Abstract
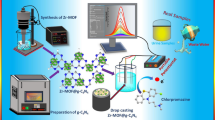
The hollow tin(IV) oxide (SnO2) nanoparticles prepared using a simple hydrothermal synthesis were served as a core for the fabrication of SnO2/polyaniline (PANI) nanocomposites using in situ chemical oxidative polymerization. The chemical and structure of the nanocomposites were characterized using Fourier transform infrared, X-ray diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy. The nanocomposites were then coated with nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) obtained by hydrothermal synthesis through electrostatic interaction. The catalytic behavior of nanocomposites modified glass carbon electrode towards dopamine (DA) has been investigated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry. The EIS test for prepared SnO2/PANI/N-GQD nanocomposites shows the very low charge-transfer resistance. The electrochemical performance of SnO2/PANI/N-GQD nanocomposites present the large peak currents, indicating the nanocomposites reveal better electrochemical activity of the presence of N-GQD. The SnO2/PANI/N-GQD nanocomposites contained linear response of detecting DA in the concentration range of 5 × 10−7–2 × 10−4 M with detection limit 2.2 × 10−7 M (S/N = 3). The fabricated nanocomposites also show excellent determination of DA at the presence of a mixture of l-ascorbic acid and uric acid. Because of the excellent electrochemical performance obtained in this report, we believe that the SnO2/PANI/N-GQD nanocomposites will be a promising biosensor material for the detection of dopamine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Robinson, A. Hermans, A.T. Seipel, R.M. Wightman, Monitoring rapid chemical communication in the brain. Chem. Rev. 108, 2554–2584 (2008)
A. Abbaspour, A. Khajehzadeh, A. Ghaffarinejad, A simple and cost-effective method as an appropriate alternative for visible spectrophotometry: development of a dopamine biosensor. Analyst 134, 1692–1698 (2009)
Y. Lin, C. Chen, C. Wang, F. Pu, J. Ren, X. Qu, Silver nanoprobe for sensitive and selective colorimetric detection of dopamine via robust Ag-catechol interaction. Chem. Commun. 47, 1181–1183 (2011)
V. Carrera, E. Sabater, E. Vilanova, M.A. Sogorb, A simple and rapid HPLC-MS method for the simultaneous determination of epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine: application to the secretion of bovine chromaffin cell cultures. J. Chromatogr. B 847, 88–94 (2007)
M. Liu, Q. Chen, C. Lai, Y. Zhang, J. Deng, H. Li, S. Yao, A double signal amplification platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen based on a nanocomposite of ferrocene thiolate stabilized Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles with graphene sheet. Biosens Bioelectron 48, 75–81 (2013)
E. Canbay, E. Akyilmaz, Design of a multiwalled carbon nanotube–Nafion–cysteamine modified tyrosinase biosensor and its adaptation of dopamine determination. Anal. Biochem. 444, 8–15 (2014)
W. Zhang, R. Yuan, Y.Q. Chai, Y. Zhang, S.H. Chen, A simple strategy based on lanthanum–multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposites for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and nitrite. Sensors Actuators B 166, 601–607 (2012)
H. Zhu, W. Wu, H. Zhang, L. Fan, S. Yang, Highly selective and sensitive detection of dopamine in the presence of excessive ascorbic acid using electrodes modified with C60-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube film. Electroanalysis 21, 2660–2666 (2009)
Y. Li, L. Zhang, M. Li, Z. Pan, D. Li, A disposable biosensor based on immobilization of laccase with silica spheres on the MWCNTs doped screen-printed electrode. Chem. Cent. J. 6, 103 (2012)
K. Min, Y.J. Yoo, Amperometric detection of dopamine based on tyrosinase-SWNTs-PPy composite electrode. Talanta 80, 1007–1011 (2009)
Z.H. Sheng, X.Q. Zheng, J.Y. Xu, W.J. Bao, F.B. Wang, X.H. Xia, Electrochemical sensor based on nitrogen doped graphene: simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Biosens Bioelectron 34, 125–131 (2012)
C. Xiao, X. Chu, Y. Yang, X. Li, X. Zhang, J. Chen, Hollow nitrogen-doped carbon microspheres pyrolyzed from self-polymerized dopamine and its application in simultaneous electrochemical determination of uric acid, ascorbic acid and dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 26, 2934–2939 (2011)
X. Zhou, P. Ma, A. Wang, C. Yu, T. Qian, S. Wu, J. Shen, Dopamine fluorescent sensors based on polypyrrole/graphene quantum dots core/shell hybrids. Biosens Bioelectron 64, 404–410 (2015)
S. Zhu, J. Zhang, C. Qiao, S. Tang, Y. Li, W. Yuan, B. Li, L. Tian, F. Liu, R. Hu, Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 47, 6858–6860 (2011)
J. Shen, Y. Zhu, X. Yang, C. Li, Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 48, 3686–3699 (2012)
L.S. Li, X. Yan, Colloidal graphene quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1, 2572–2576 (2010)
J. Peng, W. Gao, B.K. Gupta, Z. Liu, R. Romero-Aburto, L. Ge, L. Song, L.B. Alemany, X. Zhan, G. Gao, S.A. Vithayathil, B.A. Kaipparettu, A.A. Marti, T. Hayashi, J.J. Zhu, P.M. Ajayan, Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 12, 844–849 (2012)
L. Tang, R. Ji, X. Cao, J. Lin, H. Jiang, X. Li, K.S. Teng, C.M. Luk, S. Zeng, J. Hao, Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 6, 5102–5110 (2012)
C. Zhou, W. Jiang, B.K. Via, Facile synthesis of soluble graphene quantum dots and its improved property in detecting heavy metal ions. Colloids Surf. B 118, 72–76 (2014)
J.J. Liu, Z.T. Chen, D.S. Tang, Y.B. Wang, L.T. Kang, J.N. Yao, Graphene quantum dots-based fluorescent probe for turn-on sensing of ascorbic acid. Sensors Actuators B 212, 214–219 (2015)
J. Zhao, G. Chen, L. Zhu, G. Li, Graphene quantum dots-based platform for the fabrication of electrochemical biosensors. Electrochem. Commun. 13, 31–33 (2011)
H.T. Liu, Y.Q. Liu, D.B. Zhu, Chemical doping of graphene. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 3335–3345 (2011)
K.P. Gong, F. Du, Z.H. Xia, M. Durstock, L.M. Dai, Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays with high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction. Science 323, 760 (2009)
Y. Li, Y. Zhao, H. Cheng, Y. Hu, G. Shi, L. Dai, L. Qu, Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots with oxygen-rich functional groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 15–18 (2012)
P. Manivel, M. Dhakshnamoorthy, A. Balamurugan, N. Ponpandian, D. Mangalaraj, C. Viswanathan, Conducting polyaniline-graphene oxide fibrous nanocomposites: preparation, characterization and simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. RSC Adv 3, 14428–14437 (2013)
Z.M. Tahir, E.C. Alocilja, D.L. Grooms, Polyaniline synthesis and its biosensor application. Biosens Bioelectron 20, 1690–1695 (2005)
T.M. Wu, Y.W. Lin, C.S. Liao, Preparation and characterization of polyaniline/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites. Carbon 43, 734–740 (2005)
Z. Miao, P. Wang, A. Zhong, M. Yang, Q. Xu, S. Hao, X. Hu, Development of a glucose biosensor based on electrodeposited gold nanoparticles-polyvinylpyrrolidone-polyaniline nanocomposites. J Electroanal Chem 756, 153–160 (2015)
Ghanbari KH, Babaei Z, Fabrication and characterization of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on ternary NiO/CuO/polyaniline nanocomposite. Anal. Biochem. 498, 37–46 (2016)
Y. Xie, S. Yu, Y. Zhong, Q. Zhang, Y. Zhou, SnO2/graphene quantum dots composited photocatalyst for efficient nitric oxide oxidation under visible light. Appl Surf Sci 448, 655–661 (2018)
A. Wei, L. Pan, W. Huang, Recent progress in the ZnO nanostructure-based sensors. Mater Sci Eng B 176, 1409–1421 (2011)
J.F. Qian, P. Liu, Y. Xiao, Y. Jiang, Y.L. Cao, X.P. Ai, H.X. Yang, TiO2-coated multilayered SnO2 hollow microspheres for dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv Mater 21, 3663–3667 (2009)
N. Wang, X. Cao, Guo, Facile one-pot solution phase synthesis of SnO2 nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 12616–12622 (2008)
W. Wu, S. Zhang, J. Zhou, X. Xiao, F. Ren, C. Jiang, Controlled synthesis of monodisperse sub-100 nm hollow SnO2 nanospheres: a template- and surfactant-free solution-phase route, the growth mechanism, optical properties, and application as a photocatalyst. Chem. Eur. J. 17, 9708–9719 (2011)
Y.N. Hao, H.L. Guo, L. Tian, X. Kang, Enhanced photoluminescence of pyrrolic-nitrogen enriched graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv 5, 43750–43755 (2015)
H.J. Wang, F.Q. Sun, Y. Zhang, L.S. Li, H.Y. Chen, Q.S. Wu, J.C. Yu, Photochemical growth of nanoporous SnO2 at the air-water interface and its high photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 5641–5645 (2010)
Y.C. Lin, F.H. Hsu, T.M. Wu, Enhanced conductivity and thermal stability of conductive polyaniline/graphene composite synthesized by in situ chemical oxidation polymerization with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Synth. Met. 184, 29–34 (2013)
H.K. Chaudhari, D.S. Kelkar, Investigation of structure and electrical conductivity in doped polyaniline. Polym Int 42, 380–384 (1997)
J. Wang, Y. Li, J. Ge, B.P. Zhang, W. Wan, Improving photocatalytic performance of ZnO via synergistic effects of Ag nanoparticles and graphene quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 18645–18652 (2015)
Y. Li, Y. Jiang, T. Mo, H. Zhou, Y. Li, S. Li, Highly selective dopamine sensor based on graphene quantum dots self-assembled monolayers modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem 767, 84–90 (2016)
M. Bagherzadeh, S.A. Mozaffari, M. Momeni, Fabrication and electrochemical characterization of dopamine-sensing electrode based on modified graphene nanosheets. Anal. Methods 7, 9317–9323 (2015)
K.J. Huang, J.Z. Zhang, Y.J. Liu, L.L. Wang, Novel electrochemical sensing platform based on molybdenum disulfide nanosheets-polyaniline composites and Au nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B 194, 303–310 (2014)
L. Liu, S. Li, L. Liu, D. Deng, N. Xia, Simple, sensitive and selective detection of dopamine using dithiobis (succinimidyl propionate)-modified gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Analyst 137, 3794–3799 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) under Grand MOST 107-2212-E-005-020 and the Ministry of Education under the project of Innovation and Development Center of Sustainable Agriculture (IDCSA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, WF., Wu, TM. Electrochemical sensor based on conductive polyaniline coated hollow tin oxide nanoparticles and nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots for sensitively detecting dopamine. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 8449–8456 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01165-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01165-8