Abstract
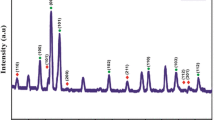
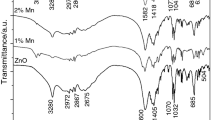
In this present study, we have reported the synthesis of ZnMn2O4, transitional metal oxide by sol–gel method. The structural and morphological properties are confirmed using various characterization techniques namely XRD, FT-IR and SEM with EDX. Dielectric studies of ZnMn2O4 are measured at the frequency varying from 50 Hz to 5 MHz for the temperature range of 303–573 K. The temperature dependent electrical parameters like impedance and modulus exhibit a strong correlation with the grains, grain boundaries and space charge effects in the synthesized material. Diffusion of oxygen vacancies in the dipoles and defects in the material due to oxygen vacancy complexes are investigated by the activation energy obtained from Arrhenius plot. It was found that the relaxation process was dominated by the hopping mechanism between the Mn3+ and Mn4+. Nyquist plot of impedance was attributed to the existence of space charge interface, grain boundary and grain conduction mechanism of the material.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Gherbi, Y. Bessekhouad, M. Trari, Structure, optical and transport properties of Mg-doped ZnMn2O4. J. Alloys Compd. 655, 188–197 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.192
P. Zhang, X. Li, Q. Zhao, S. Liu, Synthesis and optical property of one- dimensional spinel ZnMn2O4 nanorods. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 323 (2011). doi:10.1186/1556-276X-6-323
S.V. Lakshmi, S. Pauline, Structural, morpological and optical properties of hetarolite—ZnMn2O4 nano particle by hydrothermal method. Int. J. Sci. Res. 3, 8–9 (2014)
Y. Deng, S. Tang, Q. Zhang, Z. Shi, L. Zhang, S. Zhan et al., Controllable synthesis of spinel nano-ZnMn2O4 via a single source precursor route and its high capacity retention as anode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 11987 (2011). doi:10.1039/c1jm11575h
R.N. Jadhav, V. Puri, Effect of film thickness and pH of zinc manganite on microwave absorption and complex permittivity. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 44, 1426–1428 (2014). doi:10.1080/15533174.2013.809744
F. Méndez-martínez et al., Znx−1CuxMn2O4 spinels; synthesis, structural characterization and electrical evaluation. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 54(1), 2–6 (2010)
M. Khairy, M.A. Mousa, Electrical and catalytic properties of gamma-irradiated and unirradiated ZnMn2O4 nanoparticles. Am. J. Chem. 2(6), 306–311 (2012)
J. Takahashi, A. Miura, H. Itoh, K. Sawayama, T. Akazawa, Phase change and electrical resistivity of Zn–Mn–Ni–O-based NTC thermistors produced using IZC powder recycled from used dry batteries. Ceram. Int. 34, 853–857 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.09.035
C.C. Wang, C.M. Lei, G.J. Wang, X.H. Sun, T. Li, Oxygen-vacancy-related dielectric relaxations in SrTiO3 at high temperatures. J. Appl. Phys. 094103, 1–10 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4794349
C. Elissalde, J. Ravez, Ferroelectric ceramics: defects and dielectric relaxations. J. Mater. Chem. (2001). doi:10.1039/b010117f
Y. Bessekhouad, M. Trari, Photocatalytic hydrogen production from suspension of spinel powders AMn2O4 (A = Cu and Zn). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 27, 357–362 (2002)
J. Xu, Z. Yang, Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, H.U.A. Wang, Bipolar resistive switching behaviours in ZnMn2O4 film deposited on p+-Si substrate by chemical solution deposition. Bull. Mater. Sci. 37, 1657–1661 (2014)
P. Li, J. Liu, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Z. Li, W. Wu et al., Three-dimensional ZnMn2O4/porous carbon framework from petroleum asphalt for high performance lithium-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 180, 164–172 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2015.08.095
C. Dong, PowderX: Windows-95-based program for powder X-ray diffraction data processing. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 32(4), 838 (1999)
J. Langford II, A.J.C. Wilson, Scherrer after sixty years: a survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 11(2), 102–113 (1978). doi:10.1107/S0021889878012844
N. Kumari, V. Kumar, S.K. Singh, Structural, dielectric and magnetic investigations on Al3+ substituted Zn ferrospinels. RSC Adv. 5, 37925–37934 (2015). doi:10.1039/C5RA03745J
H. Rahmouni, M. Smari, B. Cerif, E. Dhahri, K. Khirouni, Conduction mechanisum, impedance spectroscopic investigation and dielectric behavior of La0.5Ca0.5-xAgxMnO3 manganites with the composition below the concentration limit of silver solubility in perovskites (0 < x<0.2). Dalton Trans. (2015). doi:10.1039/C5DT00444F
S. Singh, S.E. Shirsath, Structural phases and Maxwell–Wagner relaxation in magnetically soft-ZnFe2O4 and hard-Sr2Cu2Fe12O22 nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.023
O. Padmaraj, M. Venkateswarlu, N. Satyanarayana, Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of spinel type MgAl2O4 nanocrystalline ceramic particles synthesized by the gel-combustion method. Ceram. Int. 41, 3178–3185 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.10.169
T. Javed, A. Maqsood, Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of Co–Mn spinel nanoferrites prepared by co-precipitation technique. J Supercond. Nov. Magn. 4, 2137–2144 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10948-011-1168-7
C. Sujatha, K.V. Reddy, K.S. Babu, A.R. Chandra, M.B. Suresh, K.H. Rao, Effect of Co substitution of Mg and Zn on electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74, 917–923 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jpcs.2013.02.005
M. Gerstl, E. Navickas, M. Leitgeb, G. Friedbacher, F. Kubel, J. Fleig, The grain and grain boundary impedance of sol-gel prepared thin layers of yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ). Solid State Ion. 225, 732–736 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2012.02.012
M. Gerstl, E. Navickas, G. Friedbacher, F. Kubel, M. Ahrens, J. Fleig, The separation of grain and grain boundary impedance in thin yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) layers. Solid State Ion. 185, 32–41 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2011.01.008
W. Chen, W. Zhu, C. Ke, Z. Yang, L. Wang, X.F. Chen et al., Impedance spectroscopy and conductivity mechanism of CoFe2O4–Pb(Zr 0.53Ti0.47)O3 composite thick films. J. Alloys Compd. 508, 141–146 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.08.029
A. Mekap, P.R. Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, Dielectric, magnetic and electrical properties of ZnFe2O4 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 4757–4763 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10854-013-1470-1
L.S. Lobo et al., Investigation of electrical studies of spinel FeCo2O4 synthesized by sol-gel method. Superlattices Microstruct. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2015.09.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lobo, L.S., Ruban Kumar, A. Investigation of structural and electrical properties of ZnMn2O4 synthesized by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 7398–7406 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4714-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4714-z