Abstract
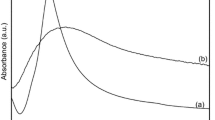
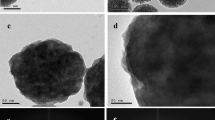
Silica/silver core–shell nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized by coating silver NPs on silica core particles (size ~300 ± 10 nm) via electro less reduction method. The core–shell NPs were characterized for their structural, morphological, compositional and optical behavior using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray analysis and UV–Visible spectroscopy, respectively. The size (16–35 nm) and loaded amount of silver NPs on the silica core were found to be dependent upon reaction time and activation method of silica. The bactericidal activity of the NPs was tested by broth micro dilution method against both Bacillus subtilis (gram positive) and Escherichia coli ATCC25922 (gram negative) bacterium. The bactericidal activity of silica/silver core–shell NPS is more against E. coli ATCC25922, when compared to B. subtilis. The minimal inhibitory concentration of the core–shell NPs ranged from 7.8 to 250 μg/mL and is found to be dependent upon the amount of silver on silica, the core. These results suggest that silica/silver core–shell NPs can be utilized as a strong substitutional candidate to control pathogenic bacterium, which are otherwise resistant to antibiotics, making them applicable in diverse medical devices.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlos Caro PMC, Klippstein R, Pozo D, Zaderenko AP. Silver nanoparticles: sensing and imaging applications. Silver Nanopart. 2010;. doi:10.5772/8513.
Welles AE. Silver nanoparticles: properties, characterization and applications. New York: Nova Science; 2010.
Abou El-Nour KMM, Eftaiha AA, Al-Warthan A, Ammar RAA. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arab J Chem. 2010;3(3):135–40. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.04.008.
Gurunathan S, Kalishwaralal K, Vaidyanathan R, Venkataraman D, Pandian SRK, Muniyandi J, et al. Biosynthesis, purification and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Escherichia coli. Colloids Surf B. 2009;74(1):328–35. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.07.048.
Prabhu S, Poulose E. Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett. 2012;2(1):1–10. doi:10.1186/2228-5326-2-32.
Quang Huy Tran VQN, Le Anh-Tuan. Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, toxicology, applications and perspectives. Adv Nat Sci. 2013;4(3):033001. doi:10.1088/2043-6262/4/3/033001.
http://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Silver_as_an_Antimicrobial_Agent#Silver_salts. Accessed 8 Aug 2013.
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim J-H, Park SJ, Lee HJ, et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2007;3(1):95–101.
Choi O, Deng KK, Kim N-J, Ross L Jr, Surampalli RY, Hu Z. The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res. 2008;42(12):3066–74. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.02.021.
Sukumaran Prabhu EKP. Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett. 2012;2(32):1–10. doi:10.1186/2228-5326-2-32.
Bondarenko O, Ivask A, Käkinen A, Kurvet I, Kahru A. Particle-cell contact enhances antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64060.
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73(6):1712–20. doi:10.1128/aem.02218-06.
Martínez-Castañón GA, Niño-Martínez N, Martínez-Gutierrez F, Martínez-Mendoza JR, Ruiz F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J Nanopart Res. 2008;10(8):1343–8. doi:10.1007/s11051-008-9428-6.
Egger S, Lehmann RP, Height MJ, Loessner MJ, Schuppler M. Antimicrobial properties of a novel silver–silica nanocomposite material. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(9):2973–6. doi:10.1128/aem.01658-08.
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E. Bactericidal effects of Ag nanoparticles immobilized on surface of SiO2 thin film with high concentration. Curr Appl Phys. 2009;9(6):1381–5. doi:10.1016/j.cap.2009.03.003.
Mahltig B, Gutmann E, Reibold M, Meyer DC, Böttcher H. Synthesis of Ag and Ag/SiO2 sols by solvothermal method and their bactericidal activity. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol. 2009;51(2):204–14. doi:10.1007/s10971-009-1972-8.
Jasiorski M, Leszkiewicz A, Brzeziński S, Bugla-Płoskońska G, Malinowska G, Borak B, et al. Textile with silver silica spheres: its antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol. 2009;51(3):330–4. doi:10.1007/s10971-009-1902-9.
Fateixa S, Neves MC, Almeida A, Oliveira J, Trindade T. Anti-fungal activity of SiO2/Ag2S nanocomposites against Aspergillus niger. Colloids Surf B. 2009;74(1):304–8. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.07.037.
Suchita Kalele SWG. Nanoshell particles: synthesis, properties and applications. Curr Sci. 2006;91(8):1038–105.
Devi P, Vishal, Singla ML. Effect of surfactant concentration, solvents and particle size on ∏: a isotherm of silica nanoparticles. Mater Lett. 2013;107:107–10. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2013.05.125.
Kobayashi Y, Salgueiriño-Maceira V, Liz-Marzán LM. Deposition of silver nanoparticles on silica spheres by pretreatment steps in electroless plating. Chem Mater. 2001;13(5):1630–3. doi:10.1021/cm001240g.
Christy AA. Effect of heat on the adsorption properties of silica gel. Int J Eng Technol. 2012;4(4):484–8.
Jiang Z-J, Liu C-Y. Seed-mediated growth technique for the preparation of a silver nanoshell on a silica sphere. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107(45):12411–5. doi:10.1021/jp035060g.
Taglietti A, Diaz Fernandez YA, Amato E, Cucca L, Dacarro G, Grisoli P, et al. Antibacterial activity of glutathione-coated silver nanoparticles against gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Langmuir. 2012;28(21):8140–8. doi:10.1021/la3003838.
Hernandez-Ortiz M, Acosta-Torres L, Hernandez-Padron G, Mendieta A, Bernal R, Cruz-Vazquez C, et al. Biocompatibility of crystalline opal nanoparticles. BioMed Eng Online. 2012;11(1):78.
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2004;275(1):177–82. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to both CSIR-CSIO and IIT Roorkee for infrastructural and experimental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, P., Patil, S.D., Jeevanandam, P. et al. Synthesis, characterization and bactericidal activity of silica/silver core–shell nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 1267–1273 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5165-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5165-9