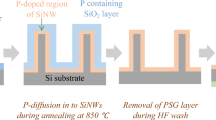
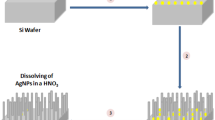
Abstract
Si nanowires (SiNWs) are receiving tremendous attention due to their significant optical and electrical properties; however, porosity on the nanowires opens an opportunity for further improvement. The work establishes a connection between morphological changes in the optical and electrical characteristics of the porous SiNWs (PSiNWs) because of H2O2 concentration (0.1 M, 0.2 M, 0.3 M) variation during metal-assisted chemical etching. The directional etching controls the porosity; a modification to the classical gravimetric method is introduced to measure the porosity. PSiNWs fabricated at 0.2 M H2O2 concentration achieve the minimal average reflectance of 8.29% in the visible range and a band gap of 1.39 eV. The work discusses the effect of the decrease in saturation current and broad diode biasing voltage on the open-circuit voltage of solar cells, considering the optical and electrical properties of the PSiNWs. The optimization of H2O2 concentration to fabricate the PSiNWs for photovoltaic applications (photon absorption and antireflection properties) is illustrated.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript.
References
E. Xifré-Pérez, L.F. Marsal, J. Ferré-Borrull, J. Pallarès, Porous silicon omnidirectional mirrors and distributed Bragg reflectors for planar waveguide applications. J. Appl. Phys. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/12784019
P. Yu, J. Wu, S. Liu, J. Xiong, C. Jagadish, Z.M. Wang, Design and fabrication of silicon nanowires towards efficient solar cells. Nano Today 11, 704–737 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2016.10.001
Y. Cui, C.M. Lieber, Functional nanoscale electronic devices assembled using silicon nanowire building blocks. Science 291, 851–853 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.291.5505.851
N. Dimov, S. Kugino, M. Yoshio, Carbon-coated silicon as anode material for lithium ion batteries: advantages and limitations. Electrochim. Acta 48, 1579–1587 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(03)00030-6
S. Ohara, J. Suzuki, K. Sekine, T. Takamura, A thin film silicon anode for Li-ion batteries having a very large specific capacity and long cycle life. J. Power. Sources 136, 303–306 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.03.014
H. Kang, Crystalline silicon vs. Amorphous silicon: the significance of structural differences in photovoltaic applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 726, 6–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/726/1/012001
R. Chandra Muduli, P. Kale, Chemically modified surface of silicon nanostructures to enhance hydrogen uptake capabilities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.06.030
Y.D. Ivanov, T.S. Romanova, K.A. Malsagova, T.O. Pleshakova, A.I. Archakov, Use of silicon nanowire sensors for early cancer diagnosis. Molecules 26, 3734 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123734
V. Kashyap, C. Kumar, N. Chaudhary, N. Goyal, K. Saxena, Comparative study of quantum confinements effect present in silicon nanowires using absorption and Raman spectroscopy. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 121, 111538 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111538
S. Maurya, S.P. Muduli, S. Nayak, P. Kale, Optimization of controlling parameters of porous silicon synthesis using Taguchi design of experiment. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 97, 749–755 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024423040295
S.P. Muduli, P. Kale, State-of-the-art passivation strategies of c-Si for photovoltaic applications: a review. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 154, 107202 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.107202
S.P. Muduli, P. Kale, Free-standing nanowire layer-transfer parametric optimisation of multi-response process by Grey Taguchi design. Mater. Sci. Technol. (United Kingdom) 39, 591–599 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2022.2129203
D.A. Rudd, N.H. Voelcker, R.S. Minhas, E. Eduardo Antunez, T.M. Guinan, T.R. Gengenbach, Fluorocarbon plasma gas passivation enhances performance of porous silicon for desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. ACS Sens. 5, 3226–3236 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01532
R. Chandra Muduli, P. Kale, Silicon nanostructures for solid-state hydrogen storage: a review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 48, 1401–1439 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.10.055
S. Li, W. Ma, Y. Zhou, X. Chen, Y. Xiao, M. Ma, W. Zhu, F. Wei, Fabrication of porous silicon nanowires by MACE method in HF/H2O2/AgNO3 system at room temperature. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 1–8 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-196
K.A. Gonchar, D.V. Moiseev, I.V. Bozhev, L.A. Osminkina, Influence of H2O2 concentration on the structural and photoluminescent properties of porous silicon nanowires fabricated by metal-assisted chemical etching. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 125, 105644 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105644
J. Charrier, A. Najar, P. Pirasteh, Study of optical absorbance in porous silicon nanowires for photovoltaic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 283, 828–832 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.07.026
L. Lin, S. Guo, X. Sun, J. Feng, Y. Wang, Synthesis and photoluminescence properties of porous silicon nanowire arrays. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 1822–1828 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9719-6
C. Lai, X. Li, C. Liu, X. Guo, Z. Xiang, B. Xie, L. Zou, Improvement in gravimetric measurement for determining the porosity and thickness of porous silicon using an optimized solution. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 26, 501–505 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.05.046
N. Geyer, N. Wollschläger, B. Fuhrmann, A. Tonkikh, A. Berger, P. Werner, M. Jungmann, R. Krause-Rehberg, H.S. Leipner, Influence of the doping level on the porosity of silicon nanowires prepared by metal-assisted chemical etching. Nanotechnology 26, 245301 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/26/24/245301
Y. Qu, L. Liao, Y. Li, H. Zhang, Y. Huang, X. Duan, Electrically conductive and optically active porous silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 9, 4539–4543 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl903030h
X. Zhong, Y. Qu, Y.C. Lin, L. Liao, X. Duan, Unveiling the formation pathway of single crystalline porous silicon nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3, 261–270 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/am1009056
B. Rajesh Kumar, T. Subba Rao, AFM studies on surface morphology, topography and texture of nanostructured zinc aluminum oxide thin films. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures. 7, 1881–1889 (2012)
S. Maurya, R.C. Muduli, P. Kale, Physical forces responsible for agglomeration of silicon nanowires arrays synthesized by metal-assisted chemical etching. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 97, 1990–2000 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024423090224
C. Zhang, S. Li, W. Ma, Z. Ding, X. Wan, J. Yang, Z. Chen, Y. Zou, J. Qiu, Fabrication of ultra-low antireflection SiNWs arrays from mc-Si using one step MACE. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 8510–8518 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6573-7
S. Li, W. Ma, X. Chen, K. Xie, Y. Li, X. He, X. Yang, Y. Lei, Structure and antireflection properties of SiNWs arrays form mc-Si wafer through Ag-catalyzed chemical etching. Appl. Surf. Sci. 369, 232–240 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.028
Q. Wang, W. Zhou, F. Chen, R. Yang, The effect of surface microstructure on the optical reflectance of monocrystalline silicon. Mater. Res. Express. 3, 125020 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/3/12/125020
M.K. Basher, M.K. Hossain, M.J. Uddin, M.A.R. Akand, K.M. Shorowordi, Effect of pyramidal texturization on the optical surface reflectance of monocrystalline photovoltaic silicon wafers. Optik (Stuttg) 172, 801–811 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.07.116
R. Chandra Muduli, M. Kumar Sahoo, P. Kale, Wetting behavior of silicon nanowires array fabricated by metal-assisted chemical etching. Mater. Today Proc. 62, 5917–5922 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.635
S. Gao, S. Hong, S. Park, H.Y. Jung, W. Liang, Y. Lee, C.W. Ahn, J.Y. Byun, J. Seo, M.G. Hahm, H. Kim, K. Kim, Y. Yi, H. Wang, M. Upmanyu, S.G. Lee, Y. Homma, H. Terrones, Y.J. Jung, Catalyst-free synthesis of sub-5 nm silicon nanowire arrays with massive lattice contraction and wide bandgap. Nat. Commun. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31174-x
S.A. Moiz, A.N.M. Alahmadi, A.J. Aljohani, Design of silicon nanowire array for PEDOT:PSS-silicon nanowire-based hybrid solar cell. Energies 13, 3797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13153797
S. Praveenkumar, D. Lingaraja, P. Mahiz Mathi, G. Dinesh Ram, An experimental study of optoelectronic properties of porous silicon for solar cell application. Optik (Stuttg) 178, 216–223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.09.176
J. Müller, B. Rech, J. Springer, M. Vanecek, TCO and light trapping in silicon thin film solar cells. Sol. Energy 77, 917–930 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2004.03.015
L.F. Cui, R. Ruffo, C.K. Chan, H. Peng, Y. Cui, Crystalline-amorphous core-shell silicon nanowires for high capacity and high current battery electrodes. Nano Lett. 9, 491–495 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl8036323
W. Shockley, H.J. Queisser, Detailed balance limit of efficiency of p-n junction solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 510–519 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1736034
M.K. Sahoo, S.P. Muduli, P. Kale, Tailoring electrical characteristics of Si-nanowires and etched Si by MACE temperature variation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1275 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10709-y
W.L. Sung, Y.S. Yang, Y. Li, Work-Function fluctuation of gate-all-around silicon nanowire n-MOSFETs: a unified comparison between cuboid and voronoi methods. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 9, 151–159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2020.3046608
S. Pinilla, R. Barrio, N. González, R. Pérez Casero, F. Márquez, J.M. Sanz, C. Morant, Role of Hydrogen in the preparation of amorphous silicon nanowires by metal-assisted chemical etching. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 22667–22674 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b05332
T.S. Orlova, A.V. Ankudinov, A.M. Mavlyutov, N.N. Resnina, Effect of grain boundaries on the electron work function of ultrafine grained aluminum. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 57, 110–115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/rams-2018-0053
G. Shao, Work function and electron affinity of semiconductors: doping effect and complication due to fermi level pinning. Energy Environ. Mater. 4, 273–276 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12218
F. Léonard, J. Tersoff, Role of fermi-level pinning in nanotube Schottky diodes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 4693–4696 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.4693
C. Canevali, M. Alia, M. Fanciulli, M. Longo, R. Ruffo, C.M. Mari, Influence of doping elements on the formation rate of silicon nanowires by silver-assisted chemical etching. Surf. Coatings Technol. 280, 37–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.08.013
C.P.Y. Wong, C. Troadec, A.T.S. Wee, K.E.J. Goh, Gaussian thermionic emission model for analysis of Au/Mo S2 Schottky–Barrier devices. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 54027 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.14.054027
N. Ngo, H. Niu, P. Bharadwaj, H. Bhatti, S. Adhikari, Van der Pauw resisitivity measurement. Tech. Rep. (2017). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.23468.67208
Y. Xu, T. Gong, J.N. Munday, The generalized Shockley–Queisser limit for nanostructured solar cells. Sci. Rep. 5, 13536 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13536
Funding
The research is a part of the project funded by SERB-DST, Govt. of India, with sanction no. CRG/2021/006956 dated 12-Mar-2022 under the Core Research Grant (CRG) scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SPM and MAK contributed to the conceptualization, experimentation, data collection, analysis, manuscript preparation, review, and editing. PK participated in the supervision, conceptualization, resources, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Muduli, S.P., Khan, M.A. & Kale, P. Interdependence of morphological attributes and optoelectronic properties of porous silicon-nanowires. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1977 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11314-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11314-9