Abstract
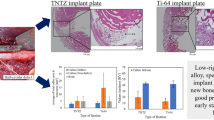
In order to investigate bone tissue reaction to the low rigidity titanium alloy of TNTZ in bone plate fixation, animal experiment with rabbit was performed with X-ray follow-up and histological observation. Experimental fractures were made in rabbit tibiae, and fixed by different bone plates of SUS316L, Ti–6Al–4V and TNTZ. Although there was no significant difference in fracture healing, bone atrophy was observed in cortical bone especially under the bone plate, which was different in time course among three materials. The bone atrophy under the bone plate was confirmed as porous or poor bone tissue in histological observation. In addition, the diameter of the tibia bone was increased in TNTZ as the result of bone remodeling with a new cortical bone. It is confirmed that the elastic modulus of the bone plate will naturally influence bone tissue reaction to the bone plate fixation according to the Wolff’s law of functional restoration.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Niinomi, Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 243, 231–236 (1998)
M. Niinomi, D. Kuroda et al., in Non-Aerospace Application of Titanium and Its Alloys, ed. by F.H. Froes, P.G. Allen, M. Niinomi. New Beta Type Titanium Alloys with High Biocompatibility (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2001), pp. 217–233
M. Niinomi, T. Hattori, S. Niwa, in Biomaterials In Orthopedics, ed. by M.J. Yaszemski, D.J. Trantolo. Material Characteristics and Bio-compatibility of Low Rigidity Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Applications (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2003), pp. 55–60
J. Wolff, The Law of Bone Remodeling, (trans: P. Maquet, R. Furlong) (Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 1986)
R. Huiskes et al., Adaptive bone-modeling theory applied to prosthetic-design analysis. J. Biomech. 20, 1135–1150 (1987)
C.T. Rubin et al., Osteoregulatory nature of mechanical stimuli: function as a determinant for adaptive remodeling in bone. J. Orthop. Res. 5, 300–310 (1987)
T.P. Ruedi, W.M. Murphy, AO Principles of Fracture Management, 1st edn. (AO Publishing, Davos, 2003). First Japanese edition 2003, Igaku-Shoin Ltd., Tokyo
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sumitomo, N., Noritake, K., Hattori, T. et al. Experiment study on fracture fixation with low rigidity titanium alloy. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 1581–1586 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3372-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3372-y