Abstract
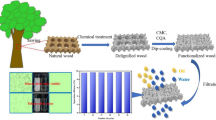
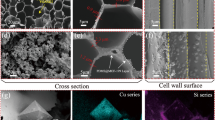
Due to frequent industrial wastewater discharge and oil spills, there is a need to develop sustainable and efficient absorbents and treatment methods. Herein, based on the unique microstructure of wood and functional requirements, super-hydrophobic, recyclable, and renewable wood sponges (SHWSs) with an ultralight density (35.4 mg cm−3) and high porosity (98.68%) were prepared from anisotropic natural balsa wood via a scalable and sustainable silanization reaction using liquid-phase deposition (LPD). The super-hydrophobicity of the SHWSs (contact angle = 159.2°) was due to the formation of polysiloxanes on the surface via silanization. The internal contact angle (CA) reached 137.2°, which was attributed to the uniformity of LPD. The SHWSs exhibited a high absorption capacity for various organic solvents and oils (23–60 g g−1) and reusability, allowing it to reach a contact angle of 150.8° and an absorption capacity of 52 g g−1 for CCl4 after 50 absorption cycles. The SHWSs also showed excellent super-hydrophobicity under acidic, alkaline, and saline conditions, as well as in hot water, demonstrating their excellent durability. A continuous oil/water separation device was made by using the SHWSs, which showed a high separation efficiency, with a flux rate of up to 72.8 L h−1 g−1. This green strategy for treating natural balsa wood with LPD provides a scalable way to produce sustainable oil/water separation materials while also developing high-value-added applications of natural balsa wood.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kang L, Wang B, Zeng J, Cheng Z, Li J, Xu J, Gao W, Chen K (2019) Degradable dual superlyophobic lignocellulosic fibers for high-efficiency oil/water separation. Green Chem 22:504–512
Li L, Zhang J, Wang A (2018) Removal of organic pollutants from water using superwetting materials. Chem Rec 18:118–136
MingBang W, Sheng H, TingYu L, Jian W, Seema A, Andreas G, ZhiKang X (2020) Compressible carbon sponges from delignified wood for fast cleanup and enhanced recovery of crude oil spills by joule heat and photothermal effect. Adv Funct Mater 31:504–512
Bo F, Qiqi Y, Fan Y (2020) Flexible underwater oleophobic cellulose aerogels for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Omega 5:9984–9994
Wang K, Liu X, Tan Y, Zhang W, Zhang S, Li J (2019) Two-dimensional membrane and three-dimensional bulk aerogel materials via top-down wood nanotechnology for multibehavioral and reusable oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 371:769–780
Yue X, Li Z, Zhang T, Yang D, Qiu F (2019) Design and fabrication of superwetting fiber-based membranes for oil/water separation applications. Chem Eng J 364:292–309
Hu L, Xiaoyu C, Yanjun Z, Dianbo Z, Ye Z, Chunfeng W, Caofeng P, Chuntai L, Changyu S (2021) Lightweight, superelastic, and hydrophobic polyimide nanofiber/mxene composite aerogel for wearable piezoresistive sensor and oil/water separation applications. Adv Funct Mater 31:2008006. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202008006
Ji Z, Enhui D, Yu H, Yunde F, Yong Y, Bin T (2020) Preparation of carbonized kapok fiber/reduced graphene oxide aerogel for oil-water separation. Chem Eng Technol 43:2418–2427
Yeh SK, Tsai YB, Gebremedhin KF, Chien TY, Chang RY, Tung KL (2021) Preparation of polypropylene/high-melt-strength PP open-cell foam for oil absorption. Polym Eng Sci 61:1139–1149
Wu M-B, Zhang C, Pi J-K, Liu C, Yang J, Xu Z-K (2019) Cellulose nanocrystals as anti-oil nanomaterials for separating crude oil from aqueous emulsions and mixtures. J Mater Chem A 7:7033–7041
Li Y, Zhu L, Grishkewich N, Tam KC, Yuan J, Mao Z, Sui X (2019) CO2-responsive cellulose nanofibers aerogels for switchable oil–water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:9367–9373
Yu W, Wang C, Yi Y, Wang H, Zeng L, Li M, Yang Y, Tan Z (2020) Comparison of deep eutectic solvents on pretreatment of raw ramie fibers for cellulose nanofibril production. ACS Omega 5:5580–5588
Xu Y, Ma S, Liu C, Wang L, Wang H, Xu W, Zhuang Y, Yang H (2021) Wood-inspired polyacrylonitrile foam with hierarchically aligned porous structure for application in water purification. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.50870
Zhu M, Li Y, Chen G, Jiang F, Yang Z, Luo X, Wang Y, Lacey SD, Dai J, Wang C (2017) Tree-inspired design for high-efficiency water extraction. Adv Mater 29:1704107. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704107
Che W, Xiao Z, Wang Z, Li J, Wang H, Wang Y, Xie Y (2019) Wood-based mesoporous filter decorated with silver nanoparticles for water purification. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:5134–5141
Li T, Li SX, Kong W, Chen C, Hitz E, Jia C, Dai J, Zhang X, Briber R, Siwy Z (2019) A nanofluidic ion regulation membrane with aligned cellulose nanofibers. Sci Adv 5(2):eaau4238. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aau4238
Jianwei S, Chaoji C, Shuze Z, Mingwei Z, Jiaqi D, Upamanyu R, Yiju L, Yudi K, Yongfeng L, Nelson Q, Yonggang Y, Amy G, H LU, A BH, Y ZJ, Azhar V, Heng L, L MM, Zheng J, Ashlie M, Teng L, Liangbing H, (2018) Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material. Nature 554:224–228
Li T, Song J, Zhao X, Yang Z, Pastel G, Xu S, Jia C, Dai J, Chen C, Gong A, Jiang F, Yao Y, Fan T, Yang B, Wågberg L, Yang R, Hu L (2018) Anisotropic, lightweight, strong, and super thermally insulating nanowood with naturally aligned nanocellulose. Sci Adv 4(3):eear3734. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar3724
Qiliang F, Farhan A, Qi Z, A BL, (2018) Wood nanotechnology for strong, mesoporous, and hydrophobic biocomposites for selective separation of oil/water mixtures. ACS Nano 12(3):2222–2230
Chen C, Kuang Y, Zhu S, Burgert I, Keplinger T, Gong A, Li T, Berglund L, Eichhorn SJ, Hu L (2020) Structure–property–function relationships of natural and engineered wood. Nat Rev Mater 5:642–666
Wu M-B, Hong Y-M, Liu C, Yang J, Wang X-P, Agarwal S, Greiner A, Xu Z-K (2019) Delignified wood with unprecedented anti-oil properties for the highly efficient separation of crude oil/water mixtures. J Mater Chem A 7:16735–16741
Chen C, Song J, Zhu S, Li Y, Kuang Y, Wan J, Kirsch D, Xu L, Wang Y, Gao T (2018) Scalable and sustainable approach toward highly compressible, anisotropic, lamellar carbon sponge. Chem 4:544–55423
Jia C, Chen C, Kuang Y, Fu K, Wang Y, Yao Y, Kronthal S, Hitz E, Song J, Xu F (2018) From wood to textiles: top-down assembly of aligned cellulose nanofibers. Adv Mater 30:1801347. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201801347
Garemark J, Yang X, Sheng X, Cheung O, Sun L, Berglund LA, Li Y (2020) Top-down approach making anisotropic cellulose aerogels as universal substrates for multifunctionalization. ACS Nano 14:7111–7120
Berglund LA, Burgert I (2018) Bioinspired wood nanotechnology for functional materials. Adv Mater 30:1704285. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704285
Borrega M, Ahvenainen P, Serimaa R, Gibson L (2015) Composition and structure of balsa (Ochroma pyramidale) wood. Wood Sci Technol 49:403–420
Borrega M, Gibson LJ (2015) Mechanics of balsa ( Ochroma pyramidale ) wood. Mech Mater 84:75–90
Li Z, Chen C, Mi R, Gan W, Dai J, Jiao M, Xie H, Yao Y, Xiao S, Hu L (2020) A Strong, tough, and scalable structural material from fast-growing bamboo. Adv Mater 32:1906308. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201906308
Sun J, Guo H, Schädli GN, Tu K, Schär S, Schwarze FW, Panzarasa G, Ribera J, Burgert I (2021) Enhanced mechanical energy conversion with selectively decayed wood. Sci Adv 7(11):eabd9138. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abd9138
Arie M, Zhe Z, Yulin D (2016) Fluorine-free oil absorbents made from cellulose nanofibril aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:2732–2740
Yongzhen W, Zhongjun C, Zhenguo L, Hongjun K, Yuyan L (2018) Cellulose nanofibers/polyurethane shape memory composites with fast water-responsivity. J Mater Chem B 6:1668–1677
Li T, Chen C, Brozena AH, Zhu J, Xu L, Driemeier C, Dai J, Rojas OJ, Isogai A, Wågberg L (2021) Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 590:47–56
Chao W, Wang S, Li Y, Cao G, Zhao Y, Sun X, Wang C, Ho S-H (2020) Natural sponge-like wood-derived aerogel for solar-assisted adsorption and recovery of high-viscous crude oil. Chem Eng J 400:125865
Mi H-Y, Jing X, Politowicz AL, Chen E, Huang H-X, Turng L-S (2018) Highly compressible ultra-light anisotropic cellulose/graphene aerogel fabricated by bidirectional freeze drying for selective oil absorption. Carbon 132:199–209
Xuexia Z, Minghui L, Hankun W, Ning Y, Zhiyong C, Yan Y (2019) Ultralight, hydrophobic, anisotropic bamboo-derived cellulose nanofibrils aerogels with excellent shape recovery via freeze-casting. Carbohydr Polym 208:232–240
Guan H, Cheng Z, Wang X (2018) Highly compressible wood sponges with a spring-like lamellar structure as effective and reusable oil absorbents. ACS Nano 12:10365–10373
Gao R, Xiao S, Gan W, Liu Q, Amer H, Rosenau T, Li J, Lu Y (2018) Mussel adhesive-inspired design of superhydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels for oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:9047–9055
Zhang Z, Sèbe G, Rentsch D, Zimmermann T, Tingaut P (2014) Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem Mater 26:2659–2668
Zhou S, Liu P, Wang M, Zhao H, Yang J, Xu F (2016) Sustainable, reusable, and superhydrophobic aerogels from microfibrillated cellulose for highly effective oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:6409–6416
Deki S, Aoi Y (1998) Synthesis of metal oxide thin films by liquid-phase deposition method. J Mater Res 13:325–328
Jan J, Benjamin A, Wolfgang G-A, Christian H (2020) Superhydrophobic coatings on wood made of plant oil and natural wax. Prog Org Coat 148:105891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105891
Jiajie F, Li Z, Jiaguo Y, Gang L (2012) The effect of calcination temperature on the microstructure and photocatalytic activity of TiO2-based composite nanotubes prepared by an in situ template dissolution method. Nanoscale 4:6597–6603
Lin W, Huang Y, Li J, Liu Z, Yang W, Li R, Chen H, Zhang X (2018) Preparation of highly hydrophobic and anti-fouling wood using poly (methylhydrogen) siloxane. Cellulose 25:7341–7353
Zhang M, Zheng R, Chen J, Huang H (2010) Investigation on the determination of lignocellulosics components by NREL method. Chin J Anal Lab 29:15–18
Lee W (2000) Cellular solids, structure and properties, 2nd edn. Springer, London
Belaadi A, Bezazi A, Bourchak M, Scarpa F, Zhu C (2014) Thermochemical and statistical mechanical properties of natural sisal fibres. Compos B Eng 67:481–489
Kumar GV, Deepak P, Shilpi A, Shikha S (2014) Amputation of congo red dye from waste water using microwave induced grafted Luffa cylindrica cellulosic fiber. Carbohyd Polym 111:556–566
Jiang F, Hsieh Y-L (2015) Cellulose nanocrystal isolation from tomato peels and assembled nanofibers. Carbohyd Polym 122:60–68
Pandey KK, Pitman AJ (2003) FTIR studies of the changes in wood chemistry following decay by brown-rot and white-rot fungi. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 52:151–160
Rodrigues J, Faix O, Pereira H (2009) Determination of lignin content of eucalyptus globulus wood using FTIR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 52:46–50
Luo X, Gleisner R, Tian S, Negron J, Zhu W, Horn E, Pan X, Zhu J (2010) Evaluation of mountain beetle-infested lodgepole pine for cellulosic ethanol production by sulfite pretreatment to overcome recalcitrance of lignocellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:8258–8266
Jing Z, Hao W, He X, Fan J, Zhang Y, Miao J, Jin F (2016) A novel hydrothermal method to convert incineration ash into pollucite for the immobilization of a simulant radioactive cesium. J Hazard Mater 306:220–229
Othman MBH, Ahmad Z, Akil HM, Zakaria MR, Ullah F (2015) The effects of the SiOSi segment presence in BAPP/BPDA polyimide system on morphology and hardness properties for opto-electronic application. Mater Design 82:98–105
Tianliang Z, Qifeng Z, Zhiyong C, Lih-Sheng T, Hesheng X, Shaoqin G (2015) Poly(vinyl alcohol)/cellulose nanofibril hybrid aerogels with an aligned microtubular porous structure and their composites with polydimethylsiloxane. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:7436–7444
Sai H, Fu R, Xing L, Xiang J, Li Z, Li F, Zhang T (2015) Surface modification of bacterial cellulose aerogels’ web-like skeleton for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:7373–7381
Jiang F, Hsieh Y-L (2014) Amphiphilic superabsorbent cellulose nanofibril aerogels. J Mater Chem A 2:6337–6342
Zhang X, Ying X, Zhang M, Yu X, Sun G, You B (2019) Investigation of reinforced performance of modified graphene oxide/high solid content polysiloxane nanocomposite coating films. J Mater Sci 54:3052–3068
Artus GRJ, Jung S, Zimmermann J, Gautschi HP, Marquardt K, Seeger S (2006) Silicone nanofilaments and their application as superhydrophobic coatings. Adv Mater 18:2758–2762
Kj T, Marjo K, A RRH, Olli I, (2011) Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:1813–1816
Duan B, Gao H, He M, Zhang L (2014) Hydrophobic modification on surface of chitin sponges for highly effective separation of oil. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:19933–19942
Kathleen R, Yuanyuan L, Hongli Z, Zhen L, Jiaqi D, Julia A, Liangbing H (2014) A cellulose based hydrophilic, oleophobic hydrated filter for water/oil separation. ChemComm 50:13296–13299
Oliver B, Erich H, Sebastian K, Florian M-P (2001) Hydrophilicity and lipophilicity of cellulose crystal surfaces. Angew Chem Int Ed 40:3822–3825
Kettunen M, Silvennoinen RJ, Houbenov N, Nykänen A, Ruokolainen J, Sainio J, Pore V, Kemell M, Ankerfors M, Lindström T (2011) Photoswitchable superabsorbency based on nanocellulose aerogels. Adv Funct Mater 21:510–517
Yang Y, Deng Y, Tong Z, Wang C (2014) Renewable lignin-based xerogels with self-cleaning properties and superhydrophobicity. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1729–1733
Yang Y, Yi H, Wang C (2015) Oil absorbents based on melamine/lignin by a dip adsorbing method. A ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:3012–3018
Donath S, Militz H, Mai C (2004) Wood modification with alkoxysilanes. Wood Sci Technol 38:555–566
Yi L, Yang J, Fang X, Xia Y, Zhao L, Wu H, Guo S (2020) Facile fabrication of wood-inspired aerogel from chitosan for efficient removal of oil from Water. J Hazard Mater 385:121507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100264
Cheng Z, Li J, Wang B, Zeng J, Xu J, Gao W, Zhu S, Hu F, Dong J, Chen K (2020) Scalable and robust bacterial cellulose carbon aerogels as reusable absorbents for high-efficiency oil/water separation. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3:7483–7491
Vitas S, Keplinger T, Reichholf N, Figi R, Cabane E (2018) Functional lignocellulosic material for the remediation of copper (II) ions from water: Towards the design of a wood filter. J Hazard Mater 355:119–127
Chang J, Shi Y, Wu M, Li R, Shi L, Jin Y, Qing W, Tang C, Wang P (2018) Solar-assisted fast cleanup of heavy oil spills using a photothermal sponge. J Mater Chem A 6:9192–9199
Cheng H, Gu B, Pennefather MP, Nguyen TX, Phan-Thien N, Duong HM (2017) Cotton aerogels and cotton-cellulose aerogels from environmental waste for oil spillage cleanup. Mater Design 130:452–458
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge financial support from the Opening Foundation of Key Laboratory of National Forestry and Grassland Administration/Beijing for Bamboo & Rattan Science and Technology (ICBR-2020-07) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2021ZY20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stephen Eichhorn.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Huang, Y., Huang, Q. et al. Liquid-phase deposition functionalized wood sponges for oil/water separation. J Mater Sci 56, 19075–19092 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06440-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06440-w