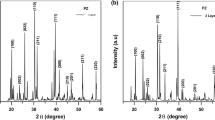
Abstract
In this study, the dielectric properties of PbZrO3 thin films are studied as a function of the water/acetic acid solvent ratio of the precursor sol–gel solution. By increasing the water ratio from 35/65 to 85/15, the saturation polarization increases from 24.3 to 27.2 µC/cm2 and the antiferroelectric–ferroelectric field transition (EAF) from 528 to 564 kV/cm. When the hydrolysis rate is higher, the antiferroelectric phase is stabilized due to a denser antiferroelectric matrix with lower defects. As the consequence, the energy storage performances are better for a higher hydrolysis rate: the recoverable energy density increases from 6.3 to 10 J/cm3 and the efficiency from 67 to 71%. A higher permittivity and lower dielectric losses confirm also the enhancement of the antiferroelectric matrix when increasing the amount of water in the precursor solution. In order to obtain better energy storage and dielectric properties, it is preferable to have a high ratio water/acetic acid in the precursor sol–gel solution.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available within the article.
References
G. Yi, M. Sayer, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402590
B.E. Yoldas, J. Mater. Sci. (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01117399
J. Phalippou, L. Kocon, Elaboration des gels et des aérogels. in Techniques de l′ingénieur. Génie des procédés, J2230 (2004)
C. Koch, I. Ovid’ko, S. Seal, S. Veprek, Structural Nanocrystalline Materials: Fundamentals and Applications (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2007).
C.J. Brinker, G.W. Scherer, Sol–Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol–Gel Processing (Academic press, Cambridge, 2013).
C. Sanchez, J. Livage, M. Henry, F. Babonneau, J. Non-Cryst, Solids (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(88)90007-5
C. Wolf, C. Rüssel, J. Mater. Sci. (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545451
G. Koster, M. Huijben, G. Rijnders, Epitaxial Growth of Complex Metal Oxides (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2015).
K. Sinkó, Materials (2010). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3010704
C.D. Lakeman, D.A. Payne, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. (1992). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1992.tb04392.x
J. Ge, D. Remiens, X. Dong, Y. Chen, J. Costecalde, F. Gao, F. Cao, G. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4896156
Y.Z. Li, Z.J. Wang, Y. Bai, Z.D. Zhang, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.11.063
M.D. Coulibaly, C. Borderon, R. Renoud, H.W. Gundel, Appl. Phys. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0017984
C.K. Kwok, S.B. Desu, Appl. Phys. Lett. (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.107312
M.D. Coulibaly, C. Borderon, R. Renoud, H.W. Gundel, Thin Solid Films (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2020.138432
T. Tani, J. Li, D. Viehland, D.A. Payne, J. Appl. Phys. (1994). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.356146
S. Kalpat, K. Uchino, J. Appl. Phys. (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1385580
Y. Zhao, H. Gao, X. Hao, Q. Zhang, Mater. Res. Bull. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.08.005
W. Zhu, W. Ren, H. Xin, P. Shi, X. Wu, J. Adv. Dielectr. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1142/S2010135X13500112
J.G. Bleazard, T.F. Sun, A.S. Teja, Int. J. Thermophys. (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01448214
V.R. Mudinepalli, L. Feng, W.C. Lin, B.S. Murty, J. Adv. Ceram. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-015-0130-8
T.M. Butler, B.D. MacCraith, C. McDonagh, J. Non-Cryst, Solids (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(97)00481-X
C.A. Milea, C. Bogatu, A. Duta, Bull. Transilv. Univ. Bras. Ser. I Eng. Sci. 4, 53 (2011)
C.W. Ahn, G. Amarsanaa, S.S. Won, S.A. Chae, D.S. Lee, I.W. Kim, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Interfaces (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b08786
C. Borderon, K. Nadaud, M.D. Coulibaly, R. Renoud, H.W. Gundel, Int. J. Adv. Res. Phys. Sci. 6(2), 1 (2019)
L. Padurariu, V.A. Lukacs, G. Stoian, N. Lupu, L.P. Curecheriu, Materials (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194386
D. Hanft, J. Exner, M. Schubert, T. Stöcker, P. Fuierer, R. Moos, J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. (2015). https://doi.org/10.4416/JCST2015-00018
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MDC contributed to conceptualization, methodology, and writing—review and editing. CB performed supervision, visualization, and writing—review and editing. RR performed supervision, visualization, and review and editing. HWG was involved in supervision and visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coulibaly, M.D., Borderon, C., Renoud, R. et al. Effect of zirconium hydrolysis degree on the dielectric properties of PbZrO3. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 15964–15970 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06146-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06146-4