Abstract
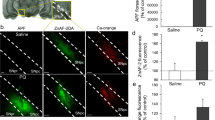
Mitochondria are essential for survival. Their primary function is to support aerobic respiration and to provide energy for intracellular metabolic pathways. Paraquat is a redox cycling agent capable of generating reactive oxygen species. The aim of the present study was to evaluate changes in cortical and striatal mitochondrial function in an experimental model of acute paraquat toxicity and to compare if the brain areas and the molecular mechanisms involved were similar to those observed after chronic exposure. Sprague-Dawley rats received paraquat (25 mg/Kg i.p.) or saline and were sacrificed after 24 h. Paraquat treatment decreased complex I and IV activity by 37 and 21 % respectively in striatal mitochondria. Paraquat inhibited striatal state 4 and state 3 KCN-sensitive respiration by 80 % and 62 % respectively, indicating a direct effect on respiratory chain. An increase of 2.2 fold in state 4 and 2.3 fold in state 3 in KCN-insensitive respiration was observed in striatal mitochondria from paraquat animals, suggesting that paraquat redox cycling also consumed oxygen. Paraquat treatment increased hydrogen peroxide production (150 %), TBARS production (42 %) and cardiolipin oxidation/depletion (12 %) in striatal mitochondria. Also, changes in mitochondrial polarization was induced after paraquat treatment. However, no changes were observed in any of these parameters in cortical mitochondria from paraquat treated-animals. These results suggest that paraquat treatment induced a clear striatal mitochondrial dysfunction due to both paraquat redox cycling reactions and impairment of the mitochondrial electron transport, causing oxidative damage. As a consequence, mitochondrial dysfunction could probably lead to alterations in cellular bioenergetics.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DiOC6 :
-
3, 3″-dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- FCCP:
-
carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- H2O2 :
-
hydrogen peroxide
- NAO:
-
acridine orange 10-nonyl bromide
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- TBARS:
-
thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances
References
Agarwal R, Srinivas R, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D (2006) Experience with paraquat poisoning in a respiratory intensive care unit in North India. Singap Med J 47:1033–1037
Agarwal R, Srinivas R, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D (2007) Immunosuppressive therapy in lung injury due to paraquat poisoning: a meta-analysis. Singap Med J 48:1000–1005
Block K, Gorin Y, Abboud HE (2009) Subcellular localization of Nox4 and regulation in Diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14385–14390
Boveris A (1984) Determination of the production of superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide in mitochondria. Methods Enzymol 105:429–435
Boveris A, Costa LE, Cadenas E, Poderoso JJ (1999) Regulation of mitochondrial respiration by adenosine diphosphate, oxygen, and nitric oxide. Methods Enzymol 301:188–198
Breckenridge CB et al. (2013) Pharmacokinetic, neurochemical, stereological and neuropathological studies on the potential effects of paraquat in the substantia nigra pars compacta and striatum of male C57BL/6 J Mice. Neurotoxicology 37:1–14
Bustamante J, Di Libero E, Fernandez-Cobo M, Monti N, Cadenas E, Boveris A (2004) Kinetic Analysis of Thapsigargin-Induced Thymocyte Apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1490–1498
Case AJ, Li S, Basu U, Tian J, Zimmerman MC (2013) Mitochondrial-localized NADPH oxidase 4 is a source of superoxide in angiotensin II-stimulated neurons. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 305:H19–H28
Czerniczyniec A, Karadayian AG, Bustamante J, Cutrera RA, Lores-arnaiz S (2011) Paraquat induces behavioral changes and cortical and striatal mitochondrial dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 51:1428–1436
Czerniczyniec A, Lores-Arnaiz S, Bustamante J (2013) Mitochondrial susceptibility in a model of paraquat neurotoxicity. Free Radic Res 47:614–623
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA, Sanchez-Navarro A, Remiao F, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2008) Paraquat poisonings: mechanisms of lung toxicity, clinical features, and treatment. Crit Rev Toxicol 38:13–71
Dinis-Oliveira RJ et al. (2007) Sodium salicylate prevents paraquat-induced apoptosis in the rat lung. Free Radic Biol Med 43:48–61
Eble KS, Coleman WB, Hantgan RR, Cunningham CC (1990) Tightly associated cardiolipin in the bovine heart mitochondrial ATP synthase as analyzed by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biol Chem 265:19434–19440
Estabrook R (1967) Mitochondrial respiratory control and the polarographic measurement of ADP:O ratios. Methods Enzymol 10:41–47
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH, Dianzani MU, Poli G, Slater TF (1982) Separation and characterization of the aldehydic products of lipid peroxidation stimulated by ADP-Fe2+ in rat liver microsomes. Biochem J 208:129–140
Gardner PR (2002) Aconitase: sensitive target and measure of superoxide. Methods Enzymol 349:9–23
Gocgeldi E et al. (2008) Establishing the use of melatonin as an adjuvant therapeutic against paraquat-induced lung toxicity in rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233:1133–1141
Gomez-Puyou A, Tuena de Gomez-Puyou M, Klapp M, Carafoli E (1979) The effect of calcium on the translocation of adenine nucleotides in rat liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys 194:399–404
Gram TE (1997) Chemically reactive intermediates and pulmonary xenobiotic Toxicity. Pharmacol Rev 49:297–341
Hatefi Y (1985) The mitochondrial electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation System. Annu Rev Biochem 54:1015–1069
Huang CL et al. (2015) Paraquat Induces Cell Death Through Impairing Mitochondrial Membrane Permeability Mol Neurobiol
Korshunov SS, Skulachev VP, Starkov AA (1997) High protonic potential actuates a mechanism of production of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria. FEBS Lett 416:15–18
Kuroda J, Ago T, Matsushima S, Zhai P, Schneider MD, Sadoshima J (2010) NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) is a major source of oxidative stress in the failing heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:15565–15570
Lin C, Yen TH, Juang YY, Lin JL, Lee SH (2014) Psychiatric comorbidity and its impact on mortality in patients who attempted suicide by paraquat poisoning during 2000–2010. PLoS One 9:e112160
Lores-Arnaiz S, Coronel M, Boveris A (1999) Nitric oxide, superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production in brain mitochondria after haloperidol treatment. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 3:235–243
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Madison DV, Edson EB (2001) Preparation of hippocampal brain slices Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter 6:Unit 6 4
Mainwaring G et al. (2006) Identification of early molecular pathways affected by paraquat in rat lung. Toxicology 225:157–172
McCormack AL, Thiruchelvam M, Manning-Bog AB, Thiffault C, Langston JW, Cory-Slechta DA, Di Monte DA (2002) Environmental risk factors and parkinson's disease: selective degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons caused by the herbicide paraquat. Neurobiol Dis 10:119–127
McMillin JB, Dowhan W (2002) Cardiolipin and apoptosis biochim. Biophys Acta 1585:97–107
Nakahara I et al. (1992) Changes in major phospholipids of mitochondria during postischemic reperfusion in rat brain. J Neurosurg 76:244–250
Nomura K, Imai H, Koumura T, Kobayashi T, Nakagawa Y (2000) Mitochondrial phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase inhibits the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria by suppressing the peroxidation of cardiolipin in hypoglycaemia-induced apoptosis. Biochem J 351:183–193
Onyeama HP, Oehme FW (1984) A literature review of paraquat toxicity. Vet Hum Toxicol 26:494–502
Ossowska K et al. (2005) A slowly developing dysfunction of dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons induced by long-term paraquat administration in rats: an animal model of preclinical stages of Parkinson's disease? Eur J Neurosci 22:1294–1304
Palmeira CM, Moreno AJ, Madeira VM (1995) Mitochondrial bioenergetics is affected by the herbicide paraquat Biochim Biophys Acta 1229:187–192
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Pistolese M, Ruggiero FM (2000) The effect of reactive oxygen species generated from the mitochondrial electron transport chain on the cytochrome c oxidase activity and on the cardiolipin content in bovine heart submitochondrial particles. FEBS Lett 466:323–326
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Pistolese M, Ruggiero FM (2001) Reactive oxygen species generated by the mitochondrial respiratory chain affect the complex iii activity via cardiolipin peroxidation in beef-heart submitochondrial particles. Mitochondrion 1:151–159
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Pistolese M, Ruggiero FM (2002) Reactive oxygen species affect mitochondrial electron transport complex i activity through oxidative cardiolipin damage. Gene 286:135–141
Paraquat information center on behalf of Syngenta crop protection AG. Global registration status of paraquat (Gramoxone). (2015) Retrieved from http://paraquat.com/safety/regulation. Accessed 20 March 2015).
Petit JM, Maftah A, Ratinaud MH, Julien R (1992) 10 N-nonyl acridine orange interacts with cardiolipin and allows the quantification of this phospholipid in isolated Mitochondria. Eur J Biochem 209:267–273
Pickrell AM, Fukui H, Wang X, Pinto M, Moraes CT (2011) The striatum is highly susceptible to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation dysfunctions. J Neurosci 31:9895–9904
Prasad K, Winnik B, Thiruchelvam MJ, Buckley B, Mirochnitchenko O, Richfield EK (2007) Prolonged toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of paraquat in mouse brain. Environ Health Perspect 115:1448–1453
Roman I, Clark A, Swanson PD (1981) The interaction of calcium transport and adp phosphorylation in brain mitochondria. Membr Biochem 4:1–9
Santos RS et al. (2011) Effects of oleanolic acid on pulmonary morphofunctional and biochemical variables in experimental acute lung Injury. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 179:129–136
Sen T, Sen N, Tripathi G, Chatterjee U, Chakrabarti S (2006) Lipid peroxidation associated cardiolipin loss and membrane depolarization in rat brain mitochondria. Neurochem Int 49:20–27
Senarathna L, Eddleston M, Wilks MF, Woollen BH, Tomenson JA, Roberts DM, Buckley NA (2009) Prediction of outcome after paraquat poisoning by measurement of the plasma paraquat concentration. Qjm 102:251–259
Shimizu K, Matsubara K, Ohtaki K, Fujimaru S, Saito O, Shiono H (2003) Paraquat induces long-lasting dopamine overflow through the excitotoxic pathway in the striatum of freely moving rats. Brain Res 976:243–252
Shimizu K et al. (2001) Carrier-mediated processes in blood–brain barrier penetration and neural uptake of paraquat. Brain Res 906:135–142
Sittipunt C (2005) Paraquat poisoning. Respir Care 50:383–385
Starkov AA, Fiskum G (2003) Regulation of brain mitochondrial H2O2 production by membrane potential and NAD(P)H redox state. J Neurochem 86:1101–1107
Thiruchelvam M, Richfield EK, Baggs RB, Tank AW, Cory-slechta DA (2000) The nigrostriatal dopaminergic system as a preferential target of repeated exposures to combined paraquat and maneb: implications for parkinson's disease. J Neurosci 20:9207–9214
Wesseling C, van Wendel de Joode B, Ruepert C, Leon C, Monge P, Hermosillo H, Partanen TJ (2001) Paraquat in Developing countries. Int J Occup Environ Health 7:275–286
Wright MM, Howe AG, Zaremberg V (2004) Cell membranes and apoptosis: role of cardiolipin, phosphatidylcholine, and anticancer lipid Analogues. Biochem Cell Biol 82:18–26
Wu B, Song B, Yang H, Huang B, Chi B, Guo Y, Liu H (2013) Central nervous system damage due to acute paraquat poisoning: an experimental study with rat. Model Neurotoxicology 35C:62–70
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czerniczyniec, A., Lanza, E.M., Karadayian, A.G. et al. Impairment of striatal mitochondrial function by acute paraquat poisoning. J Bioenerg Biomembr 47, 395–408 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-015-9624-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-015-9624-x