Abstract
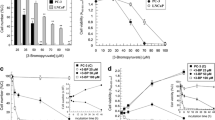
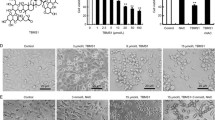
In the present study we analyzed the mechanisms of simvastatin toxicity for the PC3 human prostate cancer cell line. At 10 μM, simvastatin induced principally apoptosis, which was prevented by mevalonic acid but not by cyclosporin A, the inhibitor of calcineurin and mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT). At 60 μM, simvastatin induced the necrosis of PC3 cells insensitive to mevalonic acid. Cell necrosis was preceded by a threefold increase in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration and a significant decrease in both respiration rate and mitochondrial membrane potential. Both mitochondrial dysfunction and necrosis were sensitive to the compounds cyclosporin A and bongkrekic acid, as well as the calcineurin inhibitor FK506. We have concluded that simvastatin-induced PC3 cells apoptosis is dependent on 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A reductase inhibition and independent of MPT, whereas necrosis is dependent on mitochondrial dysfunction caused, at least in part, by calcineurin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida S, Domingues A, Rodrigues L et al (2004) Neurobiol Dis 17:435–444
Ankarcrona M, Dypbukt JM, Orrenius S et al (1996) FEBS Lett 394:321–324
Campos CBL, Degasperi GR, Pacífico DS et al (2004) Biochem Pharmacol 68:2197–2206
Collins R, Armitage J, Parish S et al (2003) Lancet 361:2005–2016
Dawson TM, Steiner JP, Dawson VL et al (1993) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:9808–9812
Degasperi GR, Velho JA, Zecchin KG et al (2006) J Bioenerg Biomembr 38:1–10
Demierre M-F, Higgins PDR, Gruber SB et al (2005) Nat Rev Cancer 5:930–942
Ghosh PM, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Moyer ML et al (1999) Oncogene 18:4120–4130
Gunter KK, Gunter TE (1994) J Bioenerg Biomembr 26:471–485
Halestrap AP, Brenner C (2003) Curr Med Chem 10:1507–1525
Halestrap AP, Connern CP, Griffths EJ et al (1997) Mol Cell Biochem 174:167–172
Hara MR, Snyder SH (2007) Toxicol 47:117–141
Hindler K, Cleeland CS, Rivera E et al (2006) Oncologist 11:306–315
Holden MJ, Sze H (1989) Plant Physiol 91:1296–1302
Hoque A, Chen H, Xu XC (2008) Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17:88–94
Kowaltowski AJ, Castilho RF, Vercesi AE (2001) FEBS Lett 495:12–15
Kroemer G, Galluzi L, Brenner C (2007) Physiol Rev 87:99–163
Li YC, Park MJ, Ye S-K et al (2006) Am J Pathol 168:1107–1118
Liu J, Farmer JDJ, Lane WS, Friedman J et al (1991) Cell 66:807–815
Manev H, Favaron M, Candeo P et al (1993) Brain Res 624:331–335
Marcelli M, Glenn RC, Haidacher SJ et al (1998) Cancer Res 58:76–83
Park C, Lee I, Kang WK (2001) Carcinogenesis 22:1727–1731
Platz EA, Leitzmann MF, Visvanathan K et al (2006) J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1819–1825
Rao S, Porter DC, Chen X et al (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7797–7802
Shepherd J, Cobbe SM, Ford I et al (1995) N Engl J Med 333:1301–1307
Shibasaki F, McKeon F (1995) Cell Biol 131:735–743
Sivaprasad U, Abbas T, Dutta A (2006) Mol Cancer Ther 5:2310–2316
Springer JE, Azbill RD, Nottingham SA et al (2000) J Neurosci 20:7246–7251
Ukomadu C, Dutta A (2003) J Biol Chem 278:4840–4846
Velho JA, Okanobo H, Degasperi GR et al (2006) Toxicology 219:124–132
Vercesi AE, Kowaltowski AJ, Oliveira HCF et al (2006) Front Biosc 11:2554–2564
Wang HG, Pathan N, Ethell IM et al (1999) Science 284:339–343
Weitz-Schmidt G, Welzenbach K, Brinkmann V et al (2001) Nat Med 7:687–692
Zecchin KG, Seidinger ALO, Degasperi GR et al (2007) J Bioenerg Biomembr 39:186–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, K.A.P., Zecchin, K.G., Alberici, L.C. et al. Simvastatin inducing PC3 prostate cancer cell necrosis mediated by calcineurin and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Bioenerg Biomembr 40, 307–314 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-008-9155-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-008-9155-9