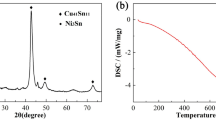
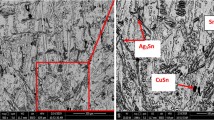
Abstract
Solidification behavior, melting range, microstructure evolution plus tensile characteristics of Sn-6.5Zn–0.3Cu–(x = 0.0, 1.0, 3.0) wt% Sb alloys have been researched [it is abbreviated as SZC–xSb]. Solidification behavior has supported by creating an insoluble intermetallic compounds (IMCs) which sacrificed themselves to act as additional nucleation embryos. Microstructure of the SZC–xSb alloys included black irregular stars of γ-Zn8 (Cu–Sn)5 besides dark gray polygons of new Sb2ZnSn IMC which have been created in solid solution of β-Sn phase. Furthermore, merging of Sb element enhanced most of tensile parameters as results of solid solution formation and uniformly dispersion of IMCs. Furthermore, Garofalo Model was employed to detriment the deformation mechanism from values of activation energy (Q) and stress exponent (n) of investigated alloys. The Q value of SZC–3.0Sb ally is more than SZC–1.0Sb and SZC–0.0Sb by 31.7% and 96.2%, respectively. The augment in Q values with increasing of Sb addition can be attributed to solid solution hardening and dispersion strengthening mechanisms. Based on values of Q and n the deformation mechanism can be proposed as a dislocation climb which dominating with dislocation pipe diffusion as well as lattice diffusion mechanism in range of tested temperature.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abtewa, G. Selvaduray, Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 27, 95–141 (2000)
K.J. Puttlitz, K.A. Stalter, Handbook of Lead-Free Solder Technology for Microelectronic Assemblies. (Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, 2004) pp. 292–294
K. N. Subramanian, “Lead-Free Electronic Solders”, A Special Issue of the Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (Springer Science Business Media, LLC, New York, 2007) pp. 191–210
I. Shohji, T. Yoshida, T. Takahashi, S. Hioki, Comparison of Low-melting lead free solders in tensile properties with Sn-Pb eutectic solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 15, 219–223 (2004)
A.B. El Basaty, A.M. Deghady, E.A. Eid, Influence of small addition of antimony (Sb) on thermal behavior, microstructural and tensile properties of Sn-9.0Zn-0.5Al Pb-free solder alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 701, (2017) 245–253 (2017)
G. Ren, I.J. Wilding, M.N. Collins, Alloying influences on low melt temperature Sn-Zn and Sn-Bi solder alloys for electronic interconnections. J. Alloy. Compd. 665, 251–260 (2016)
X. Wei, H. Huang, L. Zhou, M. Zhang, X. Liu On the advantages of using a hypoeutectic Sn–Zn as lead-free solder material. Mater. Lett. 61, 655–658 (2007)
A.A. El-Daly, A.E. Hammad, G.A. Al-Ganainy, A.A. Ibrahiem, Design of lead-free candidate alloys for low-temperature soldering applications based on the hypoeutectic Sn–6.5Zn alloy. Mater. Des. 56, 594–603 (2014)
V. Sarihan Temperature dependent viscoplastic simulation of controlled collapse under thermal cycling. J. Electron. Packag. 115, 16–21 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2909295
H.G. Song Jr., J.W. Morris, F. Hua Anomalous creep in Sn-rich solder joints. Mater. Trans. 43, 1847–1858 (2002) No.8 )
G. Ren, M.N. Collins, The effects of antimony additions on microstructures, thermal and mechanical properties of Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloys. Mater. Des. 119, 133–140 (2017)
A.A. El-Daly, W.M. Desoky, A.F. Saad, N.A. Mansor, E.H. Lotfy, H.M. Abd-Elmoniem, H. Hashem The effect of undercooling on the microstructure and tensile properties of hypoeutectic Sn–6.5Zn–xCu Pb-free solders. Mater. Des. 80, 152–162 (2015)
A.A. El-Daly, A.E. Hammad, G.A. Al-Ganainy, A.A. Ibrahiem Enhancing mechanical response of hypoeutectic Sn–6.5Zn solder alloy using Ni and Sb additions. Mater. Des. 52, 966–973 (2013)
A.A. El-Daly, H.A. Hashem, N. Radwan, F. El-Tantawy, T.R. Dalloul, N.A. Mansour, H.M. Abd-Elmoniem, E.H. Lotfy, Robust effects of Bi doping on microstructure development and mechanical properties of hypoeutectic Sn–6.5Zn solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 2950–2962 (2016)
G.S. AlGanainy, A.A. ElDaly, A. Fawzy, N. Hussein, Effect of adding nanometric ZnO particles on thermal, microstructure and tensile creep properties of Sn–6.5 wt% Zn–3 wt% In solder alloy” J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7166-1
A.M. Yassin, H.Y. Zahran, A.F. Abd El-Rehim Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles addition on the thermal, microstructural and room-temperature creep behavior of Sn-Zn based solder. J. Electron. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6624-8
I. Shafiq, Y.C. Chan, N.B. Wong, W.K.C. Yung, Influence of small Sb nanoparticles additions on the microstructure, hardness and tensile properties of Sn–9Zn binary eutectic solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 1427–1434 (2012)
L. Chen, G.Y. Li, An investigation of effects of Sb on the intermetallic formation in Sn–3.5Ag–0.7Cu solder joints. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 28(3), 534–541 (2005)
G.Y. Li, X.D. Bi, Q. Che, X.Q. Shi, Influence of dopant on growth of intermetallic layers in Sn-Ag-Cu solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 40(2), 165–175 (2011)
E.A. Eid, A.M. Deghady, A.N. Fouda, Enhanced microstructural, thermal and tensile characteristics of heat treated Sn-5.0Sb-0.3Cu (SSC-503) Pb-free solder alloy under high pressure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 743, 726–732 (2019)
Y.-C. Huang, S.-W. Chen, K.-S. Wu, Size and substrate effects upon undercooling of Pb-free solders. J. Electron. Mater. 39(1), 109–114 (2010)
J. Wu, S. Xue, J. Wang, S. Liu, Y. Han, L. Wang, Recent progress of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solders bearing alloy elements and nanoparticles in electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 12729–12763 (2016)
E.A. Eid, A.B. ElBasaty, A.M. Deghady, S. Kaytbay, A. Nassar, “Influence of nano metric Al2O3 particles addition on thermal behavior, microstructural and tensile characteristics of hypoeutectic Sn-5.0Zn-0.3Cu Pb-free solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00726-1
O. Zobac, J. Sopousek, J. Bursik, U.A. Zemanova, P. Roupcova, Experimental study of the Sb-Sn-Zn alloy systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2104-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eid, E.A., El-Khawas, E.H. & Abd-Elrahman, A.S. Impact of Sb additives on solidification performance, microstructure enhancement and tensile characteristics of Sn-6.5Zn-0.3Cu Pb-free solder alloy. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 6507–6518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00956-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00956-3