Abstract
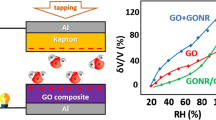
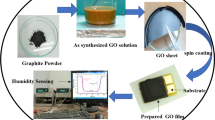
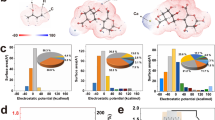
Environmental energy harvesting devices hold great prospect for the next generation electronics, which have attracted intensive attentions recently. In this research, a gradient polyoxometalates-modified graphene oxide (g-POMs-GO) with three-dimensional cross-linking inner structure is synthesized by a weak reductant of GO with ethylenediamine and a special soaking treatment in phosphotungstic acid (HPW). Owing to the gradient introduction of HPW, the as-prepared g-POMs-GO is able to provide moisture-enabled current output of 6.2 uA cm−2 with a power density of ≈ 0.7 mW m−2 by harvesting energy from moisture. Moreover, the humidity-to-electric conversion device of g-POMs-GO provides a new, practical method to track the respiratory activity of subjects and can directly use to record and analyze patterns of human breathing.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu M, Johnston MB, Snaith HJ (2013) Efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells by vapour deposition. Nature 501:395–398
Burschka J, Pellet N, Moon SJ, Humphrybaker R, Gao P, Nazeeruddi MK (2013) Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature 499:316–319
Tian B, Zheng X, Kempa TJ, Fang Y, Yu N, Yu G, Huang J, Lieber CM (2007) Coaxial silicon nanowires as solar cells and nanoelectronic power sources. Nature 449:885–889
Huynh WU, Dittmer JJ, Alivisatos AP (2002) Hybrid nanorod-polymer solar cells. Science 295:2425–2427
Gratzel M (2001) Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature 414:338–344
Wang ZL, Song J (2006) Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312:242–246
Yang R, Qin Y, Dai L, Wang ZL (2009) Power generation with laterally packaged piezoelectric fine wires. Nat Nanotechnol 4:34–39
Wang X, Song J, Liu J, Wang ZL (2007) Direct current nanogenerator driven by ultrasonic wave. Science 316:102–105
Jeong CK, Park KI, Son JH, Hwang GT, Lee SH, Park DY, Lee HE, Lee HK, Byun M, Lee KJ (2014) Self-powered fully-flexible light-emitting system enabled by flexible energy harvester. Energy Environ Sci 7:4035–4043
Zhu G, Pan C, Guo W, Chen CY, Zhou Y, Yu R, Wang ZL (2012) Triboelectric-generator-driven pulse electrodeposition for micropatterning. Nano Lett 12:4960–4965
Wang S, Lin L, Xie Y, Jing Q, Niu S, Wang ZL (2013) Sliding-triboelectric nanogenerators based on in-plane charge-separation mechanism. Nano Lett 13:2226–2233
Zhu G, Chen J, Zhang T, Jing Q, Wang Z (2014) Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat Commun 5:3426–3432
Jing Q, Xie Y, Zhu G, Han RP, Wang ZL (2015) Self-powered thin-film motion vector sensor. Nat Commun 6:8031–8037
Jeong CK, Baek KM, Niu S, Nam TW, Hur YH, Park DY, Lee KJ (2014) Topographically-designed triboelectric nanogenerator via block copolymer self-assembly. Nano Lett 14:7031–7038
Ghosh S, Sood AK, Kumar N (2003) Carbon nanotube flow sensors. Science 299:1042–1044
Dhiman P, Yavari F, Mi X, Gullapalli H, Shi YP, Ajayan M, Koratkar N (2011) Harvesting energy from water flow over graphene. Nano Lett 11:3123–3127
Guo W, Cheng C, Wu Y, Jiang Y, Gao J, Li D, Jiang L (2013) Bio-inspired two-dimensional nanofluidic generators based on a layered graphene hydrogel membrane. Adv Mater 25:6064–6068
Yin J, Li X, Yu J, Zhang Z, Zhou J, Guo W (2014) Generating electricity by moving a droplet of ionic liquid along graphene. Nat Nanotechnol 9:378–383
Wan S, Li Y, Mu J, Aliev AE, Fang S, Kotov NA, Jiang L, Cheng Q, Baughman RH (2018) Sequentially bridged graphene sheets with high strength, toughness, and electrical conductivity. PNAS 115:5359–5364
Gong S, Ni H, Jiang L, Cheng Q (2017) Learning from nature: constructing high performance graphene-based nanocomposites. Mater Today 20:210–219
Wan S, Peng J, Jiang L, Cheng Q (2016) Bioinspired graphene-based nanocomposites and their application in flexible energy devices. Adv Mater 28:7862–7898
Zhang Y, Gong S, Zhang Q, Ming P, Wan S, Peng J, Jiang L, Cheng Q (2016) Graphene-based artificial nacre nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 45:2378–2395
Gao W, Wu G, Janicke MT, Cullen DA, Mukundan R, Baldwin JK, Brosha EL, Galande C, Ajayan PM, More KL, Dattelbaum AM, Zelenay P (2014) Ozonated graphene oxide film as a proton-exchange membrane. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:3588–3593
Hatakeyama K, Karim MR, Ogata C, Tateishi H, Funatsu A, Taniguchi T, Koinuma M, Hayami S, Matsumoto Y (2014) Proton conductivities of graphene oxide nanosheets: single, multilayer, and modified nanosheets. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:6997–7000
Karim MR, Hatakeyama K, Matsui T, Takehira H, Taniguchi T, Koinuma M, Matsumoto Y, Akutagawa T, Nakamura T, Noro S, Yamada T, Kitagawa H, Hayami S (2013) Graphene oxide nanosheet with high proton conductivity. J Am Chem Soc 135:8097–8100
Gao W, Singh N, Song L, Liu Z, Reddy AL, Ci L, Vajtai R, Zhang Q, Wei B, Ajayan PM (2011) Direct laser writing of micro-supercapacitors on hydrated graphite oxide films. Nat Nanotechnol 6:496–500
Liu Y, Liu S, Lai X, Miao J, He D, Li N, Luo F, Shi Z, Liu S (2015) Polyoxometalates-modified sponge-like graphene oxide monolith with high proton-conducting performance. Adv Funct Mater 25:4480–4485
Kim S, Zhou S, Hu Y, Acik M, Chabal YJ, Berger C, de Heer W, Bongiorno A, Riedo E (2012) Room-temperature metastability of multilayer graphene oxide films. Nat Mater 11:544–549
Cheng H, Hu Y, Zhao F, Dong Z, Wang Y, Chen N, Zhang Z, Qu L (2014) Moisture-activated torsional graphene-fiber motor. Adv Mater 26:2909–2913
Zhao F, Cheng H, Zhang Z, Jiang L, Qu L (2015) Direct power generation from a graphene oxide film under moisture. Adv Mater 27:4351–4357
Zhao F, Liang Y, Cheng H, Jiang L, Qu L (2016) Highly efficient moisture-enabled electricity generation from graphene oxide frameworks. Energy Environ Sci 9:912–916
Liu K, Yang P, Li S, Li J, Ding T, Xue G, Chen Q, Feng G, Zhou J (2016) Induced potential in porous carbon films through water vapor absorption. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:8003–8007
Katsoulis DE (1998) A Survey of applications of polyoxometalates. Chem Rev 98:359–387
Kozhevnikov IV (1998) Catalysis by heteropoly acids and multicomponent polyoxometalates in liquid-phase reactions. Chem Rev 98:171–198
Yoon M, Suh K, Natarajan S, Kim K (2013) Proton conduction in metal-organic frameworks and related modularly built porous Solids. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:2688–2700
Liu J, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Cheng H, Hu C, Jiang L, Qu L (2012) Three-dimensional graphene-polypyrrole hybrid electrochemical actuator. Nanoscale 4:7563–7568
Dreyer DR, Park S, Bielawski CW, Ruoff RS (2009) The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem Soc Rev 39:228–240
Zhu Y, Murali S, Cai W, Li X, Suk JW, Potts JR, Ruoff RS (2010) Graphene-based materials: graphene and graphene oxide: synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv Mater 22:3906–3924
Nakamura O, Kodama T, Ogino I, Miyake Y (1979) High-conductivity solid proton conductors: dodecamolybdophosphoric acid and dodecatungstophosphoric acid crystals. Chem Lett 8:17–18
Acknowledgements
This project is sponsored by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DC. 201502080403), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11804044, 61771092), and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2015020072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Qi, Y., Liu, D. et al. Moisture-enabled electricity generation from gradient polyoxometalates-modified sponge-like graphene oxide monolith. J Mater Sci 54, 4831–4841 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3183-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3183-6