progressive and fetal cardiovascular disease. Tripartite motif 32 (TRIM32) is a member of TRIM family that has been found to be involved in cardiovascular disease. However, the role of TRIM32 in PAH remains unclear. Here we investigated the effects of TRIM32 on hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) in vitro. Our results showed that TRIM32 protein level in the plasma samples from PAH patients was decreased as compared with healthy volunteers. Exposure to hypoxia condition caused a significant decrease in TRIM32 expression in PASMCs. Overexpression of TRIM32 inhibited hypoxia-induced proliferation and migration of PASMCs. TRIM32 overexpression elevated the increased apoptotic rate and caspase-3 activity in hypoxia-induced PASMCs. Moreover, overexpression of TRIM32 reversed hypoxia-induced down-regulation of myocardin, SM 22 and calponin, as well as up-regulation of osteopontin (OPN). Whereas, TRIM32 knockdown shwed the opposite effect. Furthermore, overexpression of TRIM32 inhibited hypoxia-induced activation of PI3K/Akt with decreased phosphorylated level of PI3K and Akt. Additionally, activation of PI3K/Akt by IGF-1 treatment reversed the effects of TRIM32 on hypoxia-induced PASMCs. In conclusion, these findings indicated that TRIM32 was involved in the development of PAH through regulating the proliferation, migration, apoptosis and dedifferentiation of PASMCs, which might be mediated by the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Thus, TRIM32 might be a potential target for PAH treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basatemur GL, Jorgensen HF, Clarke MCH, Bennett MR, Mallat Z (2019) Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol 16(12):727–744
Bawa S, Brooks DS, Neville KE, Tipping M, Sagar MA, Kollhoff JA, Chawla G, Geisbrecht BV, Tennessen JM, Eliceiri KW, Geisbrecht ER (2020) Drosophila TRIM32 cooperates with glycolytic enzymes to promote cell growth. Elife 9(1):e52358
Borlepawar A, Rangrez AY, Bernt A, Christen L, Sossalla S, Frank D, Frey N (2017) TRIM24 protein promotes and TRIM32 protein inhibits cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via regulation of dysbindin protein levels. J Biol Chem 292(24):10180–10196
Brigant B, Demont Y, Ouled-Haddou H, Metzinger-Le, Meuth V, Testelin S, Garçon L, Metzinger L, Rochette J (2020) TRIM37 is highly expressed during mitosis in CHON-002 chondrocytes cell line and is regulated by miR-223. Bone 137(1):115393
Cai C, Xiang Y, Wu Y, Zhu N, Zhao H, Xu J, Lin W, Zeng C (2019) Formononetin attenuates monocrotalineinduced pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibiting pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats. Mol Med Rep 20(6):4984–4992
Cecchettini A, Rocchiccioli S, Boccardi C, Citti L (2011) Vascular smooth-muscle-cell activation: proteomics point of view. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 288(1):43–99
Chen L, Huang J, Ji Y, Zhang X, Wang P, Deng K, Jiang X, Ma G, Li H (2016) Tripartite motif 32 prevents pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Clin Sci (Lond) 130(10):813–828
Cohen S, Lee D, Zhai B, Gygi SP, Goldberg AL (2014) Trim32 reduces PI3K-Akt-FoxO signaling in muscle atrophy by promoting plakoglobin-PI3K dissociation. J Cell Biol 204(5):747–758
Coons JC, Pogue K, Kolodziej AR, Hirsch GA, George MP (2019) Pulmonary arterial hypertension: a pharmacotherapeutic update. Curr Cardiol Rep 21(11):141
Dodson MW, Brown LM, Elliott CG (2018) Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart Fail Clin 14(3):255–269
Fang X, Chen X, Zhong G, Chen Q, Hu C (2016) Mitofusin 2 downregulation triggers pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis imbalance in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via the PI3K/Akt and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 67(2):164–174
Frismantiene A, Philippova M, Erne P, Resink TJ (2018) Smooth muscle cell-driven vascular diseases and molecular mechanisms of VSMC plasticity. Cell Signal 52(1):48–64
Ghigo A, Li M (2015) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: friend and foe in cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol 6(1):169
Hayashi K, Saga H, Chimori Y, Kimura K, Yamanaka Y, Sobue K (1998) Differentiated phenotype of smooth muscle cells depends on signaling pathways through insulin-like growth factors and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 273(44):28860–28867
He RL, Wu ZJ, Liu XR, Gui LX, Wang RX, Lin MJ (2018) Calcineurin/NFAT signaling modulates pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 49(1):172–189
Hou J, Liu B, Zhu B, Wang D, Qiao Y, Luo E, Nawabi AQ, Yan G, Tang C (2019) Role of integrin-linked kinase in the hypoxia-induced phenotypic transition of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: Implications for hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Exp Cell Res 382(2):111476
Huang LJ, Zhang CC, Zhao MP, Zheng MX, Ying L, Chen XW, Wang WT (2017) The regulation of MAPK signaling pathway on cell proliferation and apoptosis in hypoxic PASMCs of rats. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 33(3):226–230
Isenovic ER, Kedees MH, Tepavcevic S, Milosavljevic T, Koricanac G, Trpkovic A, Marche P (2009) Role of PI3K/AKT, cPLA2 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in insulin regulation of vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets 9(3):172–180
Lacolley P, Regnault V, Nicoletti A, Li Z, Michel JB (2012) The vascular smooth muscle cell in arterial pathology: a cell that can take on multiple roles. Cardiovasc Res 95(2):194–204
Lan NSH, Massam BD, Kulkarni SS, Lang CC (2018) Pulmonary arterial hypertension: pathophysiology and treatment. Diseases 6(2):38
Leopold JA, Maron BA (2016) Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int J Mol Sci 17(5):761–774
Liu T, Li Y, Lin K, Yin H, He B, Zheng M, Wang G (2012) Regulation of S100A4 expression via the JAK2-STAT3 pathway in rhomboid-phenotype pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells exposure to hypoxia. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(8):1337–1345
Liu H, Tao Y, Chen M, Yu J, Li WJ, Tao L, Li Y, Li F (2016) Upregulation of microRNA-214 contributes to the development of vascular remodeling in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via targeting CCNL2. Sci Rep 6(1):24661
Montani D, Chaumais MC, Guignabert C, Gunther S, Girerd B, Jais X, Algalarrondo V, Price LC, Savale L, Sitbon O, Simonneau G, Humbert M (2014) Targeted therapies in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pharmacol Ther 141(2):172–191
Morello F, Perino A, Hirsch E (2009) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in the vascular system. Cardiovasc Res 82(2):261–271
Parikh V, Bhardwaj A, Nair A (2019) Pharmacotherapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Thorac Dis 11(Suppl 14):S1767–S1781
Peng X, Li HX, Shao HJ, Li GW, Sun J, Xi YH, Li HZ, Wang XY, Wang LN, Bai SZ, Zhang WH, Zhang L, Yang GD, Wu LY, Wang R, Xu CQ (2014) Involvement of calcium-sensing receptors in hypoxia-induced vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension by promoting phenotypic modulation of small pulmonary arteries. Mol Cell Biochem 396(1–2):87–98
Peng X, Wei C, Li HZ, Li HX, Bai SZ, Wang LN, Xi YH, Yan J, Xu CQ (2019) NPS2390, a selective calcium-sensing receptor antagonist controls the phenotypic modulation of hypoxic human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells by regulating autophagy. J Transl Int Med 7(2):59–68
Quatredeniers M, Nakhleh MK, Dumas SJ, Courboulin A, Vinhas MC, Antigny F, Phan C, Guignabert C, Bendifallah I, Vocelle M, Fadel E, Dorfmuller P, Humbert M, Cohen-Kaminsky S (2019) Functional interaction between PDGFbeta and GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 316(3):L445–L455
Southgate L, Machado RD, Graf S, Morrell NW (2020) Molecular genetic framework underlying pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol 17(2):85–95
Stenmark KR, Fagan KA, Frid MG (2006) Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Circ Res 99(7):675–691
Sysol JR, Chen J, Singla S, Zhao S, Comhair S, Natarajan V, Machado RF (2018) Micro-RNA-1 is decreased by hypoxia and contributes to the development of pulmonary vascular remodeling via regulation of sphingosine kinase 1. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 314(3):L461–L472
Tajsic T, Morrell NW (2011) Smooth muscle cell hypertrophy, proliferation, migration and apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension. Compr Physiol 1(1):295–317
Thompson AAR, Lawrie A (2017) Targeting vascular remodeling to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension. Trends Mol Med 23(1):31–45
Wang J, Fang Y, Liu T (2020) TRIM32 promotes the growth of gastric cancer cells through enhancing AKT activity and glucose transportation. Biomed Res Int 2020(1):4027627–4027636
Wu X, Zhang F, Xiong X, Lu C, Lian N, Lu Y, Zheng S (2015) Tetramethylpyrazine reduces inflammation in liver fibrosis and inhibits inflammatory cytokine expression in hepatic stellate cells by modulating NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. IUBMB Life 67(4):312–321
Yu X, Li T, Liu X, Yu H, Hao Z, Chen Y, Zhang C, Liu Y, Li Q, Mao M, Zhu D (2015) Modulation of pulmonary vascular remodeling in hypoxia: role of 15-LOX-2/15-HETE-MAPKs pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 35(6):2079–2097
Yu X, Zhao X, Zhang J, Li Y, Sheng P, Ma C, Zhang L, Hao X, Zheng X, Xing Y, Qiao H, Qu L, Zhu D (2019) Dacomitinib, a new pan-EGFR inhibitor, is effective in attenuating pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension. Eur J Pharmacol 850(1):97–108
Yue Y, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Chen S, Guo Y, Hong Y (2018) miR-143 and miR-145 promote hypoxia-induced proliferation and migration of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells through regulating ABCA1 expression. Cardiovasc Pathol 37(1):15–25
Zhang H, Gong Y, Wang Z, Jiang L, Chen R, Fan X, Zhu H, Han L, Li X, Xiao J, Kong X (2014) Apelin inhibits the proliferation and migration of rat PASMCs via the activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal and the inhibition of autophagy under hypoxia. J Cell Mol Med 18(3):542–553
Zhang Q, Cao Y, Luo Q, Wang P, Shi P, Song CEM, Ren J, Fu B, Sun H (2018) The transient receptor potential vanilloid-3 regulates hypoxia-mediated pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Prolif 51(3):e12436
Zheng Z, Yu S, Zhang W, Peng Y, Pu M, Kang T, Zeng J, Yu Y, Li G (2017) Genistein attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats by activating PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling. Histol Histopathol 32(1):35–41
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Basic research plan of Natural Science in Shaanxi Province (2020JM-378) in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhi Hu designed and wrote this manuscript. Qiang Song, Hui Ma and Yaozhang Guo performed experiments. Tingting Zhang analyzed the data. Hang Xie and Xiaohui Luo revised the language of the manuscript; all the authors approved the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Z., Song, Q., Ma, H. et al. TRIM32 inhibits the proliferation and migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells through the inactivation of PI3K/Akt pathway in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Bioenerg Biomembr 53, 309–320 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09880-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09880-w