Abstract
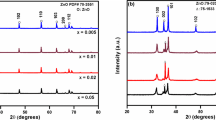
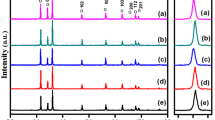
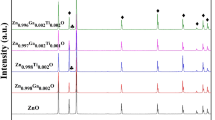
Thermoelectric properties, phase and microstructural investigation of (Zn1−x−yAlxGay)O, where x = 0.02, y = 0.04, 0.05 and x = 0.03, y = 0.01, 0.02 are studied at a high temperature of 1450 °C in this article. We have focused on the effects of sintering atmospheres on thermoelectric properties, phase, and microstructure in the air as well in the argon atmosphere. The Seebeck coefficient (S) and electrical resistivities (ρ) measured in air and argon atmospheres have an evidential large difference. The air sintered Al, Ga co-doped ZnO has higher power factor (S2σ) of the order 720.9 µW K− 2 m− 1 and lower electrical resistivity (ρ) of 5.803 mΩ cm for the nominal formula (Zn1− x−yAlxGay)O, with x = 0.03, y = 0.01 as compared to the power factor 543.6 µW K− 2 m− 1 and electrical resistivity of the order 1.550 mΩ cm at 692.2 °C sintered in the argon atmosphere at the same temperature i.e. 1450 °C. The power factor of the air sintered sample with x = 0.03, y = 0.01 is 1.4 times higher than the argon sintered sample with the same composition. The difference in power factors and electrical resistivities are linked to sintering atmospheres. We will investigate the effects of sintering atmospheres of the co-doped ZnO and will study thermoelectric properties, phase, and microstructures of the co-doped ZnO.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.L. Wang, J. Song, Science 312, 242 (2006)
J. Xu, J. Han, Y. Zhang, Y. Sun, B. Xie, Sens. Actuators B 132, 334 (2008)
F. Jiang, Z. Peng, Y. Zhang, X. Fu, J. Adv. Ceram. 2, 201 (2013)
T. Tsubota, M. Ohtaki, K. Eguchi, H. Arai, J. Mater. Chem. 7, 85 (1997)
C. Wood, D. Emin, Phys. Rev. B 29, 4582 (1984)
S. Yugo, T. Sato, T. Kimura, Appl. Phys. Lett. 46, 842 (1985)
G. Joshi, H. Lee, Y. Lan, X. Wang, G. Zhu, D. Wang, R.W. Gold, D.C. Cuff, M.Y. Tang, M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, Z. Ren, Nano Lett. 8, 4670 (2008)
X.W. Wang, H. Lee, Y.C. Lan, G.H. Zhu, G. Joshi, D.Z. Wang, J. Yang, A.J. Muto, M.Y. Tang, J. Klatsky, S. Song, M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, Z.F. Ren, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 193121 (2008)
V.F. Litvinenko, A.R. Kopan, Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 48, 77 (2009)
J.F. Nakahara, T. Takeshita, M.J. Tschetter, B.J. Beaudry, K.A. Gschneidner Jr., J. Appl. Phys. 63, 2331 (1988)
W. Macklin, P. Moseley, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 7, 111 (1990)
T.O. Mason, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 10, 257 (1991)
S. Teehan, H. Efstathiadis, P. Haldar, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 1094 (2011)
D. Bérardan, C. Byl, N. Dragoe., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 2352 (2010)
K. Park, H.K. Hwang, J.W. Seo, W.S. Seo, Energy 54, 139 (2013)
L. Fang, X.F. Yang, L.P. Peng, K. Zhou, F. Wu, Q.L. Huang, C.Y. Kong, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 23, 889 (2010)
D.B. Zhang, B.P. Zhang, D.S. Ye, Y.C. Liu, S. Li, J. Alloys Compd. 656, 784 (2016)
U. Holzwarth, N. Gibson, Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 534 (2011)
M. Deore, G. Jain, Int. J. Nanopart. 7, 57 (2014)
M.A.L. Nobre, S. Lanfredi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2284 (2003)
O. Bamiduro, H. Mustafa, R. Mundle, R.B. Konda, A.K. Pradhan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 252108 (2007)
L. Hui, Q. Hong, Y. Mingpeng, C. Xiaobai, Mater. Chem. Phys. 126, 866 (2011)
S.B. Zhang, S.H. Wei, A. Zunger, Phys. Rev. B 63, 075205 (2001)
H. Colder, E. Guilmeau, C. Harnois, S. Marinel, R. Retoux, E. Savary, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 2957 (2011)
L. Han, L.T. Hung, N.V. Nong, N. Pryds, S. Linderoth, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 1573 (2013)
Y. Kinemuchi, C. Ito, H. Kaga, T. Aoki., J. Mater. Res. 22, 1942 (2007)
S. Katsuyama, Y. Takagi, M. Ito, K. Majima, H. Nagai, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 1391 (2002)
K.H. Jung, K.H. Li, W.S. Seo, S.M. Choi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 253902 (2012)
J.P. Wiff, Y. Kinemuchi, H. Kaga, C. Ito, K. Watari, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 1413 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support extended by the key laboratory of advanced materials and state key laboratory of crystal materials, Shandong University. The financial support provided by the government of China under fundamental research fund (No. 2015TB019), Jinan 250100, People’s Republic of China is also highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matiullah, Wang, C., Su, W.B. et al. Effects of sintering atmospheres on thermoelectric properties, phase, microstructure and lattice parameters c/a ratio of Al, Ga dual doped ZnO ceramics sintered at high temperature. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 9555–9563 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8990-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8990-7