Abstract
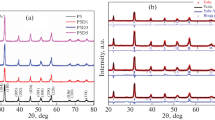
The present work describes the systematic study on inducing multiferroic properties in non-magnetic Dy2O3 system. The ceramic compounds of Dy2−xFexO3 (where x = 0.1–1.5) have been prepared by solid state reaction method. The powder X-ray diffraction patterns of all the prepared compounds reveal the strong influence of transition metal ion (Fe) in the Dy2O3 crystal structure. By Rietveld analysis, it is determined that with respect to increasing concentration of Fe3+ ion at Dy3+ site leads to transformation of crystal structure from Cubic to Orthorhombic with varying concentration of DyFeO3 phase and further increase in Fe3+ concentration leads to the formation of Garnet phase in Dy2−xFexO3 compounds. The scanning electron microscopic images of the samples confirm the change in surface morphology with increasing grain boundaries and porosity due to the substitution of Fe in Dy2O3 system which may effects on the electrical transport properties of the materials and increasing concentration of Fe in Dy2O3 system is also analyzed by energy dispersive analysis spectra. By Raman spectral analysis, it is identified that the strong absorption band of Cubic Dy2O3 compound at 373 cm−1 is gradually shifted to 257 cm−1 which indicates the molecular stretching motion of RE–O bond in REO6 octahedra and the large deviation in position of intense Raman bands below 300 cm−1 confirms the incorporation of Fe3+ ion in the host Dy2O3 lattice and imparting large polarizability in the prepared compounds due to translational motions of ReO6 octahedrons by variation in bond length and reduced mass of the bonding atoms. Diffused reflectance spectroscopy analysis implies the semiconducting nature of all the prepared compounds. It is also identified that the energy gap values goes on decreasing till DyFeO3 and then starts increasing due to change in crystal structure by cubic to orthorhombic and then orthorhombic to garnet phase. From the magnetization studies, it is found that till even substitution of Fe (i.e. x = 0.1–0.9) in Dy2−xFexO3 system, the compounds exhibits paramagnetic nature whereas from x = 1.0 i.e. DyFeO3, the samples exhibits ferromagnetic nature. The variation of magnetization behaviour from paramagnetic to ferromagnetic in higher concentration of Fe explicit the feasibility of attaining ferroic behaviour in Garnet mixed phase ceramic compounds. The electric polarization analysis reveal that while substituting Fe3+ ion in Dy3+ site by more than 50% of molecular ratio, the compounds exhibits non-zero remanance and coercivity values with respect to applied d.c. electric field and evident peculiar ferroelectric characteristic of those compounds. The maximum saturation polarization achieved in Dy0.6Fe1.4O3 compound is 0.2 µC/cm2 and found comparable with the results observed from Bismuth Ferrite related compounds.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Schmid, Ferroelectrics 162, 317–338 (1994)
J. Wang, J.B. Neaton, H. Zheng, V. Nagarajan, S.B. Ogale, B. Liu, D. Viehland, V. Vaithyanathan, D.G. Schlom, U.V. Waghmare, N.A. Spaldin, K.M. Rabe, M. Wuttig, R. Ramesh, Science 299, 1719–1722 (2003)
T. Kimura, T. Goto, H. Shintani, K. Ishizaka, T. Arima, Y. Tokura, Nature 426, 55–58 (2003)
N. Hur, S. Park, P.A. Sharma, J.S. Ahn, S. Guha, S.-W. Cheong, Nature 429, 392–395 (2004)
C. Ederer, N.A. Spaldin, Phys. Rev. B 71, 060401 (2005)
S.T. Shen, H.S. Weng, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 37, 2654–2661 (1998)
V.V. Kharton, A.A. Yaremchenko, A.V. Kovalevsky, A.P. Viskup, E.N. Naumovich, P.F. Kerko, J. Membr. Sci 163, 307–317 (1999)
V.V. Kharton, A.A. Yaremchenko, E.N. Naumovich, J. Solid State Electrochem. 3, 303–326 (1999)
D. Kuscer, M. Hrovat, J. Holc, S. Bernik, D. Kolar, J. Power Sources 61, 161–165 (1996)
E. Traversa, S. Matsushima, G. Okada, Y. Sadaoka, Y. Sakai, W. Watanabe, Sensors and Actuators B 25, 661–664 (1995)
D.S. Schmool, N. Keller, M. Guyot, R. Krishnan, M. Tessier, J. Appl. Phys 86, 5712–5717 (1999)
H. Sakakima, M. Satomi, E. Hirota, H. Adachi, IEEE Trans. Magn. 35, 2958–2960 (1999)
V. Anbarasu, A. Manigandan, S. Sathiyakumar, K. Kaliyaperumal, K. Jayabalan, J. Rare Earths 27, 1013–1017 (2009)
V. Anbarasu, A. Manigandan, T. Karthik, K. Sivakumar, J. Mater. Sci. 23, 1201–1209 (2012)
M. Ristic, S. Popovic, I. Czako-Nagy, S. Music. Mater. Lett. 27, 337–341 (1996)
H.I. Adiguzel, M.A. Aksan, M.E. Yakinci, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 207, 258–264 (2008)
A. Ubaldini, M.M. Carnasciali, J. Alloys Compd. 454, 374–378 (2008)
Fu Xiaojian, Xu Yuanda, Ji Zhou, J. Mater. Sci. 47, 1697–1701 (2012)
Abrashev, Todorov, Geshev, J. Appl. Phys. 116, 103508 (2014)
H. Zhang, Q. Yang, B. Zhang, L. Shenzhou, J Raman Spectrosc. 42, 1384–1387 (2011)
J. Torrent, V. Barron, Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of iron oxides. Encycl. Surf. Colloid Sci. 1, 1438–1446 (2002)
S. Jie, L. Xiaomei, C. Zhang, J. Zhang, S. Peng, W. Xiaobo, K. Min, F. Huang, J. Zhu, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 3488–3492 (2011)
Y.P. Wang, L. Zhou, M.F. Zhang, X.Y. Chen, J.-M. Liu, Z.G. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1731–1733 (2004)
K. Jawahar, R.N.P. Choudhary, Solid State Commun. 142, 449–452 (2007)
I. Coondoo, N. Panwar, A.K. Jha, Phys. B 406, 374–381 (2011)
K. Kamala Bharathi, J. Arout Chelvane, G. Markandeyulu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3677–3680 (2009)
P. Singh, A. Roy, A. Garg, R. Prasad, J. Appl. Phys. 117, 184104 (2015)
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Department of Science and Technology – Science and Engineering Research Board (DST – SERB) for the financial support (SERB/F/4297/2013-14 dated 04.10.2013) provided to carry out the research work. Authors would like to thank Dr. N V. Giridharan, Assistant Professor, Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli 620 015 for providing Electric Polarization facility. The authors thank Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Facility (SAIF), Indian Institute of Technology–Madras, Chennai–600036 and Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF), Pondicherry University, Puducherry for providing necessary facilities to carry out the characterization work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anbarasu, V., Dhilip, M., Saravana Kumar, K. et al. Effect of trivalent transition metal ion substitution in multifunctional properties of Dy2O3 system. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 8976–8985 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6628-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6628-9