Abstract
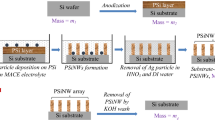
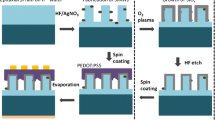
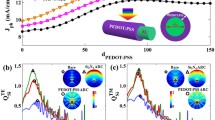
Si nanowires (SiNWs) are preferred over bulk Si for photovoltaics owing to near-zero optical reflection and band gap tunability. However, the cost-effective fabrication of phosphorus-doped SiNWs poses challenges. The work employs metal-assisted chemical etching for SiNW array fabrication and spin-on doping with P2O5 as the phosphorus source to form an n-type emitter. The P2O5 concentration in the phosphosilicate glass (PSG) sol–gel controls the phosphorus-doping level on the SiNWs. Morphological analysis detects a marginal reduction in the SiNW lengths with P2O5 concentration after PSG layer removal. The optical studies show a significant decrease of the average reflectance to 3.99% and a band gap of 1.59 eV for the optimized doping density (fabricated with a P2O5 concentration of 5 mM), leading to a 34.5% improvement in the ultimate efficiency. Raman asymmetric ratio and photoluminescence emission spectra elucidate the possible surface and bulk defects causing the recombination. The resistivity of the optimized phosphorus-doped SiNW array decreases to 3.37 Ω cm due to a significant increase in the donner concentration. The study compares various methods to estimate the internal cell resistances from the illuminated current–voltage measurement and considers the single-diode model accurate. The power conversion efficiency and the fill factor of the optimized solar cell are 4.09% and 43.4%, respectively, limited by the increased series resistance and decreased shunt resistance.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript.
References
P. Yu, J. Wu, S. Liu, J. Xiong, C. Jagadish, Z.M. Wang, Design and fabrication of silicon nanowires towards efficient solar cells. Nano Today. 11, 704–737 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2016.10.001
B. Zhang, J. Jie, X. Zhang, X. Ou, X. Zhang, Large-Scale Fabrication of Silicon Nanowires for Solar Energy Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 34527–34543 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b06620
M. Seo, S. Yoon, H. Cho, S. Lee, K. Kim, B.D. Kong, M. Meyyappan, C.K. Baek, Solar Cell using hourglass-shaped Silicon nanowires for increased light-trapping path. IEEE J. Photovoltaics. 10, 475–479 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOTOV.2020.2964329
A. Rahman, A. Ashraf, H. Xin, X. Tong, P. Sutter, M.D. Eisaman, C.T. Black, Sub-50-nm self-assembled nanotextures for enhanced broadband antireflection in silicon solar cells. Nat. Commun. 6, 5963 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6963
M.K. Sahoo, S.P. Muduli, P. Kale, Tailoring electrical characteristics of Si-nanowires and etched Si by MACE temperature variation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1275 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10709-y
V. Kashyap, C. Kumar, N. Chaudhary, N. Goyal, K. Saxena, Comparative study of quantum confinements effect present in Silicon Nanowires using absorption and Raman spectroscopy. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 121, 111538 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111538
Y. Yao, F. Li, S.T. Lee, Oriented silicon nanowires on silicon substrates from oxide-assisted growth and gold catalysts. Chem. Phys. Lett. 406, 381–385 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2005.03.027
Z. Huang, H. Fang, J. Zhu, Fabrication of silicon nanowire arrays with controlled diameter, length, and density. Adv. Mater. 19, 744–748 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200600892
H.P. Phan, T. Kozeki, T. Dinh, T. Fujii, A. Qamar, Y. Zhu, T. Namazu, N.T. Nguyen, D.V. Dao, Piezoresistive effect of p-type silicon nanowires fabricated by a top-down process using FIB implantation and wet etching. RSC Adv. 5, 82121–82126 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra13425k
R. Chandra Muduli, P. Kale, Chemically modified surface of silicon nanostructures to enhance hydrogen uptake capabilities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.06.030
J. Huang, S.Y. Chiam, H.H. Tan, S. Wang, W.K. Chim, Fabrication of silicon nanowires with precise diameter control using metal nanodot arrays as a hard mask blocking material in chemical etching. Chem. Mater. 22, 4111–4116 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm101121c
J. Yeom, D. Ratchford, C.R. Field, T.H. Brintlinger, P.E. Pehrsson, Decoupling diameter and pitch in silicon nanowire arrays made by metal-assisted chemical etching. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 106–116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201301094
S.P. Muduli, M.A. Khan, P. Kale, Structural Optimization of Si Nanowires for Ultimate Efficiency Improvement via tuning Optical properties. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-023-00474-4
M. Perego, F. Caruso, G. Seguini, E. Arduca, R. Mantovan, K. Sparnacci, M. Laus, Doping of silicon by phosphorus end-terminated polymers: drive-in and activation of dopants. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 10229–10237 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tc01856b
G. Dong, F. Liu, J. Liu, H. Zhang, M. Zhu, Realization of radial p-n junction silicon nanowire solar cell based on low-temperature and shallow phosphorus doping. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 1–17 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-8-544
X.X. Lin, X. Hua, Z.G. Huang, W.Z. Shen, Realization of high performance silicon nanowire based solar cells with large size. Nanotechnology. 24, 235402 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/23/235402
M.L. Hoarfrost, K. Takei, V. Ho, A. Heitsch, P. Trefonas, A. Javey, R.A. Segalman, Spin-on organic polymer dopants for silicon. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 4, 3741–3746 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jz4019095
B.R. Huang, Y.K. Yang, T.C. Lin, W.L. Yang, A simple and low-cost technique for silicon nanowire arrays based solar cells. Sol Energy Mater. Sol Cells. 98, 357–362 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLMAT.2011.11.031
L. Chu, S. Zhai, W. Ahmad, J. Zhang, Y. Zang, W. Yan, Y. Li, High-performance large-area perovskite photovoltaic modules. Nano Res. Energy. 1, e9120024 (2022). https://doi.org/10.26599/NRE.2022.9120024
Z. Wang, X. Yang, X. He, H. Xue, X. Wang, H. Dong, J. Zhu, W. Mao, X.L. Xu, X. Li, Roles of oxygen vacancy and ferroelectric polarization in photovoltaic effects of BiFeO3 based devices. Solid State Commun. 360, 115042 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2022.115042
B.R. Huang, Y.K. Yang, W.L. Yang, Efficiency improvement of silicon nanostructure-based solar cells. Nanotechnology. 25, 035401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/25/3/035401
S.P. Muduli, M.A. Khan, P. Kale, Interdependence of morphological attributes and Optoelectronic properties of Porous Silicon-Nanowires, Jouranl Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1977 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11314-9
A. Mohamed Elnahrawy, A. Ibrahim Ali, Influence of reaction conditions on Sol-Gel process producing SiO2 and SiO2-P2O5 gel and glass. New. J. Glas Ceram. 04, 42–47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4236/njgc.2014.42006
H. Wagner, A. Dastgheib-Shirazi, B. Min, A.E. Morishige, M. Steyer, G. Hahn, C. Del, T. Cañizo, P.P. Buonassisi, Altermatt, Optimizing phosphorus diffusion for photovoltaic applications: Peak doping, inactive phosphorus, gettering, and contact formation. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 185704 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4949326
S. Maurya, R.C. Muduli, P. Kale, Physical forces responsible for agglomeration of Silicon nanowires arrays synthesized by metal-assisted Chemical etching. Russ J. Phys. Chem. A 97, 1990–2000 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024423090224
P. Yogi, D. Poonia, S. Mishra, S.K. Saxena, S. Roy, V. Kumar, P.R. Sagdeo, R. Kumar, Spectral anomaly in Raman scattering from p-Type Silicon Nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 5372–5378 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b12811
M.K. Sahoo, P.G. Kale, Micro-raman study of growth parameter restraint for silicon nanowire synthesis using MACE. Superlattices Microstruct. 135, 106289 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2019.106289
B.G. Burke, J. Chan, K.A. Williams, Z. Wu, A.A. Puretzky, D.B. Geohegan, Raman study of Fano interference in p-type doped silicon. J. Raman Spectrosc. 41, 1759–1764 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2614
R. Plugaru, E. Fakhri, C. Romanitan, I. Mihalache, G. Craciun, N. Plugaru, H.O. Arnason, M.T. Sultan, G.A. Nemnes, S. Ingvarsson, H.G. Svavarsson, A. Manolescu, Structure and electrical behavior of silicon nanowires prepared by MACE process. Surf. Interfaces. 33, 102167 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102167
W.B. Yu, G. Ouyang, Geometry-dependent band shift and dielectric modification of nanoporous Si nanowires. Sci. Rep. 7, 14456 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14647-8
ASTM, Standard Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: Direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface, Astm. 03, (2013) 1–21. http://enterprise.astm.org/SUBSCRIPTION/filtrexx40.cgi?+REDLINE_PAGES/G173.htm (accessed June 27, 2023)
S.P. Muduli, P. Kale, State-of-the-art passivation strategies of c-Si for photovoltaic applications: a review. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 154, 107202 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.107202
A.P. Baraban, S.N. Samarin, V.A. Prokofiev, V.A. Dmitriev, A.A. Selivanov, Y. Petrov, Luminescence of SiO2 layers on silicon at various types of excitation. J. Lumin. 205, 102–108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.09.009
N. Ding, J. Xu, Q. Zhang, J. Su, Y. Gao, X. Zhou, T. Zhai, Controllable carrier type in Boron Phosphide nanowires toward Homostructural Optoelectronic devices, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 10296–10303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b17204
R. Venkatesan, J. Mayandi, J.M. Pearce, V. Venkatachalapathy, Influence of metal assisted chemical etching time period on mesoporous structure in as-cut upgraded metallurgical grade silicon for solar cell application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 8676–8685 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01191-6
M. Rahmani, L. Jerbi, A. Meftah, Strong photoluminescence enhancement of silicon nanowires by poly(3-hexylthiophene) deposition. J. Lumin. 217, 116805 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116805
G. Masetti, M. Severi, S. Solmi, B.-D. Silicon, Modeling of Carrier Mobility Against Carrier Concentration in Arsenic-, Phosphorus-, and, B.-D. Silicon. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 30(7), 764–769 (1983)
S.A. Moiz, A.N.M. Alahmadi, A.J. Aljohani, Design of Silicon Nanowire Array for PEDOT:PSS-Silicon Nanowire-based hybrid solar cell. Energies. 13, 3797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13153797
F. Ghani, M. Duke, J. Carson, Numerical calculation of series and shunt resistances and diode quality factor of a photovoltaic cell using the Lambert W-function. Sol Energy. 91, 422–431 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2012.09.005
E.L. Meyer, Extraction of Saturation Current and Ideality factor from measuring V Oc and I sc of Photovoltaic modules. Int. J. Photoenergy. 2017, 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8479487
Acknowledgements
The research is a part of the project funded by SERB-DST, Govt. of India, with sanction no. CRG/2021/006956 dated 12-Mar-2022 under the Core Research Grant (CRG) scheme. The authors thankfully acknowledge Subhasri Subudhi and Dr. Pitamber Mahanandia for the illuminated J-V measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sakti Prasanna Muduli: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft, review and editing, Validation, Visualization; Paresh kale: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Resources, Project administration, Writing—Conceptualization, review and editing, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Muduli, S.P., Kale, P. Effect of diffusion doping-induced defects on shunt resistance affecting Si-nanowire solar cell performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 430 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12190-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12190-7