Abstract
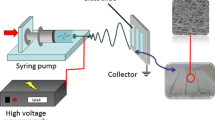
This study reports the preparation of a flexible nanofibrous probe for the rapid colorimetric detection of dopamine. To this aim, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were immobilized on the surface of electrospun nanofibrous membrane to obtain a new hybrid material. This hybrid structure would benefit from the properties of both nanofibers and AuNP, being (a) the porosity and high surface area of nanofibers, and (b) the unique optical properties of AuNP. The electrospun poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) nanofibrous membrane was alkaline treated in NaOH aqueous solution, followed by immersion in the AuNP solution. The morphology of AuNP-PET membranes was characterized using a field emission scanning electron microscopy. The AuNP-PET probes showed quick, visible color change (from red to dark blue) in the presence of dopamine at the physiological pH values. The visual detection limit was 0.5 μM. The color difference based on the formula of the L*a*b* color space was used to quantify the concentration of dopamine. The color difference increased almost linearly in the 0.5–500 µM concentration range. The presence of electrostatically adsorbed AuNP on the surface of nanofibers, along with the flexibility of the nanofibrous membrane, was responsible for fast, sensitive, and on-site detection of dopamine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marega C, Maculan J, Rizzi GA, Saini R, Cavaliere E, Gavioli L, Cattelan M, Giallongo G, Marigo A, Granozzi G (2015) Polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers containing Ag nanoparticles used as sensors for the detection of biogenic amines. Nanotechnology 26(7):075501
Gorbunova MV, Apyari VV, Zolotov II, Dmitrienko SG, Garshev AV, Volkov PA, Bochenkov VE (2019) A new nanocomposite optical sensor based on polyurethane foam and gold nanorods for solid-phase spectroscopic determination of catecholamines. Gold Bull 52(3–4):115–124
Wang X, Wu M, Tang W, Zhu Y, Wang L, Wang Q, He P, Fang Y (2013) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using a palladium nanoparticle/graphene/chitosan modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem 15(695):10–16
Gare M, Haviv YS, Ben-Yehuda A, Rubinger D, Bdolah-Abram T, Fuchs S, Gat O, Popovtzer MM, Gotsman MS, Mosseri M (1999) The renal effect of low-dose dopamine in high-risk patients undergoing coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 34(6):1682–1688
Xu J, Li Y, Wang L, Huang Y, Liu D, Sun R, Luo J, Sun C (2015) A facile aptamer-based sensing strategy for dopamine through the fluorescence resonance energy transfer between rhodamine B and gold nanoparticles. Dyes Pigm 1(123):55–63
Peng J, Han CL, Ling J, Liu CJ, Ding ZT, Cao QE (2018) Selective fluorescence quenching of papain–Au nanoclusters by self-polymerization of dopamine. Luminescence 33(1):168–173
Chen Z, Zhang C, Zhou T, Ma H (2015) Gold nanoparticle based colorimetric probe for dopamine detection based on the interaction between dopamine and melamine. Microchim Acta 182(5–6):1003–1008
Gorbunova MV, Apyari VV, Dmitrienko SG, Garshev AV (2016) Formation of core-shell Au@ Ag nanorods induced by catecholamines: a comparative study and an analytical application. Anal Chim Acta 14(936):185–194
Palanisamy S, Zhang X, He T (2015) Fast, sensitive and selective colorimetric gold bioassay for dopamine detection. J Mater Chem B 3(29):6019–6025
Huang ZM, Zhang YZ, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 63(15):2223–2253
Gualandi C, Celli A, Zucchelli A, Focarete ML (2014) Nanohybrid materials by electrospinning. In: Organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials. Springer, Cham, pp 87–142
Liu Z, Yan Z, Jia L, Song P, Mei L, Bai L, Liu Y (2017) Gold nanoparticle decorated electrospun nanofibers: a 3D reproducible and sensitive SERS substrate. Appl Surf Sci 1(403):29–34
Senthamizhan A, Balusamy B, Aytac Z, Uyar T (2016) Ultrasensitive electrospun fluorescent nanofibrous membrane for rapid visual colorimetric detection of H2O2. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(5):1347–1355
Senthamizhan A, Celebioglu A, Balusamy B, Uyar T (2015) Immobilization of gold nanoclusters inside porous electrospun fibers for selective detection of Cu (II): a strategic approach to shielding pristine performance. Sci Rep 22(5):15608
Sapountzi E, Braiek M, Vocanson F, Chateaux JF, Jaffrezic-Renault N, Lagarde F (2017) Gold nanoparticles assembly on electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (ethyleneimine)/glucose oxidase nanofibers for ultrasensitive electrochemical glucose biosensing. Sens Actuators B Chem 1(238):392–401
Chen C, Tang Y, Vlahovic B, Yan F (2017) Electrospun polymer nanofibers decorated with noble metal nanoparticles for chemical sensing. Nanoscale Res Lett 12(1):451
Korivi NS (2015) Preparation, characterization, and applications of poly (ethylene terephthalate) nanocomposites. In: Manufacturing of nanocomposites with engineering plastics. Woodhead Publishing, pp 167–198
Ma Z, Kotaki M, Yong T, He W, Ramakrishna S (2005) Surface engineering of electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers towards development of a new material for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials 26(15):2527–2536
Hadjizadeh A, Ajji A, Jolicoeur M, Liberelle B, De Crescenzo G (2013) Effects of electrospun nanostructure versus microstructure on human aortic endothelial cell behavior. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9(7):1195–1209
Ngomane N, Torto N, Krause R, Vilakazi S (2015) A colorimetric probe for dopamine based on gold nanoparticles-electrospun nanofibre composite. Mater Today Proc 2(7):4060–4069
Hadjizadeh A, Ajji A, Bureau MN (2011) Nano/micro electro-spun polyethylene terephthalate fibrous mat preparation and characterization. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4(3):340–351
Ng R, Zhang X, Liu N, Yang ST (2009) Modifications of nonwoven polyethylene terephthalate fibrous matrices via NaOH hydrolysis: effects on pore size, fiber diameter, cell seeding and proliferation. Process Biochem 44(9):992–998
Kimling J, Maier M, Okenve B, Kotaidis V, Ballot H, Plech A (2006) Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J Phys Chem B 110(32):15700–15707
Khalafalla MA, Mesli A, Widattallah HM, Sellai A, Al-Harthi S, Al-Lawati HA, Suliman FO (2014) Size-dependent conductivity dispersion of gold nanoparticle colloids in a microchip: contactless measurements. J Nanopart Res 16(8):2546
Amendola V, Pilot R, Frasconi M, Marago OM, Iati MA (2017) Surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles: a review. J Phys: Condens Matter 29(20):203002
Haiss W, Thanh NT, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV−Vis spectra. Anal Chem 79(11):4215–4221
Bellino MG, Calvo EJ, Gordillo G (2004) Adsorption kinetics of charged thiols on gold nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6(2):424–428
Apyari VV, Arkhipova VV, Gorbunova MV, Volkov PA, Isachenko AI, Dmitrienko SG, Zolotov YA (2016) Towards the development of solid-state platform optical sensors: aggregation of gold nanoparticles on polyurethane foam. Talanta 1(161):780–788
Pruneanu S, Biris AR, Pogacean F, Socaci C, Coros M, Rosu MC, Watanabe F, Biris AS (2015) The influence of uric and ascorbic acid on the electrochemical detection of dopamine using graphene-modified electrodes. Electrochim Acta 1(154):197–204
Zhang Y, Li B, Xu C (2010) Visual detection of ascorbic acid via alkyne–azide click reaction using gold nanoparticles as a colorimetric probe. Analyst 135(7):1579–1584
Manjunatha H, Nagaraju DH, Suresh GS, Venkatesha TV (2009) Detection of uric acid in the presence of dopamine and high concentration of ascorbic acid using PDDA modified graphite electrode. Electroanal Int J Devoted Fundam Pract Asp Electroanal 21(20):2198–2206
Zhang Y, Li B, Chen X (2010) Simple and sensitive detection of dopamine in the presence of high concentration of ascorbic acid using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Microchim Acta 168(1–2):107–113
Yusoff N, Pandikumar A, Ramaraj R, Lim HN, Huang NM (2015) Gold nanoparticle based optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 182(13–14):2091–2114
Rotaru R, Savin M, Tudorachi N, Peptu C, Samoila P, Sacarescu L, Harabagiu V (2018) Ferromagnetic iron oxide–cellulose nanocomposites prepared by ultrasonication. Polym Chem 9(7):860–868
Park JY, Myung SW, Kim I, Choi DK, Kwon SJ, Yoon SH (2012) Simultaneous measurement of serotonin, dopamine and their metabolites in mouse brain extracts by high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry following derivatization with ethyl chloroformate. Biol Pharm Bull 36(2):252–258
Guo L, Zhang Y, Li Q (2009) Spectrophotometric determination of dopamine hydrochloride in pharmaceutical, banana, urine and serum samples by potassium ferricyanide-Fe (III). Anal Sci 25(12):1451–1455
Josypčuk O, Barek J, Josypčuk B (2018) Amperometric determination of catecholamines by enzymatic biosensors in flow systems. Electroanalysis 30(6):1163–1171
Tao Y, Lin Y, Ren J, Qu X (2013) A dual fluorometric and colorimetric sensor for dopamine based on BSA-stabilized Aunanoclusters. Biosens Bioelectron 15(42):41–46
Wang HB, Li Y, Dong GL, Gan T, Liu YM (2017) A convenient and label-free colorimetric assay for dopamine detection based on the inhibition of the Cu(ii)-catalyzed oxidation of a 3, 3′, 5, 5′-tetramethylbenzidine–H2O2 system. New J Chem 41(23):14364–14369
Funding
The funding was provided by Amirkabir University of Technology (Grant No. GN1396-97).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostami, A., Hadjizadeh, A. & Mahshid, S. Colorimetric determination of dopamine using an electrospun nanofibrous membrane decorated with gold nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 55, 7969–7980 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04547-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04547-0