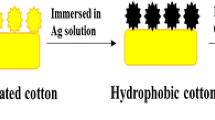
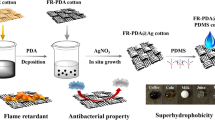
Abstract
Flame-retardant and superhydrophobic coatings over cotton fabric are fabricated by solution immersion method using green-based flame retardants, i.e. DNA, silver nitrate and octadecyltriethoxysilane are used to get flame-retardant cotton with superhydrophobic nature. The results of this work showed that the as-prepared cotton fabric with a maximal contact angle of 157° was obtained and surfaces before and after were characterised by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and FT-IR studies. Some typical flame tests and TGA/DTG studies were done to evaluate the flame retardant property and thermal stability of the coated cotton samples. These results demonstrated that solution immersion strategy is a relatively simple and convenient method to fabricate superhydrophobic and flame-retardant cotton fabric.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laufer G, Kirkland C, Morgan AB, Grunlan JC (2012) Intumescent multilayer nanocoating, made with renewable polyelectrolytes, for flame-retardant cotton. Biomacromol 13:2843–2848. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm300873b
Shen Q, Song L, Pan H, Pan Y, Hu Y, Lu Y et al (2016) Fabrication of flame retardant coating on cotton fabric by alternate assembly of exfoliated layered double hydroxides and alginate. RSC Adv 6:111950–111958. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra21804k
Zhang M, Zang D, Shi J, Gao Z, Wang C, Li J (2015) Superhydrophobic cotton textile with robust composite film and flame retardancy. RSC Adv 5:67780–67786. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra09963c
Chen S, Li X, Li Y, Sun J (2015) Al CET. Intumescent Flame-Retardant and coatings on cotton fabric. ACS Nano. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b00121
Carosio F, Laufer G, Alongi J, Camino G, Grunlan JC (2011) Layer-by-layer assembly of silica-based flame retardant thin film on PET fabric. Polym Degrad Stab 96:745–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.02.019
Becher EM, Patel H, Zhang D, Nasir Z, Shrestha SB, Peng X et al (2017) Flame retardant and hydrophobic coatings on cotton fabrics via sol-gel and self-assembly techniques. J Colloid Interface Sci 505:892–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.06.087
Suryaprabha T, Sethuraman MG (2018) Fabrication of superhydrophobic and enhanced flame-retardant coatings over cotton fabric. Cellulose 25:3151–3161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1757-8
Zhang S, Jin X, Gu X, Chen C, Li H, Zhang Z et al (2018) The preparation of fully bio-based flame retardant poly(lactic acid) composites containing casein. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46599. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46599
Faheem S, Baheti V, Tunak M, Wiener J, Militky J (2019) Comparative performance of flame retardancy, physiological comfort, and durability of cotton textiles treated with alkaline and acidic casein suspension. J Ind Text 48:969–991. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083717750885
Faheem S, Baheti V, Tunak M, Wiener J, Militky J (2019) Flame resistance behavior of cotton fabrics coated with bilayer assemblies of ammonium polyphosphate and casein. Cellulose 26:3557–3574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02296-1
Alongi J, Carletto RA, Bosco F, Carosio F, Di Blasio A, Cuttica F et al (2014) Caseins and hydrophobins as novel green flame retardants for cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 99:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.11.016
Alongi J, Carletto RA, Di Blasio A, Cuttica F, Carosio F, Bosco F et al (2013) Intrinsic intumescent-like flame retardant properties of DNA-treated cotton fabrics. Carbohydr Polym 96:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.066
Alongi J, Di Blasio A, Milnes J, Malucelli G, Bourbigot S, Kandola B et al (2015) Thermal degradation of DNA, an all-in-one natural intumescent flame retardant. Polym Degrad Stab 113:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.11.001
Cheng X-W, Guan J-P, Tang R-C, Liu K-Q (2016) Phytic acid as a bio-based phosphorus flame retardant for poly(lactic acid) nonwoven fabric. J Clean Prod 124:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.113
Feng JX, Su SP, Zhu J (2011) An intumescent flame retardant system using β-cyclodextrin as a carbon source in polylactic acid (PLA). Polym Adv Technol 22:1115–1122. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1954
Malucelli G, Bosco F, Alongi J, Carosio F, Di Blasio A, Mollea C et al (2014) Biomacromolecules as novel green flame retardant systems for textiles: an overview. RSC Adv 4:46024–46039. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA06771A
Zhang T, Yan H, Shen L, Fang Z, Zhang X, Wang J et al (2014) Chitosan/phytic acid polyelectrolyte complex: a green and renewable intumescent flame retardant system for ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:19199–19207. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie503421f
Carosio F, Di Blasio A, Alongi J, Malucelli G (2013) Green DNA-based flame retardant coatings assembled through layer by layer. Polym Guildf 54:5148–5153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2013.07.029
Quartinello F, Kremser K, Vecchiato S, Schoen H, Vielnascher R, Ploszczanski L et al (2019) Increased flame retardancy of enzymatic functionalized PET and nylon fabrics via DNA immobilization. Front Chem 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00685
Alongi J, Milnes J, Malucelli G, Bourbigot S, Kandola B (2014) Thermal degradation of DNA-treated cotton fabrics under different heating conditions. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 108:212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2014.04.014
Suryaprabha T, Sethuraman MG (2017) Fabrication of copper-based superhydrophobic self-cleaning antibacterial coating over cotton fabric. Cellulose 24:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1110-z
Afzal S, Daoud WA, Langford SJ (2014) Superhydrophobic and photocatalytic self-cleaning cotton. J Mater Chem A 2:18005–18011. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta02764g
Wang X, Hu Y, Song L, Xuan S, Xing W, Bai Z et al (2011) Flame Retardancy and Thermal Degradation of Intumescent Flame Retardant Poly(lactic acid)/Starch Biocomposites. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:713–720. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie1017157
Xue C-H, Zhang L, Wei P, Jia S-T (2016) Fabrication of superhydrophobic cotton textiles with flame retardancy. Cellulose 23:1471–1480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0885-2
Suryaprabha T, Sethuraman MG (2017) Design of electrically conductive superhydrophobic antibacterial cotton fabric through hierarchical architecture using bimetallic deposition. J Alloys Compd 724:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.07.009
Alongi J, Carletto RA, Di Blasio A, Carosio F, Bosco F, Malucelli G (2013) DNA: A novel, green, natural flame retardant and suppressant for cotton. J Mater Chem A 1:4779–4785. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta00107e
Takeshima T, Tada Y, Sakaguchi N, Watari F, Fugetsu B (2015) DNA/ag nanoparticles as antibacterial agents against gram-negative bacteria. Nanomaterials 5:284–297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5010284
Pramanik S, Chatterjee S, Saha A, Devi PS, Suresh KG (2016) Unraveling the interaction of silver nanoparticles with mammalian and bacterial DNA. J Phys Chem B 120:5313–5324. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b01586
Basu S, Jana S, Pande S, Pal T (2008) Interaction of DNA bases with silver nanoparticles: assembly quantified through SPRS and SERS. J Colloid Interface Sci 321:288–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.02.015
Zhang M, Wang C (2013) Fabrication of cotton fabric with superhydrophobicity and flame retardancy. Carbohydr Polym 96:396–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.025
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank UGC-SAP for their financial support.
Funding
Funding was provided by UGC-RFSMS (Grand No. F.No.25-1/2014-15/(BSR)/7-225/2008/(BSR)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suryaprabha, T., Sethuraman, M.G. Fabrication of a superhydrophobic and flame-retardant cotton fabric using a DNA-based coating. J Mater Sci 55, 11959–11969 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04911-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04911-0