Abstract
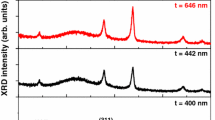
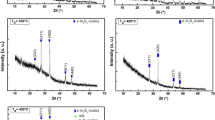
β-In2S3 thin films with different concentrations of Cu incorporation have been grown on glass substrates using vacuum thermal evaporation method. The influences of the Cu incorporation on the structural, optical and electrical properties of In2S3 thin films have been investigated. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study suggests the incorporated Cu will exist as Cu+ or Cu0. XRD analyses reveal that Cu doping will neither change the structure of In2S3 nor lead to any formation of new crystalline compounds. Scanning electron microscope views show that the surfaces of the films are flat and dense, and that the grain size increases after Cu doping. The refractive index n of the In2S3 thin films which is extracted from spectroscopic ellipsometry measurements shows a slight reduction in the long-wavelength region and a little enhancement in the short-wavelength region after Cu doping. It is also found that the band gap of the thin films is indirect and slightly increases from 1.90 to about 2.02 eV after Cu doping. Electrical measurements indicate that the incorporation of Cu will lead to n-type doping and a decrease of resistivity of the thin films.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Barreau, A. Mokrani, F. Couzinié-Devy et al., Bandgap properties of the indium sulfide thin-films grown by co-evaporation. Thin Solid Films 517(7), 2316–2319 (2009)
M. Amlouk, M.A.B. Said, N. Kamoun et al., Acoustic properties of β-In2S3 thin films prepared by spray. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38(26), 26–30 (1999)
Y. Liu, H. Xu, Y. Qian, Double-source approach to In2S3 single crystallites and their electrochemical properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 6(6), 1304–1307 (2006)
K.S.J.B.M. Kambas, Far infrared and Raman optical study of α- and β-In2S3 compounds. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 105(1), 291–296 (1981)
N. Barreau, Indium sulfide and relatives in the world of photovoltaics. Sol. Energy 83(3), 363–371 (2009)
M. Mathew, M. Gopinath, C.S. Kartha et al., Tin doping in spray pyrolysed indium sulfide thin films for solar cell applications. Sol. Energy 84(6), 888–897 (2010)
A. Timoumi, H. Bouzouita, B. Rezig, Optical constants of Na-In2S3 thin films prepared by vacuum thermal evaporation technique. Thin Solid Films 519(21), 7615–7619 (2011)
M. Mathew, C. Sudha Kartha, K.P. Vijayakumar, IN2S3:Ag, an ideal buffer layer for thin film solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20(S1), 294–298 (2009)
N. Kamoun, S. Belgacem, M. Amlouk et al., Structure, surface composition, and electronic properties of β-In2S3 and β-In2−xAlxS3. J. Appl. Phys. 89(5), 2766–2771 (2001)
W.T. Kim, W.S. Lee, C.S. Chung et al., Optical properties of In2S3:Co2+ single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 63(11), 5472–5475 (1988)
S. Acharya, M. Dutta, S. Sarkar et al., Synthesis of micrometer length indium sulfide nanosheets and study of their dopant induced photoresponse properties. Chem. Mater. 24(10), 1779–1785 (2012)
N. Barreau, C. Deudon, A. Lafond et al., A study of bulk NaxCu1−xIn5S8 and its impact on the Cu(In, Ga)Se2/In2S3 interface of solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90(12), 1840–1848 (2006)
J. Lee, H. Lee, S. Seo et al., Characterization of undoped and Cu-doped ZnO films for surface acoustic wave applications. Thin Solid Films 398–399, 641–646 (2001)
H. Tao, S. Mao, G. Dong et al., Raman scattering studies of the Ge-In sulfide glasses. Solid State Commun. 137(8), 408–412 (2006)
E. Kärber, K. Otto, A. Katerski et al., Raman spectroscopic study of In2S3 films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 25, 137–142 (2014)
M.G. Sandoval-Paz, M. Sotelo-Lerma, J.J. Valenzuela-Jáuregui et al., Structural and optical studies on thermal-annealed In2S3 films prepared by the chemical bath deposition technique. Thin Solid Films 472(1–2), 5–10 (2005)
J. Sterner, M.J. Malmstr, L. Stolt, Study on ALD In2S3/Cu(In, Ga)Se2 interface formation. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 13(3), 179–193 (2005)
P. Rao, S. Kumar, Growth of stoichiometric indium sulfide films by thermal evaporation: influence of vacuum annealing on structural and physical properties. Thin Solid Films 524, 93–99 (2012)
N.S. Orlova, I.V. Bodnar, E.A. Kudritskaya, Crystal growth and properties of the CuIn5S8 and AgIn5S8 compounds. Cryst. Res. Technol. 33(1), 37–42 (1998)
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61006003, 61306120, 61340051, and 61076063), and Natural Science Foundation of Fujian (Grant No. 2014J05073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Yu, J., Cheng, S. et al. Investigation of structural, optical and electrical properties of Cu doped β-In2S3 thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 5810–5817 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4496-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4496-3