Abstract
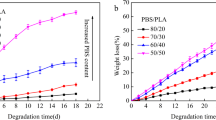
One of the most widely used fabrication methods of three dimensional porous scaffolds involves compression moulding of a polymer salt mixture, followed by salt leaching. However, the scaffolds prepared by this technique have typically limited interconnectivity. In this study, besides salt particles, an additional polymeric porogen, poly(ethylene oxide), PEO, was added to poly(L-lactic acid), PLLA, to enhance the interconnectivity of the scaffolds. Compression moulded specimens were quenched and put into water, where PEO crystallized and phase separated. Following the leaching of PEO fraction, the permeability and interconnectivity among the macropores formed by salt leaching could be observed. The porosities obtained in the prepared scaffolds were between 76 to 86%. Moreover, the highest porosity of 86% was obtained with minimum fraction of total porogen. The water absorption of the porous scaffolds prepared with PEO could vary between 280 to 450% while water uptake of pure PLLA scaffolds was about 93%. The increase of interconnectivity induced by compounding PLLA with PEO could also be obtained in porous PLLA/starch blends and PLLA/hydroxyapatite composites demonstrating the versatility and wide applicability of this preparation protocol. The simplicity of this organic solvent free preparation procedure of three-dimensional porous scaffolds with high interconnectivity and high surface area to volume ratio holds a promise for several tissue engineering applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. E. FREED, D. A. GRANDE, Z. LINGBIN, J. EMMANUAL, J. C. MARQUIS and R. LANGER, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 28 (1994).
W. L. MURPHY, D. H. KOHN and D. J. MOONEY, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 50 (2000) 50.
J. C. MIDDLETON and A. J. TIPTON, Biomaterials 21 (2000) 2335.
J. M. CHUPA, A. M. FOSTER, S. R. SUMNER, S. V. MADIHALLY and H. W. T. MATTHEW, Biomaterials. 21 (2000) 2315.
R. L. REIS and J. SAN ROMAN, in “Biodegradable Systems in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine” (CRC Press, 2005).
A. P. MARQUES, R. L. REIS and J. A. HUNT, Biomaterials 23 (2002) 1471.
M. E. GOMES, R. L. REIS, A. M. CUNHA, C. A. BLITTERSWIJK and J. D. DE BRUIJN, Biomaterials 22 (2001) 1911.
A. G. MIKOS, A. J. THORSEN, L. A. CZERWONKA, Y. BAO, R. LANGER, D. N. WINSLOW and J. P. VACANTI, Polymer. 35 (1994) 1068.
A. P. MARQUES, H. R. CRUZ, O. P. COUTINHO and R. L. REIS, J. Mater. Sci.- Mater. Med. 16 (2005) 833.
J. LI, X. NI and K. W. LEONG, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 65 (2003) 196.
J. D. DE BRUIJN, C. A. VAN BLITTERSWIJK and J. E. DAVIES, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29 (1995) 89.
J. A. JUHASZ, S. M. BEST, R. BROOKS, M. KAWASHITA, N. MIYATA, T. KOKUBO, T. NAKAMURA and W. BONFIELD, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 949.
W. L. MURPHY, M. C. PETERS, D. H. KOHN and D. J. MOONEY, Biomaterials 21 (2000) 2521.
S. FORMAN, J. KAS, F. FINI, M. STEINBERG and T. RUML, J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 13 (1999) 11.
K. WHANG, C. H. THOMAS, K. E. HEALY and G. NUBER, Polymer. 36 (1995) 837.
Q. HOU, D. W. GRIJPMA and J. FEIJEN, Biomaterials 24 (2003) 1937.
Y. HU, Y. S. HU, V. TOPOLKARAEV, A. HILTNER and E. BAER, Polymer. 44 (2003) 5711.
T. KOKUBO, H. KUSHITANI, S. SAKKA, T. KITSUGI and T. YAMAMURO, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 24 (1990) 721.
D. SHIN, K. SHIN, K. A. AAMER, G. N. TEW, T. P. RUSSELL, J. H. LEE and J. Y. JHO, Macromolecules 38 (2005) 104.
E. MEAURIO, E. ZUZA and J. R. SARASUA, Macromolecules 38 (2005) 1207.
J.BRANDRUP and E. H. IMMERGUT, in “Polymer Handbook.” (Wiley, NewYork, 1989) p. 555.
A. J. NIJENHUIS, E. COLSTEE, D. W. GRIJPMA and A. J. PENNINGS, Polymer 37 (1996) 5849.
R. G. FLEMMING, C. J. MURPHY, G. A. ABRAMS, S. L. GOODMAN and P. F. NEALEY, Biomaterials 20 (1999) 573.
J. B. RECKNOR, D. S. SAKAGUCHI and S. K. MALLAPRAGADA, Biomaterials 27 (2006) 4098.
H. TSUJI, R. SMITH, W. BONFIELD and Y. IKADA, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 75 (2000) 629.
K. A. SCHULT and D. R. PAUL, J. Polym. Sci, Part B: Polym. Phys. 35 (1997) 655.
J. REIGNIER and M. A. HUNEAULT, Polymer, 47 (2006) 4703.
P. LI, D. BAKKER and C. A. VAN BLITTERSWIJK, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 34 (1997) 79.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Viana, J.C., Reis, R.L. et al. The double porogen approach as a new technique for the fabrication of interconnected poly(L-lactic acid) and starch based biodegradable scaffolds. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 18, 185–193 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0680-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0680-y