Abstract
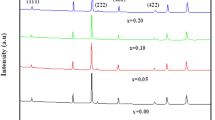
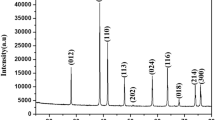
This study investigates the structural, electrical and microwave properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) which focuses on the parallel evolving relationship with their dependence on the sintering temperature. The iron oxide obtained from the steel waste product (mill scale) was used to synthesize YIG. The raw mill scale underwent the milling and Curie temperature separation technique to produce high purity iron oxide powder which is the main raw material in preparing and fabricating YIG through high energy ball milling (HEBM) process. Microstructural features such as amorphous phase, grain boundary, secondary phase and intergranular pores contribute significantly to the additional magnetic anisotropy and demagnetizing fields, affecting the electric and microwave properties accordingly. The increment in electrical resistivity and decrement in linewidth while the microstructure was evolving is believed to be a strong indicator of improved phase purity and compositional stoichiometry.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Cruickshank, 1–2 GHz dielectrics and ferrites: overview and perspectives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23, 2721–2726 (2003)
D.F. Gerald, O.E. Danial, Magnetic design for low field tunability of microwave ferrite resonators. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 4856–4858 (1999)
E. Schlomann, Behavior of ferrites in the microwave frequency range. J. Phys. 31, 443–451 (1971)
P.B.A. Fechine, H.H.B. Rocha, R.S.T. Moretzsohn, J.C. Denardin, R. Lavín, A.S.B. Sombra, (2009). Study of microwave ferrite resonator antenna, based on a ferrimagnetic composite (Gd3Fe5O12)GdIGx-(Y3Fe5O12)YIG1 – x. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 3, 1191–1198
I. Stanca, Magnetically tunable dielectric resonators and filters. J. Optoelectronics Adv. Mater. 6, 59–64 (2008)
W.R. Holmquist, C.F. Kooi, R.W. Moss, Reaction kinetics of polycrystalline yttrium iron garnet. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 44, 194–196 (1961)
F.S. Jesus, C.A. Cortes, R. Valenzuela, S. Ammarm, A.M. Bolarin-Miro, Synthesis of Y3Fe5O12 (YIG) assisted by high-energy ball miling. Ceram. Int. 38, 5257–5263 (2012)
Y. Ozturk, M.F. Ebeoglugil, E. Celik, I. Avgin, Characterization of cerium-doped yttrium iron garnet films prepared by sol–gel process. Adv. Nanoscale Magn. 122, 113–129 (2009)
Z. Abbas, R.M. Al-habashi, K. Khalid, Garnet ferrite (Y3Fe5O12) nanoparticles prepared via modified conventional mixong oxides (MCMO) method. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 36, 154–160 (2009)
S.H. Vajargah, H.R.M. Hosseini, Z.A. Nemati, Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline misch-metal-substituted yttrium iron garnet powder by the sol–gel combustion process. Int. J. Appl. Ceram Technol. 5, 464–468 (2008)
K.H.J. Buschow, Handbook of Magnetic Materials, 1st edn. (Elsevier B. V., Amsterdam, 2015)
R. Valenzuela, Magnetic Ceramics, 1st edn. (Cambridge University Press, New York, 1994)
M.N. Rahaman, Ceramic Processing and Sintering, 1st edn. (Marcel Dekker Inc Publication, New York, 1995)
R.S. Azis, M. Hashim, N.M. Saiden, N. Daud, N.N. Shahrani, Study the iron environments of the steel waste product and its possible potential applications in ferrites. Adv. Mater. Res. 1109, 295–299 (2015)
A. Feng, G. Wu, C. Pan, Y. Wang, The behavior of acid treating carbon fiber and the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of phenolic resin matrix composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17, 3859–3863 (2017)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, K. Wang, Y. Wang, A. Feng, Fabrication and characterization of OMMt/BMI/CE composites with low dielectric properties and high thermal stability for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 5592–5599 (2016)
W. Yan, W. Xinming, Z. Wenzhi, L. Chunyan, L. Jinhua, W. Yujing, Fabrication of flower-like Ni0.5Co0.5(OH)2@PANI and its enhanced microwave absorption performances. Mater. Res. Bull. 98, 59–63 (2018)
G. Wu, H. Wu, K. Wang, C. Zheng, Y. Wang, A. Feng, Facile synthesis and application of multi-shelled SnO2 hollow spheres in lithium ion battery. RSC Adv. 6, 58069–58076 (2016)
A. Feng, G. Wu, Y. Wang, C. Pan, Synthesis, preparation and mechanical property of wood fiber-reinforced poly(vinyl chloride) composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17, 3859–3863 (2017)
C. Pan, J. Zhang, K. Kou, Y. Zhang, G. Wu, Investigation of the through-plane thermal conductivity of polymer composites with in-plane oriented hexagonal boron nitride. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 120, 1–8 (2018)
T. Ramesh, G.N. Rao, T. Suneetha, R.S. Shinde, V. Rajendar, S.R. Murthy, S.A. Kumar, Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticles: sintering temperature effect on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4425-6
N.M.M. Shahrani, R.S. Azis, M. Hashim, J. Hassan, A. Zakaria, N. Daud, Effect of variation sintering temperature on magnetic permeability and grain sizes of Y3Fe5O12 via mechanical alloying technique. Mater. Sci. Forum 846, 395–402 (2016)
J. Smit, H.P.J. Wijn, Ferrites. (Philips Technical Library, Eindhovan, 1959), pp. 221–245
C.D. Veitch, Synthesis of polycrystalline yttrium iron garnet and yttrium aluminium garnet from organic precursors. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 6527–6532 (1991)
R. Chen, J. Zhou, L. Zheng, H. Zheng, P. Zheng, Z. Ying, J. Deng, Two-step sintering behavior of sol–gel derived dense and submicron-grained YIG ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6080-5
M.A. Musa, R.S. Azis, N.H. Osman, J. Hassan, T. Zangina, Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) and yttrium aluminum iron garnet (YAlG) nanoferrite via sol-gel synthesis. Results Phys. 7, 1135–1142 (2017)
R. Nazlan, M. Hashim, I.R. Ibrahim, F.M. Idris, W.N.W.A. Rahman, N.H. Abdullah, I. Ismail, S. Kanagesan, Z. Abbas, R.S. Azis, Influence of indium substitution and microstructure changes on the magnetic properties evolution of Y3Fe5 – xInxO12 (x = 0.0–0.4). J. Mater. Sci. 26, 3596–3609 (2015)
A. Goldman, (2006) Modern Ferrite Technology. (Springer Science and Business Media, Inc., Pittsburgh)
T.A. Ring, Fundamentals of Ceramic Powder Processing and Synthesis, 1st edn. (Academic Press. Inc. Publication, New York, 1996)
H.M. Widatallah, C. Johnson, S.H. Al-Harthi, A.M. Gismelseed, A.D. Al-Rawas, S.J. Stewart, M.E. Elzain, I.A. Al-Omari, A.A. Yousif, A structural and mössbauer study of Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticles prepared with high energy ball milling and subsequent sintering. Hyperfine Interact. 183, 87–92 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Graduate Putra Grants UPM Malaysia Vot. Nos. 9539100 and 9541600 for its financial assistance. The authors also would like to thank the Department of Physics of the Faculty of Science, UPM and the Materials Synthesis and Characterization Laboratories (MSCL), ITMA, UPM for the measurements facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azis, R.S., Syazwan, M.M., Shahrani, N.M.M. et al. Influence of sintering temperature on the structural, electrical and microwave properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 8390–8401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8850-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8850-5